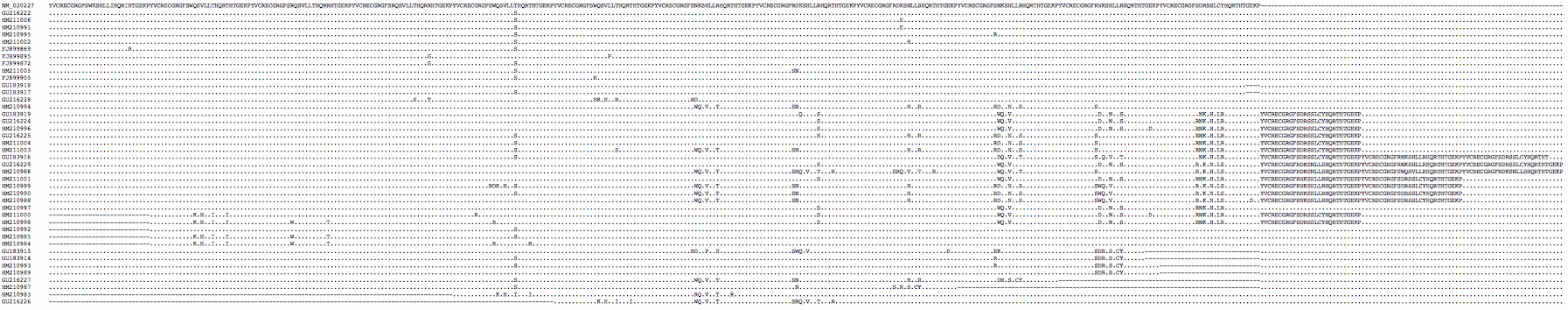PRDM9: meiosis and recombination: Difference between revisions
Tomemerald (talk | contribs) |
Tomemerald (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 538: | Line 538: | ||
Here ZNF133 and the misnamed HKR1 are the best candidates for donating (via inhomogeneous recombination) the zinc finger array to the nascent PRDM7 which was already a chimer of KRAB, SSXRD and PR(SET) domains. The relationships here might instead go the other way (domain loss in PRDM) but different intronation of the KRAB domain is incompatible with that scenario. While none of the six ZNF is capable of histone methylation, KRAB domains are [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11959841 capable of recruiting] SETDB1, a H3K9 methylase, partnering with the TIF1ß co-repressor protein (encoded by TRIM28), which interacts with many KRAB domains). | Here ZNF133 and the misnamed HKR1 are the best candidates for donating (via inhomogeneous recombination) the zinc finger array to the nascent PRDM7 which was already a chimer of KRAB, SSXRD and PR(SET) domains. The relationships here might instead go the other way (domain loss in PRDM) but different intronation of the KRAB domain is incompatible with that scenario. While none of the six ZNF is capable of histone methylation, KRAB domains are [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11959841 capable of recruiting] SETDB1, a H3K9 methylase, partnering with the TIF1ß co-repressor protein (encoded by TRIM28), which interacts with many KRAB domains). | ||
[[ | Phylogenetic variation in the zinc finger arrays of these proteins is potentially quite informative, the question being whether their variation too is focused on the four amino acid positions providing dna binding specificity in PRDM7/9. This next sections examine each protein separately for mutational variation in the zinc fingers over placental mammal evolutionary time. | ||
Here the [http://genome-test.cse.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgPal?g=knownGene&c=chr20&l=18269121&r=18297638&i=uc010gcs.2&hgsid=2970269&db=hg19 46-species genomic alignment] at UCSC serves as initial source of zinc finger arrays, which are then tested by blat back into individual species and then parsed into separate fasta files for each protein finger (the formats needed by the [http://npsa-pbil.ibcp.fr/cgi-bin/npsa_automat.pl?page=/NPSA/npsa_multalin.html Multalin2] variable width differential aligner and [http://weblogo.berkeley.edu/logo.cgi weblogo tool]). | |||
==== ZNF133 ==== | |||
Human ZNF133 is a conventional KRAB-zinc finger array. The array is a better model of PRDM9 than any of the other 14 PRDM* loci in terms of repeat character and length. Rodents cannot be used here as a model system as the mouse syntenic counterpart is a [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2922377/ known pseudogene] -- as is rat but not guinea pig or rabbit -- and ZNF133 too does not readily track back into marsupials or earlier vertebrates. | |||
As with PRDM7/9, the C-terminal run-off of ZNF133 is subject to frameshifts. However elephant and human are still 86% identical in their last exon, with zinc finger arrays even higher. Armadillo, another mammal diverging from human at 101 myr, is 91% identical in this region and has exactly the same number of zinc fingers (14.7). This suggests that the dna binding target is strongly conserved, just the opposite of PRDM7/9. However this conservation in ZNF133 weakens markedly in the distal 3 repeats. | |||
The 11 conserved zinc fingers in ZNF133 are long enough to specify nearly unique dna sites in a 3 gbp genome, even if not all fingers take part in a given site recognition. Human variation in repeat numbers has not been studied but it appears from phylogenetic considerations to be far less common than in PRDM7/9 | The 11 conserved zinc fingers in ZNF133 are long enough to specify nearly unique dna sites in a 3 gbp genome, even if not all fingers take part in a given site recognition. Note the SGEKP lockdown cap departs from canonical form in repeat 5, 7, 12, and 13 perhaps impacting binding site prediction. Human variation in repeat numbers has not been studied but it appears from phylogenetic considerations to be far less common than in PRDM7/9. | ||
Alignment of human ZNF133 zinc finger array to orthologs in Primates, Glires, Laurasiatheres, Xenarthra and Afrotheres | Alignment of human ZNF133 zinc finger array to orthologs in Primates, Glires, Laurasiatheres, Xenarthra and Afrotheres | ||
z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z | |||
homSap VNCGECGLSFSKMTNLLSHQRIHSGEKP YVCGVCEKGFSLKKSLARHQKAHSGEKP IVCRECGRGFNRKSTLIIHERTHSGEKP YMCSECGRGFSQKSNLIIHQRTHSGEKP YVCRECGKGFSQKSAVVRHQRTHLEEKT | homSap VNCGECGLSFSKMTNLLSHQRIHSGEKP YVCGVCEKGFSLKKSLARHQKAHSGEKP IVCRECGRGFNRKSTLIIHERTHSGEKP YMCSECGRGFSQKSNLIIHQRTHSGEKP YVCRECGKGFSQKSAVVRHQRTHLEEKT | ||
calJac ............................ ............................ ............................ ............................ ............................ | calJac ............................ ............................ ............................ ............................ ............................ | ||
| Line 576: | Line 576: | ||
proCap ...ED...........I.........K. ............................ .A....R...N...T..A..QL...D.L .......ED.M.....LV.....K.... ..SR.H.Q..NQ......Y.RIK. ...KS.F.S.L.T.S..S.VPV... | proCap ...ED...........I.........K. ............................ .A....R...N...T..A..QL...D.L .......ED.M.....LV.....K.... ..SR.H.Q..NQ......Y.RIK. ...KS.F.S.L.T.S..S.VPV... | ||
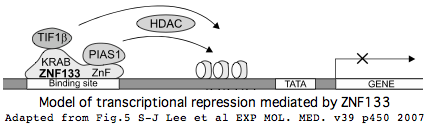
The ubiquitously expressed ZNF133 has been established by [http://www.e-emm.org/article/article_files/EMM039-04-03.pdf experiment] to be a transcriptional repressor, recognizing specific sites in dsDNA. Despite the presence of the KRAB domain (which usually has this task), the zinc finger array alone contributes to transcriptional repression, with this effect mediated by another gene product, PIAS1, which binds the main array and recruits histone deacylases. The early zinc finger is not necessary for the PIAS1 effect and though conserved, its role remains obscure. PIAS1 may also [http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0020321 have a role] in PRDM9 and recombination. | |||
[[Image:ZNF133function.png|left]] | |||
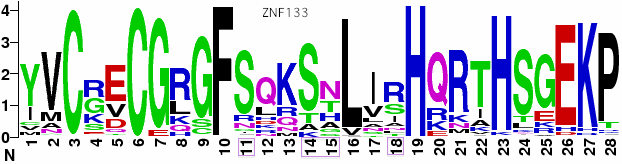
For ZNF133, the weblogo | For ZNF133, the weblogo below based on 413 repeats from 32 placentals illustrates that quite different selectional pressures have been operative here than in PRDM7/9. First, variation is not concentrated at the four special amino acid positions (purple boxes between CxxC HxxxH) but instead is distributed (though unevenly) among the non-C2H2 positions. Some of this occurs at residues primarily concerned with the zinc binding fold and not target macromolecule interactions. This establishes structural variation in the fold can be tolerated, ie PRDM7/9 is the real oddity for not exhibiting it. | ||
[[Image:Znf133Freqs.gif|left]] | |||
<br clear = all> | |||
(to be continued shortly) | (to be continued shortly) | ||
Revision as of 15:59, 14 August 2011
Introduction
PRDM9 is a gene on human chromosome 5 with a very peculiar history. Its primary function -- after many false starts -- has only recently become clear: scanning the genome with its terminal zinc finger array to locate and mark recombination hotspots with its histone methylase where its transcription factor domain can direct additional proteins to initiate the double stranded breaks needed for meiosis. Some level of recombination between homologous chromosomes is essential to proper alignment and separation into daughter cells as well as for bringing favorable alleles onto the same haplotype for adaptive evolution.
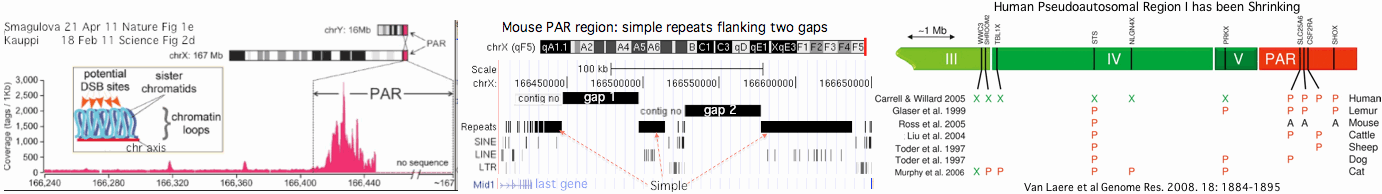
This reaches criticality in placental mammal sex chromosomes which are limited in homologous alignability to a short pseudoautosomal region (PAR). Here in male meiosis, a recognizable sequence site must be found for the double stranded break with only tens of kilobases available in mouse, the most favorable experimental situation. Here it must be noted that two large gaps remain in PAR in the most recent mouse assembly used (July 07) telomeric to the single known PAR hotspot (a situation not improved in the July 2011 release 37.2).
Such a mission-critical protein is typically highly conserved. However this is not the case here at all. Indeed, it proves exceedingly difficult to find a comprehensive set of PRDM9 orthologs even in the 39 sequenced placental mammalian genomes available on 15 July 2011, with immense confusion in the literature over paralogs, lost copies, pseudogenes, and similar composite domain proteins having only very distant homology. PRDM9 and its parent gene PRDM7 do not have a full-length orthologous counterpart in monotremes, birds, lizards, amphibians or earlier diverging vertebrates -- though similar domain combinations have arisen independently in the past.
This history does not imply post-Cambrian ab initio sequence innovation because PRDM7 (the parent of primate PRMD9) is a straightforward chimera established during the theran ancestral stem of two conventional proteins with long evolutionary histories, a SSX1-like gene and a knuckle PRDM zinc finger array. The two parental gene histories are complex in different ways -- tandem whole gene array and variable zinc finger domain-- patterns uncommon but hardly unprecedented in the overall metazoan proteome evolutionary context. Zinc finger proteins in particular are a much expanded, often chimeric family in the mammalian lineage.
Rapid evolution of the terminal region of PRDM7/9 occurs at the amino acid level, especially in the number of functioning zinc fingers and within a given finger in the four residues responsible for recognizing a specific dna trinucleotide. This is not coincidental to the role in meiosis: the process tends to destroy its recombination hotspots by biased gene conversion. Since recombination is essential, new hotspots must emerge. The race is then on for PRDM7 or its spun-off PRDM9s to rapidly evolve and define new histone markup sites.
This rapid evolution could cause breeding incompatibility between populations in the F1 generation (meiosis arrest for lack of cross-overs, notably between chrX and chrY) and thus be central to the process of speciation. However the evolution of the hotspot-defining gene takes very different forms in different mammalian lineages. In effect each major clade of placentals is evolving a qualitatively different mating system, taking its most extreme form in pecoran ruminants with 6 PRDM9 genes. This differentiation follows upon the very different structure and gene content of sex chromosomes between monotremes, marsupials and placentals which in turn are much different from those of the amniote ancestor.
Syntenic relationships can help resolve gene duplication events during mammalian evolution. Here the chromosomal gene order TUBB3+ AFG3L1+ GAS8+ has stably existed since the stem amniote some 310 million years ago, with the arrangement TUBB3+ AFG3L1+ GAS8+ PRDM7- qTer arising in placental mammals prior to Afrothere divergence (ie, between 102-125 myr ago) and maintained there since over billions of years of observable branch length. PRDM9 however is found in many syntentic contexts, depending on clade and the various segmental duplications giving rise to these secondary copies.
From the perspective of evolutionary genomics, PRDM7 is the fundamental gene, not the disparate collection of genes lumped under PRDM9 (even as those have taken over as the sole functional copy). At different times in different placental clades, PRDM7 spun off segmental duplications of itself to other sites in other chromosomes, probably because of its susceptible location at the extreme q arm of an autosomal chromosome. Because PRDM7 has stayed at its site adjacent to GAS8, it is possible to say unambiguously which of two initially identical copies is the parent gene. Because of this history, the 'PRDM9' genes do not form a distinct subtree within the overall two-gene tree under phylogenetic algorithms but instead associate more closely with their parental PRDM7 parent.
These paralogous copies -- despite all being called PRDM9 -- are not usefully considered orthologous outside their species clade of origin. Orthology requires (by long-standing definition) vertical descent from a common gene in the last common ancestor of two species. Here primate PRDM9 are descended from a common gene (namely the recent duplicate of PRDM7 in the stem common ancestor preceding speciation) but 'PRDM9' in afrotheres and pecoran ruminants etc arose from different duplications at different times during placental mammal evolution from a non-stationary parental gene and so -- despite the name -- are not vertically descended from a common PRDM9 in their last common ancestor (though all the genes here descend from a single stem euarchontogliral PRDM7).
In tandem duplications, the parental gene cannot be distinguished but here the second copy was never on an equal footing. PRDM7 can denote both parental and the GAS8-linked descendent and PRDM9 the derived offspring. PRDM7 has a long history but primate PRDM9 has none of its own prior to its creation in stem catarrhine. As PRDM numbers 1-16 are already used up, the PRDM9 arising in primates, pecoran ruminants and afrotheres might distinguished as PRDMPpri, PRDM9pec, and PRDM9afr.
Such copies are sometimes called in-paralogs within a species and co-orthologs across species. However these terms are topologically unstable (depend on the species range included in the gene tree) unlike the terms ortholog, paralog and homolog which are well-defined. Composite domain proteins such as PRDM7 give rise to a whole new level of terminological muddle as each domain can have a complex separate history of duplication and shuffling. There may be no solution really other than to a labelled gene tree.
Comparative genomics in placental mammals
In euarchontoglires, a segmental duplication of PRDM7 occurred in a stem catarrhine primate and descended through speciation events to contemporary old world monkeys and great apes. This second copy (PRDM9) relocated to and stayed within a cadherin gene complex on a different chromosome. PRDM7 persisted at its original ancestral location but became an overt pseudogene in some lineages (rhesus, gibbon, gorilla, chimp and human) but not so clearly in others (orangutan). Earlier diverging primates such as lemurs, tarsier and new world monkeys have a single PRMR7 gene adjacent to GAS8. Tree shrew has unsatisfactory coverage in this region (six exons spread out over two contigs and 3 unassembled traces, a string of Ns in the terminal zinc finger domain, and undetermined synteny).
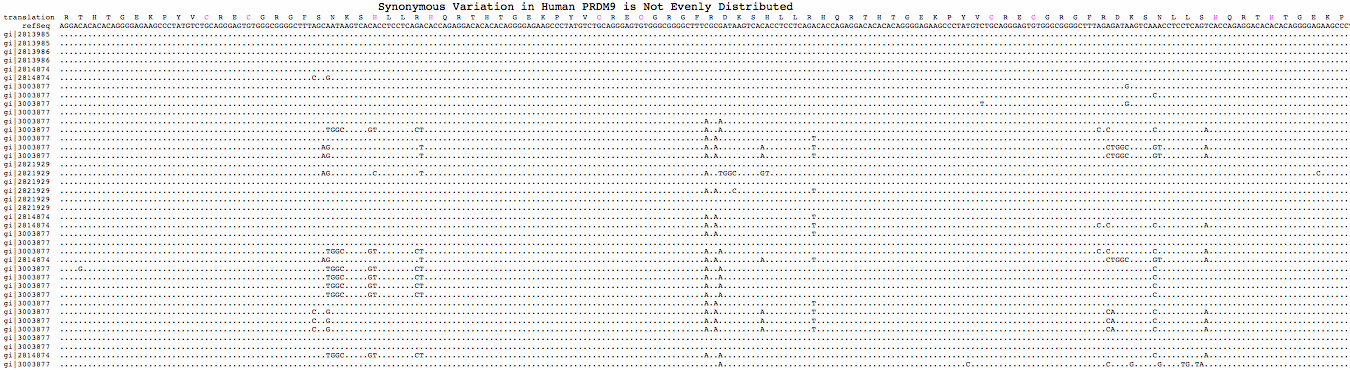
Although an obvious pseudogene, human PRDM7 is sometimes treated as a functional gene with 'isoforms'. However exon 9 of the reference sequence hg18 contains an internal direct tandem repeat of 88 nucleotides that throws off the reading frame and subsequent splice to exon 10, which itself has a frameshift (GGGG to GGG) in the second of its three zinc fingers. The protein is incorrectly described at NCBI, SwissProt and UCSC -- zinc fingers translated into the wrong reading frame cannot possibly form a stable fold, much less recognize a nucleotide sequence. Given the common comparative genomics context of duplication followed by subsequent pseudogenization (of either parent or duplicate), this feature is unquestionably a pseudogene whether it is still transcribed or not. Pseudogenization likely predated divergence of bushman and neanderthal and apparently independently of those events in other primates.
Rodents and lagomorphs have no counterpart to PRDM9, though the situation is confused by later chromosomal rearrangements (no affirming homolog or even debris adjacent to GAS8 or cadherin). The mouse gene is then orthologous to primate PRDM7, not PRDM9. The rat gene occurs in the same syntenic context as mouse; other rodent genomes are too incomplete for synteny to be assessed. Rabbit has two apparent PRDM7, called here PRDM7a and PRDM7b; neither copy is syntenic to mouse/rat or any other mammal. The pika genome is too incomplete to determine whether this duplication predated their divergence. Overall the data is consistent with a single PRDM7 locus in the last common ancestor of primate and rodent. It would be vastly more useful to complete genomes already begun than to embark on incomplete sequencing of an additional 10k vertebrate genomes.
When murid rodents are aligned, it is quite clear that PRDM7 is evolving quite orderly overall but rather rapidly in the amino acids contacting the hotspot dna motif. There are substantial differences between common strains of lab mouse and unsurprisingly these cannot always interbreed (shown below in first six lines as genome strain C57BL/6J, WSB/EiJ, MOLF/EiJ, PWD/PhJ, CAST/EiJ, and C57BL10.F):
PRDM7_musMus1 SIERQCGQYFSDKSNVNEHQKTHTGEKPYVCRECGRGFTQNSHLIQHQRTHTGEKPYVCRECGRGFTQKSDLIKHQRTHTGEKPYVCRECGRGFTQKSDLIKHQRTHTGEKPYVCRECGRGFTQKSVLIKHQRTHTGEKPYVCRECGRGFTQKSVLIKHQRTHTGEKPYVCRECGRGFTAKSVLIQHQRTHTGEKPYVCRECGRGFTAKSNLIQHQRTHTGEKPYVCRECGRGFTAKSVLIQHQRTHTGEKP-YVCRECGRGFTAKSVLIQHQRTHTGEKPYVCRECGRGFTQKSNLIKHQRTHTGEKPYVCRECGWGFTQKSDLIQHQRTHTREKP-------------------------------------------------------- PRDM7_musMus2 ....................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................A..V..Q.................R......N..K......G...YVCRECGWGFTQKSDLIQHQRTHTREK............................. PRDM7_musMus3 ........................................K.D..K........................V....................................................A..N..Q.....................A.....Q.....................Q..D..K..............................................................................E..S................................................R...A..V.........G........................................................... PRDM7_musMus4 ........................................K.D..K........................V....................................................A..N..Q.....................A.....Q.....................Q..D..K.................................................E..S..K.........................N...........................V....................R...A..V.........G........................................................... PRDM7_musMus5 .......................................AK.N...........................V..Q.................................................A..N..Q.....................E..S....................W......N........................Q..S..K........................N.............A.......W...Q..N..K.................W......D..Q......R..-----------------------------........................................................ PRDM7_musMus6 ...............................................................................................V..V.........................N.H..Q.....................A.....Q.....................QN.H........................Q..D..K.....................Q.....K......................Q..N..K.................W......D..Q......R..-----------------------------........................................................ PRDM7_musMol2 .......................................AK.N...........................V..Q.................................................A..N..Q.....................E..S....................W......N........................Q..S..K........................N.....................W...Q..N..K.................W......D..Q......R..-----------------------------........................................................ PRDM9_musCas .......................................AK.N...........................V..Q.................................................AR.N..Q........................D...........................N........................E..S..K.................W......N.........................Q..S..K.....................A.....Q........................N..K......G...YVCRECGWGFTQKSDLIQHQRTHTREKP............................ PRDM9_musPah ....................R...................K.N..T.....................G..P..R........................N..T.....................G..P..R........................H........................E..N..K.....................Q..P..R.............T.......Q..N..T....N......------------------------------------------------------------------------------------........................................................ PRDM9_musMac ........................................K.D..K.....................V..............................N..Q........................D........................V..H.TQ.....................Q..D..K........................H..K.....................Q..N............................N..K......................N.H.TQ.........S..........K......................................................................... PRDM9_musSpi ........................................K.N............-..............N..Q.....................A...........................V..H.TQ........................D...........................H.T......................Q..............................N..K......................QN.H.T..........S.......W..K...D..Q......R...----------------------------........................................................ PRDM7_musMol1 .......................................AK.N...........................V..Q.................................................A..N..Q.....................E..S....................W......N........................Q..S..K........................N.....................W...Q..N..K.................W......D..Q......R...----------------------------........................................................ PRDM9_merUng GTG.E...C.......S...R.................M.R.N..S....................M.R.N..S.....................V..V..S.....................V.PH..S..........H...........R.N..R.....................V.PH..S.....................V.PH..S.....................V.....S......................V.....R................R.....R.T..R..........H......R...RG.H.LR......G.VL........................................................ PRDM9_micAgr RVGGER..C...........R..................RK.N.NV.....................R.AL..S.......................AL..S........................Y..L.....................G..N.NV.....................Q..Y..L.....................G..L..R.....................Q..YP.L...........------------------------------------------------------------------------------------........................................................ PRDM9_arvTer RV.GE...C.N.......R.R..................RK.V..L........................V..N........................H..F........................H..L.....................W.....L........R............R..H..L.....................Q..H..L.....................R.....L......................R.....N..........--------------------------------------------------------........................................................ PRDM9_perPol R..TE...R.........S.R..SE..........Q..I.K.V..C.................Q...W..H..R.................K..IR..H..C.................Q..I...H..C.................Q.........C.................Q..IR..Y..C.................K...W..V..R......V...----------------------------.------------------------------------------------------------------------------------........................................................ PRDM9_perLeu R..TE...R......A..S.R..SE..........Q...RK.Y..C.................Q..I...V..R.................Q...R..Y..C.................Q..I......R.................Q...W.....C.................Q...R..Y..C.................Q...W..H..R.................Q...R..Y..C..................Q..IQ..H..C.................Q...R..Y..C.................Q...W..V..R......A........................................................... PRDM9_perMan RT.TE...H......A..S.R..SE..........Q...WK.V..R.................Q...W..V..C.................Q...W..V..C.................Q..I...H..R.................Q..IR..H..C.................Q..AQ.....Y.................Q...R..H..C.................Q..AQ.....C..................Q...W.....C.................Q..I...H..R.................Q..I...H..R......G........................................................... PRDM9_apoSyl RV...R..C.......S.R.G.......C...........K...NR..........H.............H.NR..........H..........L..N.NR..........C.......A.....D..Q........................N.NQ.....................R..L........................Q..D.NR...................L.Q..N.........................L..D........................R..D.NR.................R......N.........G...YVCRECGRGFTLKSDLIQHQRTHTGEKPYVCRECGRGFTRKSDLNRHQRTHTGEKP PRDM7_ratNor R.......C.......S...R........I........S.K.D..K......E....I......................E....I...........................I............D.........E....I............S..R...........I.....L...Q..N..R.L.........I.....L...R.................I.....Q.L.W..S...............I.........W..S.........V...--------------------------------------------------------........................................................
Laurasiatheres have a quite different history of gene duplication. Most species simply retain the ancestral condition of a single PRDM7 gene adjacent to GAS8. Vampire bat (but not brown bat) has an additional segmental duplication to a novel location that is today a pseudogene. Dog inexplicably has a PRDM7 pseudogene but no PRDM9 despite a rather complete assembly, even as other carnivores (cat, panda, ferret), insectivores, perissodactyls and early-diverging artiodactyls (alpaca, pig, dolphin) have a conventional single PRDM7 gene (though some of these have too few zinc fingers to recognize sufficiently long dna motifs to delimit hotspots).
Carnivores -- but not bats or horses -- have an intervening cadherin gene between GAS8 and PRDM7. This rare genomic event is not the ancestral state but is unfortunately too restricted in distribution to resolve the status of Pegasoferae:
geneSpp id chr strand start stop span PRDM7_ailMel 100% GL193502 +- 628987 644235 15249 CAD1_homSap 73% GL193502 +- 620344 624223 3880 GAS8_homSap 91% GL193502 ++ 594843 609901 15059 PRDM7_canFam 82% chr5 ++ 66560684 66567275 6592 CAD1_homSap 75% chr5 ++ 66571832 66581008 9177 GAS8_homSap 93% chr5 +- 66587321 66604940 17620 PRDM7_felCat 100% Un_ACBE01450414 +- 10493 13105 2613 CAD1_homSap 75% Un_ACBE01450414 +- 3902 4280 379 PRDM7_equCab 100% chr3 +- 36378853 36387224 8372 GAS8_homSap 93% chr3 ++ 36348528 36361906 13379
Pecoran ruminants (cow, sheep, muntjak) present a vastly more complicated situation. Cows -- even in the revised assembly -- have a PRDM7 pseudogene adjacent to GAS8 accompanied by 5 PRDM9 copies in other locations (all distinct from the primate cadherin secondary site). This is neither a recent development nor an artifact of domestication because a similar expansion is seen in provisional assemblies of sheep and muntjak (wild deer) but not dolphin, pig or vicuna, dating the expansion to stem pecoran ruminant. It is not clear which if any (or several acting in tandem) of these gene copies play a role in recombination -- the primate paradigm for meiotic markup is not immediately applicable to these species.
Atlantogenata (Afrotheres + Xenarthra) have yet another history. Elephant (best of five available assemblies) has three loci: an old PRDM7 pseudogene in GAS8 syntenic position, a seemingly functional PRDM9a with 12 terminal zinc fingers and novel syntenic location, and a fairly recent pseudogene PRDM9b. A dna assembly from fossil mammoth shows the same three genes with the same pseudogenization pattern. Although the sequences diverged separately after speciation, three identical inactivating mutations occur in both mammoth and elephant but not hyrax, thus dating gene loss relative to their speciation. This is shown for exon 9 below:
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRVIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKKELTAGR 1 PRDM9_conSeq wildtype consensus reference 1 YVNCIQD*KEQNLVAFQYHRQIFHWTCCTIRPGCELLVWYGDNYSQELGIKWGSR*KKELTSGT 1 PRDM9b_loxAfr gg bad acceptor, early stop codon, internal stop codon 1 YVNCTRDKEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYWTCHTIQPGCelLVWYGDNYGQELGIKWGSR*KKELTSGT 1 PRDM9b_mamPri gg bad acceptor, two 1 bp deletions, internal stop codon 1 YVRRARDTEERNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCCTVRPGCELLVWRGAEDSQALG SRRTMELTSQK 1 PRDM9b_proCap pseudogene with 4aa deletion 1 YVNCARDEEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRTIQPDCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSRWKKELTSGT 1 PRDM9a_loxAfr wildtype 1 YVNCARDEEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRT 1 PRDM9a_mamPri fragmentary coverage 1 YVNCARDEDEQNLVAFQYHGQIFYRTCRPVQPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIQRGSRQMKALSSQT 1 PRDM9a_proCap 17 zinc fingers 1 YVNGTQDEKEQNLVFFQYHRQIFYQTCYAVWPGCQLLVWYRDECGQELGIKWDNRGKKEFTVGT 1 PRDM7_loxAfr bad acceptor, bad donor 1 YVNGTQDEKEQNLVFFQYHRQIFYQTCYAVWPGCQLLVWYRDECGQELGIKWDNRGKKEFTVGT 1 PRDM7_mamPri bad acceptor, bad donor, 1 synon bp difference 1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRAIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKKELTAEK 1 PRDM7_choHof wildtype 1 YVNCAWDDKEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRTIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKKEFMTGT 1 PRDM7_dasNov wildtype
Marsupials and platypus: the mystery of exon 5
Tracking PRDM7 back to marsupials and beyond presents significant uncertainties. The three available marsupial assemblies are seriously incomplete, causing gene prediction problems when exons are spread over multiple small contigs, which further do not provide syntenic validation. Domain linker regions have weak amino acid conservation and so fail to give blast matches to placental queries, a problem exacerbated for short exons and pseudogenes (opossum). No expression data exist to bridge uncertain regions, meaning missing exons cannot be located nor exons in different contigs definitively connected. Because the domains here occur widely in other combinations in other proteins, a full length marsupial sequence is critical to testing whether the domain shuffle resulting in PRDM7 and PRDM9 was a placental innovation.
The most favorable situation occurs in the Monodelphis domestica assembly. Here eight of the ten expected exons (1 and 5 are missing) are readily located in a single assembly region of length 33,449 bp with a single gap (estimated at 270 bp). It is not surprising that exon 1 cannot be located because it has no known domain or reason for fixed length and is diverging rapidly in placentals. However locating exon 5 is important for distinguishing between two adjacent small genes evolving into a single fused gene only in the placental branch versus a full length gene already present in the last common ancestor.
Unless exon 5 lies within the assembly gap, it should be locatable in the 25,548 bp separating exon 4 and exon 6 (of which 8,263 bp remains after application of RepeatMasker). However blastx against a panel of 54 exon 5 sequences from placental mammal fails to give any suggestion of match, despite plausibly adequate length (all placental exon 5 sequences have 52 amino acids).
Gene prediction tools such as GenScan, NScan, Ensembl and Gnomon give useless results because they neglect comparative genomics: a few exons are correctly predicted but are otherwise embedded in time-wasting rubbish. The poor reliability of these tools does not justify GenBank clutter (eg XM_001369137) for their predictions. The 46-species whole genome alignment at UCSC (starting with PRDM7/9 'ProteinFasta' link at the description page) is a better starting point.
Here it should be noted that exon 5 has not diverged especially rapidly from the last common ancestor of placentals. Aligned to human, the full range of sequences has overall identity of 69%. Exon 5 has a number of invariant and semi-invariant residues, only possible over this time span if maintained by selective pressure. Thus it has some function even though it contains no known Pfam domains and has no crystallographic structure match. Because exon 4 has a splice donor of phase 0 and exon 6 a splice acceptor of phase 2, exon 5 in marsupials must take the form 0 xxxxxxxx 1 to conserve reading frame. This rules out non-use of exon 5 in marsupials (alternative splicing) followed by mutational decay to unrecognizability.
The opossum gene is peculiar in that 7 of the 8 exons available are quite conventional in sequence but the terminal zinc finger exon is completely broken up by frameshifts and stop codons and barely recognizable. The other exons return only PRDM7/9 as significant matches when back-blasted against the human genome establishing that they have not been confused with the many hundreds of partial homologs with KRAB, SSXRD, PR (SET) or C2H2 domains.
The Sarcophilus harrisii assembly is missing the same two exons but has a conventional terminal exon with an intact zinc finger region of seven repeats (with two distal frameshifts however). Here exons 2 occurs in contig AFEY01202902 and exons 3-4 in AFEY01156721 with 1,436 bp left over to host exon 5; exons 6-10 are found in a third contig AFEY01386448 with 8,331 bp available upstream for exon 5. It is not known whether these contigs would be adjacent in more complete assembly.The six exons comparable between tasmanian devil and opossum are 82% identical to each other as proteins and 67% identical to those of human, not indicative of anomalous or especially rapid evolution in the context of entire proteome rates.
The Macropus eugenii (wallaby) assembly is least complete, with no contig containing more than a single exon. Here exons 1, 4, 5 and 8 are missing altogether but the terminal zinc finger exon is intact with 7 C2H2 domains. It is worth noting that the exon 10 is so long and distinctive with its phase 2 reading frame and early zinc finger that there is no possibility of confusing it with those of homologs (HKR1, ZNF133, ZNF169, ZNF343, ZNF589 in human).
If marsupials had a markedly (or even totally) different exon 5 of form 0 xxxxxxxx 1, it should emerge from a tblastx comparison of the regions between exons 4-6. However no plausible candidate emerges. This implies orthology despite the assembly gaps and missing exon 5, ie the last common ancestor to marsupials and placentals had a full length PRDM7-type gene. It is uncertain whether these should be connected up into a single gene with the later exons -- the whole issue here is timing of the final gene shuffle.
The situation in platypus is curious. Only distal exons 6-10 can be reliably recognized in the current assembly, ie KRAB, SSXRD and exon 5 are missing but the knuckle, PR and zinc finger domains are present with 3-4 repeat units. However the early zinc finger in the last exon is not present. Yet the best backblast to human is still PRDM7/9. These exons occur in two tandem copies on the same strand but differ significantly from each other and so do not represent mis-assembly duplications. The intervening area is gapless so the missing exons should be locatable if present.
However they are not. Upon blastx of the repeatmasked sequence against Genbank tetrapod sequences, no matches occur, other than three worthless platypus gene models (XP_001507240, XP_001509482, XP_001509433) that predict earlier exons which however are wholly lacking in any support in any other species. Thus it appears that the gapless region does not contain any counterpart to exons 1-5 of theran mammals. Either this region has been lost in platypus or it is a stand-alone shorter distal version of PRDM7/9. The first identifiable exons begins with the expected phase 2 reading frame in both tandem copies and do not contain an in-frame methionine upstream prior to a stop codon. Hence there must be at least one earlier exon. However tblastx of the appropriate regions of repeatmasked marsupial and platypus again does not identify noteworthy peptide candidates.
Perhaps the corresponding ancestral region was shuffled together with a gene providing the proximal regions in the theran branch only, giving rise to the full length gene there. However tblastn queries of the platypus assembly, while locating numerous appropriate KRAB_A domains with the correct 0 xxxxxxxx 1 reading frame that backblast to other human proteins, do not find counterparts of the exon 1-5 region beyond exon 2. Hence there is no obvious donor for the proximal half of PRDM7/9.
Given that the PRDM and zinc finger families are greatly expanded with extensive domain shuffling in mammals with difficulties already tracing back PRDM7/9 to marsupials and monotremes, it comes as no surprise that bird, lizard and frog genomes shed no further light on the evolution of this gene. The situation in non-placental mammals could theoretically be resolved by sequencing transcripts, but these are exceedingly rare for PRDM7/9 even in placentals and so will not emerge unless explicitly sought.
Conservation of exon 5 within placentals; invariant residues in red PRDM9_homSap GMPKASFSNESSLKELSRTANLLNASGSEQAQKPVSPSGEASTSGQHSRLKL PRDM9_panTro .......N.........GMP....T............P.............. PRDM9_gorGor .....................................P.............. PRDM9_ponAbe .......N.........G.Q....T............P..........T..I PRDM9_nomLeu .................GA..................P.............. PRDM9_macMul .......N.......V.GM.....T............P...R.......... PRDM9_papHam E...T............G.P...ST.........A..P.............. PRDM7_calJac .......G......K..G...V..T..P.........P.............. PRDM7_micMur ...R.PL.DG.......G......T.....P......PR..........R.. PRDM7_otoGar ...R.PL.DG.......GP.S.P.I.....H..HM.SPR.........GR.S PRDM7_tarSyr ...R.PL.IV.......EM.....T.D....W......R.....E....K.. PRDM7_oryCun ...RLPVN.........GI.....TT...ED...SF.PK.TR......TR.. PRDM7_ratNor ET.RMPL.DK..V..VFGIE....T....H.....CSPE.GN.....FGK.. PRDM7_musMus ESSRMP..G..NV..G.GIE....T....HV.....SLE.GN......GK.. PRDM7_speTri LK.EVLL..........G......T.....V......LR...A.R....R.. PRDM9e_bosTau ..SR.PL.K.......PGA.K..KT..CK....L.P.PRK.R.PE..P.Q.V PRDM9c_oviAri ..S..LV..K.....MPGASK..KTR.PK...I..PAPR.P...E..P.Q.V PRDM9a_munMun ..SR.PLIK.......LGA.K.MKT...K...N..PHPRK.R.P...P.Q.V PRDM7_turTru AV.PVPL.......K.PGA.Q.QK...PA...S.AP.P.A....AW.T.Q.. PRDM7_lamPac ...RGPL..Q.......G..KP.KT...G.....FP.L.......R...Q.. PRDM7_susScr SDSRVPL..K......LT..EVPET.......E....P......RRR.GQE. PRDM7_canFam .I.RVPL..K.......E..K...T.SP..G..S..LP.K.....H.T.Q.. PRDM7_felCat .THRVPL.K.....DF.E..K...T.....G.....LP.......H...R.. PRDM7_ailMel .I.R.PLR.........E..K...T....LG.....LP.......HD.LQ.. PRDM7_musPut .V.R.PL..........E..K...T....HD.....HP.......H..LR.. PRDM7_pteVam A..RVPL...P......VI....K......D....F.P.K..A.R....Q.. PRDM7_myoLuc AKSR.PL..........G.....TT.....T..T.P.P.........P.S.. PRDM7_equCab R.RT.PL....R.....G..K..KT.S...V......L....S.E....R.. PRDM7_sorAra .RSRTPI.....S....G.RT...TKCTK.....LF.P.......HY.KP.. PRDM9a_loxAfr .T...LLG.......V.G..I...TT..........SP......D.P..W.. PRDM7_echTel ...GV.LR...N..V..G..I..T.AEP..PH-.G..P...T..HE.L.Q.V PRDM7a_proCap .T...LLG.......V.G..I...TT..........SP......D.P..W.. Consensus GMPRAPLSNESSLKELSGTANLLNTSGSEQAQKPVSPPGEASTSGQHSRQKL
Comparative genomics: sequence availability
As of mid-July, 2011, some 62 PRDM7 and PRDM9 genes from 36 species can be recovered from placental mammal genome projects. The encoded proteins are compiled here as tab-delimited pdf text that will paste cleanly into rows and columns of a spreadsheet such as excel, or below as exon-by-exon gene models in the Curated reference sequences section.
Of these 62 genes, 18 are pseudogenes in various states of degeneration. There has been no gain or loss of introns -- all genes have the same identically phased ten exons. No retroprocessed (intronless) genes occur despite transcription in germline tissues. However because mammalian assemblies all have gaps, 83 of 620 expected exons lack coverage or (with marsupials and monotremes) are too short or too diverged to be recognizable.
The table below shows the number of zinc fingers in the second column, phylogenetic clade in the third, and adjacent gene (synteny) in the fifth. The number and character of zinc fingers is quite variable in human populations and likely so in all mammals; the table provides that of the individual selected for reference genome project which may not be repesentative of the species.
These zinc finger arrays have been corrected in low coverage genomes for common sequencing errors -- frameshifts and premature stop codons arising from nucleotide run length mis-calls (eg, ggggg read as gggg) -- though they could actually represent valid mutant alleles in the heterozygous state (assuming the gene essential for meiosis). Indeed, these errors seem far more common than in what is seen in housekeeping genes for the same genome.
Pseudgenes are sometimes obvious (large deletions, reading frame errors at multiple locations, stop codons in early exons, amino acid substitutions not corresponding to the conservation profile) but otherwise can be difficult to distinguish from assembly error or a bad allele of a usually intact gene in the population (possibly a balanced polymorphism that reduces copy number).
A pseudogene can continue being transcribed for tens of millions of years after losing all functionality at the protein level. That is moot here because PRDM7 and PRDM9 are barely represented in the millions of mammalian transcripts at GenBank. That rarity might be explained by low levels of transcription in tissue types not widely used as mammalian mRNA sources. PRDM7/9 illustrate the futility of undirected transcript sequencing projects for determining the full coding potential of the genome. Global expression chips too have so far have produced no data.
The transcripts from mouse, rat and pig do not support the widely propagated concept that PRDM7/9 function solely in meiosis (which would limit them in effect to testis) as almost all transcripts arose elsewhere. In mouse, PRDM7's role in meiosis has strong experimental support, yet all the transcripts come from non-meiotic tissues. Human PRDM9 experimental transcripts mostly derive from a single unpublished 2011 project entitled "Exhaustive RT-PCR and sequencing of all novel TWINSCAN predictions in human" which pooled tissue from adrenal gland, bone marrow, brain, cerebellum, brain (whole), fetal brain, fetal liver, heart, kidney, liver, lung, placenta, prostate, salivary gland, skeletal muscle, testis, thymus, thyroid, trachea, uterus, and spinal cord.
Transcripts at GenBank on 25 July 2011 (est database): DB452778 PRDM9 Homo testis DB636359 PRDM9 Homo testis DB024448 PRDM9 Homo testis DB080053 PRDM9 Homo testis DT932634 PRDM9 Homo pooled including testis DT932633 PRDM9 Homo pooled including testis DV080525 PRDM9 Homo pooled including testis DV080526 PRDM9 Homo pooled including testis DV080328 PRDM9 Homo pooled including testis DV080173 PRDM9 Homo pooled including testis DV080174 PRDM9 Homo pooled including testis DV080327 PRDM9 Homo pooled including testis BU194881 PRDM9 Homo melanotic melanoma AL704902 PRDM9 Homo not reported CK032493 PRDM7 Mus placenta CJ235803 PRDM7 Mus amnion CN723438 PRDM7 Mus 4-cell embryo BI737497 PRDM7 Mus retina BB642583 PRDM7 Mus retina BG288443 PRDM7 Mus eye FM103467 PRDM7 Rattus body fat GO353654 PRDM7a Bos 4-cell embryo BX673635 PRDM7 Sus pooled including testis CO991452 PRDM7 Sus oviduct CO991452 PRDM7 Sus mucosal membrane EW469934 PRDM7 Sus mucosal membrane
The PRDM7 genes are all orthologous in the classical sense (as can be seen by adjacency to the unrelated gene GAS8) but various PRDM9 genes arose as different lineage-specific segmental duplications so are orthologous in a useful sense only when shared within a well-defined phylogenetic clade. There is currently no suitable nomenclature to distinguish these events (so they are all called PRDM9 here). In some species such as mouse, chromosomal rearrangements have scattered syntenic genes and orthology remains slightly uncertain but probably represents a simple descent from the single euarchontoglire PRDM7 gene.
- PRDM7: genes with ancestral location GAS8 synteny
- PRDM9: lineage-specific segmental duplications of PRDM7
- Pseudogenes: multiple disabling frameshifts and stop codons in parental gene (not a retrogene)
>PRDM9_homSap 13 prim gene CDH12 Homo sapiens (human) NM_020227 >PRDM9_panTro 19 prim gene CDH12 Pan troglodytes (chimp) GU166820 >PRDM9_gorGor - prim gene cdh12 Gorilla gorilla (gorilla) CABD02290264 >PRDM9_ponAbe 10 prim gene CDH12 Pongo abelii (orangutan) XR_093432 >PRDM9_nomLeu 10 prim gene cdh12 Nomascus leucogenys (gibbon) ADFV01015315 >PRDM9_macMul 9 prim gene CDH12 Macaca mulatta (rhesus) XM_001083675 >PRDM9_papHam 11 prim gene cdh12 Papio hamadryas (baboon) genome >PRDM7_homSap 3 prim gene GAS8+ Homo sapiens (human) genome >PRDM7_panTro 2 prim pseu GAS8+ Pan troglodytes (chimp) genome >PRDM7_gorGor 3 prim pseu GAS8+ Gorilla gorilla (gorilla) genome >PRDM7_ponAbe 4 prim gene GAS8+ Pongo abelii (orangutan) genome >PRDM7_nomLeu 5 prim pseu gas8+ Nomascus leucogenys (gibbon) ADFV01125891 >PRDM7_macMul 2 prim pseu GAS8+ Macaca mulatta (rhesus) genome >PRDM7_papHam 2 prim pseu gas8+ Papio hamadryas (baboon) genome >PRDM7_calJac 12 prim gene GAS8+ Callithrix jacchus (marmoset) XR_090591 >PRDM7_tarSyr - prim pseu gas8+ Tarsius syrichta (tarsier) ABRT011082008 >PRDM7_micMur 8 prim gene gas8+ Microcebus murinus (lemur) ABDC01433247 >PRDM7_otoGar 7 prim gene GAS8+ Otolemur garnettii (galago) genome >PRDM7_tupBel 9 prim gene noDet Tupaia belangeri (tree_shrew) genome >PRDM9_oryCun 8 glir gene other Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) genome >PRDM7_oryCun 4 glir gene other Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) genome >PRDM7_ochPri - glir gene noDet Ochotona princeps (pika) AAYZ01312269 >PRDM7_ratNor 10 glir gene PDCD2 Rattus norvegicus (rat) NM_001108903 >PRDM7_musMus 12 glir gene PDCD2 Mus musculus (mouse) NM_144809 >PRDM7_musMol 11 glir gene noDet Mus molossinus (wild_mouse) GU216230 >PRDM7_dipOrd - glir gene noDet Dipodomys ordii (kangaroo_rat) genome >PRDM7_speTri - glir gene noDet Spermophil tridecemlin (squirrel) AAQQ01308561 >PRDM9a_bosTau 7 laur gene noDet Bos taurus (cattle) NW_003053109 >PRDM9b_bosTau 5 laur gene noDet Bos taurus (cattle) DAAA02065087 >PRDM9c_bosTau - laur gene noDet Bos taurus (cattle) XM_002699750 >PRDM9d_bosTau 9 laur gene noDet Bos taurus (cattle) genome >PRDM9e_bosTau 9 laur gene noDet Bos taurus (cattle) genome >PRDM9e_oviAri - laur pseu noDet Ovis aries (sheep) genome >PRDM9d_oviAri - laur gene noDet Ovis aries (sheep) genome >PRDM9c_oviAri 4 laur pseu noDet Ovis aries (sheep) genome >PRDM9b_oviAri 2 laur pseu noDet Ovis aries (sheep) genome >PRDM9a_oviAri 9 laur gene noDet Ovis aries (sheep) genome >PRDM9d_munMun 4 laur gene noDet Muntiacus muntjak (muntjac) AC216498 >PRDM9c_munMun 15 laur gene noDet Muntiacus muntjak (muntjac) AC154919 >PRDM9b_munMun 13 laur gene noDet Muntiacus muntjak (muntjac) AC218859 >PRDM9a_munMun 7 laur gene noDet Muntiacus muntjak (muntjac) AC225653 >PRDM7_bosTau - laur pseu GAS8+ Bos taurus (cattle) genome >PRDM7_turTru 9 laur gene gas8+ Tursiops truncatus (dolphin) ABRN01441536 >PRDM7_lamPac 2 laur gene noDet Lama pacos (llama) scaffolds >PRDM7_susScr 9 laur gene GAS8+ Sus scrofa (pig) FP476134 >PRDM7_canFam 5 laur pseu GAS8+ Canis familiaris (dog) genome >PRDM7_felCat 11 laur gene GAS8+ Felis catus (cat) genome >PRDM7_ailMel 6 laur gene GAS8+ Ailuropoda melanoleuca (panda) GL193502 >PRDM7_musPut 3 laur gene noDet Mustela putorius (ferret) AEYP01035077 >PRDM9_pteVam 15 laur pseu noDet Pteropus vampyrus (bat) ABRP01232219 >PRDM7_pteVam 7 laur gene GAS8+ Pteropus vampyrus (bat) ABRP01250178 >PRDM7_myoLuc 6 laur gene gas8+ Myotis lucifugus (bat) AAPE02062260 >PRDM7_equCab 4 laur gene GAS8+ Equus caballus (horse) genome >PRDM7_sorAra 8 laur gene noDet Sorex araneus (shrew) AALT01000095 >PRDM9a_loxAfr 12 afro gene noDet Loxodonta africana (elephant) genome >PRDM9b_loxAfr 3 afro pseu noDet Loxodonta africana (elephant) genome >PRDM7_loxAfr 5 afro pseu GAS8+ Loxodonta africana (elephant) genome >PRDM7_echTel 5 afro pseu noDet Echinops telfairi (tenrec) genome >PRDM7a_proCap 17 afro pseu noDet Procavia capensis (hyrax) ABRQ01392668 >PRDM7b_proCap 13 afro pseu noDet Procavia capensis (hyrax) ABRQ01227339 >PRDM7_dasNov 9 xena pseu noDet Dasypus novemcinctus (armadillo) AAGV020462211 >PRDM7_choHof 2 xena pseu noDet Choloepus hoffmanni (sloth) ABVD01893961
Domain-level gene trees
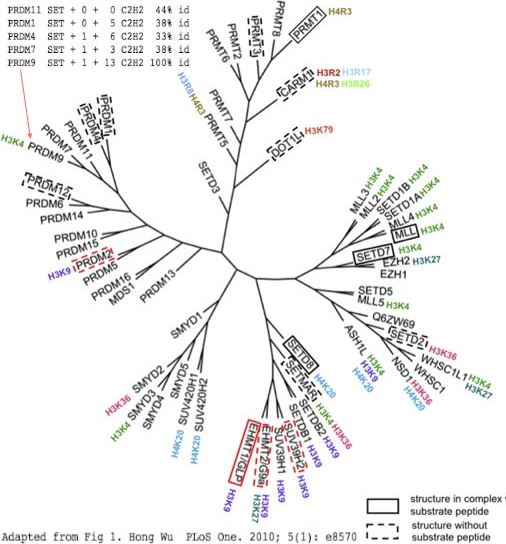
PRDM9 is one of many human proteins sharing a set of common domains, as well as various multiplicities of the zinc finger domain C2H2. The diagram at left shows an effort at organizing these into phylogenetic tree according to structural considerations of the SET domain these proteins all share.
The traditional SET domain seems too small for an enzyme with distinctive substrates so flanking sequence can be added consistent with observed amino acid conservation. Using S-adenosyl methionine as donor, PRDM9 places the third methyl group only on the fourth position lysine in mature histone H3 (which is actually position 5 prior to iMet removal: MARTKQTARK...), one of many such epigenetic methylases in the human genome. The histone recognized by such methylases correlates poorly with evolutionary grouping by SET domain (figure), suggesting gene duplications have diverged to other recognize other locations. SET domains without demonstrated methylation activity may still retain recognition capacity.
The upper left corner shows variability in domain structure. While PRDM9 and PRDM7 share the same domains (an upstream KRAB domain is not shown), of PR-class homologs, PRDM11 shares only the SET domain despite nesting deep within the PRDM9 subtree. PRDM4 has both the SET and C2H2 domains, possibly sharing the early zinc finger in an exon beginning with a phase 2 splice acceptor (as shown in reference sequence section). Overall however, PRDM9 and PRDM7 have no full length homologs with matching exon structure. Even the SET domain is intronated differently within PR-class proteins, suggesting either ancient divergence. These incongruities may have arisen from domain shuffling, gain and loss.
The human PRDM9 sequence below is annotated in color for domains relative to exon breaks. The protein can be best understood in terms of concatenated domains, not all of which may be present in antecedent and descendant homologs. The first two domains KRAB and SSXRD interact with transcription factors.
Each terminal zinc finger type C2H2 array -- so named for two cysteines and two histidines liganding to a structural zinc ion -- potentially recognizes a specific trinucleotide (more or less) and so a large concatenated array potentially recognizes quite specific binding sites along the genome, though tolerance of nucleotide variability and synergistic effects between adjacent units make it difficult to read out these sites precisely, despite immense efforts. However aberrant zinc fingers are common and not all contribute to dna binding specificity.
The concatenated C2H2 domains, conserved at the amino acid level so necessarily similar at the dna level, are apparently prone to replication slippage (or gene conversion with misalignment). This process can give rise to point mutations as well as leading to different distributions in human populations of both repeat number and repeat sequence. Taking the extremes, it is a wonder that humans can still interbreed, yet there are no known instantiations of Haldane's Rule.
Many other unrelated genes with internal repeats (such as the octapeptide region of the prion gene PRNP) are also affected by replication slippage. Such proteins regions are conveniently studied by mRNA dot plots.
Both PRDM9 and PRDM7 contain a seldom-mentioned zinc finger early in the final exon, as annotated by SwissProt and readily found by the online domain tools such as SMART regardless of species. This domain conserves the four critical residues needed for zinc binding (and so the associated fold) but lacks the terminal cap TGEKP which otherwise serves to lock down a C2H2 zinc finger after it has scanned along genomic dna to an appropriate trinucleotide. The function of this early domain and the following 112 highly variable residues are unknown -- no demonstrably homologous sequence occurs in other proteins with the possible exception of PRDM4 and PRDM10.
The main zinc finger array also resides in this long distinctive terminal exon of splicing phase 12 that has been shuffled together into various contexts during mammalian evolutionary time. For once, intron phase is not so informative because the preceding PR(SET) domain with its codon overhang of 1 bp can accept any shuffled domain with overhang of 2 bp and still maintain reading frame. Concepts such as paralogy and orthology need piecewise definitions in these composite proteins.
The first C2H2 of the main repeat region is proximally degenerate, beginning in VKY in all species (instead of YCE). The lysine cannot plausibly replace the usual cysteine for zinc binding though the other three needed residues are present and may suffice. This domain ends in a typical cap region TGEKP. Humans are the exception here where the conserved helix-ending proline has been replaced with leucine in the reference human genome, with unknown functional consequences.
As noted, PRDM7 occurs immediately telomeric to the unrelated single-copy conserved gene GAS8 (with the two genes convergently transcribed). PRDM7 is otherwise the last gene on the q arm of its chromosome in many species which may predispose it to copy number dispersal events, which may in the past have resulted in juxtaposition and functional fusion to other genes. PRDM9 is not consistently located within placental mammals, suggesting numerous independent rearrangements.
>PRDM9_homSap Homo sapiens (human) Q9NQV7 10 exons chr5:23,509,579 span 18,301 bp KRAB SSXRD zinc knuckle SET early ZNF C2H2 cap 0 MSPEKSQEESPEEDTERTERKPM 0 0 VKDAFKDISIYFTKEEWAEMGDWEKTRYRNVKRNYNALITI 1 2 GLRATRPAFMCHRRQAIKLQVDDTEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1 2 VKPPWMALRVEQRKHQK 0 0 GMPKASFSNESSLKELSRTANLLNASGSEQAQKPVSPSGEASTSGQHSRLKL 1 2 ELRKKETERKMYSLRERKGHAYKEVSEPQDDDYL 1 2 YCEMCQNFFIDSCAAHGPPTFVKDSAVDKGHPNRSALSLPPGLRIGPSGIPQAGLGVWNEASDLPLGLHFGPYEGRITEDEEAANNGYSWL 0 0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDKSWANWMR 2 1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRVIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKKELMAGR 1 2 EPKPEIHPCPSCCLAFSSQKFLSQHVERNHSSQNFPGPSARKLLQPENPCPGDQNQEQQYPDPHSRNDKTKGQEIKERSKLLNKRTWQREISRAFSSPPKGQMGSCRVGKRIMEEESRTGQKVNPGNTGKLFVGVGISRIAK VKYGECGQGFSVKSDVITHQRTHTGEKL YVCRECGRGFSWKSHLLIHQRIHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFSWQSVLLTHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFSRQSVLLTHQRRHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFSRQSVLLTHQRRHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFSWQSVLLTHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFSWQSVLLTHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFSNKSHLLRHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFRDKSHLLRHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFRDKSNLLSHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFSNKSHLLRHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFRNKSHLLRHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFSDRSSLCYHQRTHTGEKP YVCREDE* 0 -1 23 6 traditional numbering of dna recognizing amino acids HPCPSCCLAFSSQKFLSQHVERNH alignment of early C2H2 domain * * * * zinc liganding positions
Different segmental duplications relate PRDM9 and PRDM7
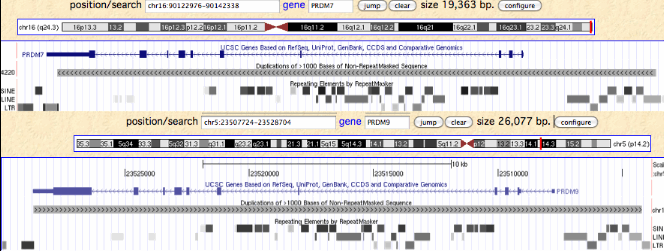
In humans, PRDM9 and PRDM7 are related by a 26 kbp segmental duplication that begins about 8 kbp upstream of the start codon and continues through most of the 3' UTR. Since the retroposon patterns are nearly identical, the duplication must be fairly recent. The overall percent identity of non-coding dna is about 93%, again inconsistent with either early (within stem placental or late divergence (post-chimpanzee). The duplication contains a potentially diagnostic 1845 bp retroposon-free region upstream of the first coding exon.
Note PRDM7 is situated at the extreme tip of chromosome 16q, perhaps predisposing it to chromosomal copy number rearrangements. The syntenic context is TUBB3+ DEFB+ AFG3L1+ DBNDD1- GAS8+ PRDM7- qTel, meaning it is transcribed convergently with GAS8, a non-homologous highly conserved single copy gene often detectable even in low coverage genomes in the small contig containing PRDM7. This association has been extremely stable over boreoeutheran placental mammal evolutionary time and so serves to reliably define PRDM7 orthologs and their spin-off copies. Elephants also have a gene pair similar to human PRDM9 and PRDM7. The former is at a syntenically novel site but the latter is an old pseudogene but still detectably adjacent to GAS8 in opposite orientation. It thus follows that 'PRDM9' in elephant is an independent earlier spin-off of its conventional PRDM7 gene. This is consistent with telomeric susceptibility to repeated rearrangements.
Recall here the actual definition of gene orthology: two genes in two species are orthologous if they are vertically descended from the same gene in their last common ancestor. Here the LCA of human and elephant is ur-placental mammal which had PRDM7 but no PRDM9. The two PRDM9 genes are thus not descended from a common ancestral PRDM9 gene but from parallel gene duplications of a common PRDM7 gene at different times in different clades during the course of mammalian speciation. Such genes are called in-paralogs within a given species and co-orthologs across them.
The syntenic context of PRDM9 is quite variable, supporting the scenario of multiple origins. This context can be used to count the number of distinct segmental duplications of PRDM7. For example, in humans, PRDM9 basically lies in a retroposon-rich gene desert but is eventually flanked by two pairs of cadherin genes at the much larger scale of 7 mbp. In rhesus, these same genes are seen (with some minor rearrangements), establishing that this PRDM9 segmental duplication preceded the divergence of old world monkeys.
Marmoset has a seemingly functional PRDM7 in the usual position facing GAS8, still at the extreme end of chromosome 20. The cadherin cluster is intact on chr2:178,954,165-180,696,523. However Blastx of the intervening dna -- which is similar in size to rhesus and human so not suggesting large deletions -- shows not even a suggestion of an old PRDM9 pseudogene. The assembly is gapless here. and Blastx is sensitive enough to detect very old pseudogenes provided they decayed by small indels and nucleotide substitutions. Thus it appears that PRDM7 never duplicated in marmoset -- placing that even in the stem to old world monkeys (or prior to tarsier divergence -- that assembly has poor coverage). Note that the marmoset PRDM7 has a respectable terminal zinc finger array of twelve units, enough to specify 36 bp.
Gene Strand Protein Start Species CDH18 - cadherin 18 19981287 homSap ponAbe macMul CDH12 - cadherin 12 22853731 homSap ponAbe macMul calJac PRDM9 + human PRDM9 23528704 homSap ponAbe macMul calJac CDH10 - cadherin 10 24644911 homSap ponAbe macMul calJac CDH9 - cadherin 9 27038689 homSap ponAbe macMul
Lemurs present a new complication. The Otolemur assembly has two distinct and seemingly functional PRDM7 copies (each with seven zinc fingers) containing GAS8 end-sequence in expected opposite orientation. One of the GAS8 copies appears to be a pseudogene. This represents a new type of lineage-specific segmental duplication. There is no sign of PRDM9. The other lemur with an assembly, Microcebus murinus, has but a single copy, again with seven zinc fingers. The only relevant contigs (ABDC01433247 and ABDC01371462) contain no coding syntenic information so this gene cannot be assigned to PRDM7 with certainty.
The tree shrew assembly, like tarsier, has low coverage and only blast matches to zinc finger arrays that cannot be assigned to the PRDM family. This cannot be totally attributed to low coverage because many ordinary genes are satisfactorily represented in these species. Other issues such as telomeric position, gene copy number (mobility), pseudogenization, deletional loss, chimerization, and individual heterozygosity must be affecting recovery of PRDM9 gene models in these species.
Moving on to laurasiatheres, Bos taurus presents a much more complicated situation. First, the GAS8 locus on chr18 contains the first two exons of a PRDM7 pseudogene in expected orientation but distal regions of the gene are completely deleted. The cadherin locus on chr20 is also intact but the 2.6 mbp region between CDH12 and CDH10 contains no indication of PRDM9, consistent with that segmental duplication being primate-specific and PRDM7 being the older parental location. This holds in the Baylor 4.0 assembly carried at UCSC, the Baylor 4.2 assembly, and the alternative assembly of the same data, UMD3.1. The latter two can be queried by the genomic blast server at NCBI.
A third locus on chr 1 hosts an unreviewed GenBank pipline entry called PRDM9, derived as NW_003053109 from the alternative bovine assembly UMD3.1 Staff corrected an unspecified frameshift to fix the reading frame -- a dangerous practise in a gene family so prone to pseudogenization. The gene, called PRDM9a here, resides on the extreme end of chromosome 1 and differs from the Baylor 4.0 assembly at two amino acids outside the zinc finger region. The syntenic context here is novel: EFHB- RAB5A+ PCAF+ ZNF596- PRDM9a- which corresponds overall to human chr 3. The juxtapositioning of two zinc finger proteins on the same strand causes PRDM9 alignments to extend spuriously into the 12 zinc fingers of ZNF596, jumping over its 5 earlier coding exons.
ZNF596 contains a KRAB domain but no SET methylase. Humans encode a best-blast protein of the same assigned name on chr 8 (77% identity). Note the early exons of ZNF596 can be added to end of PRDM9a to form an artificial probe for this association in other species, though the two genes have a 43,400 bp spacer in cow, which is large relative to contig size in low coverage assemblies. The sole fragmentary transcript from yak testis (EF432551) is nearly identical to this PRDM9a, suggesting that the gene -- and perhaps its syntenic location -- became established prior to yak-cow divergence and is still functional. However its array of seven zinc fingers could recognize at most a region of 21 bp.
ZNF596 did not arise from a PRDM9-like gene through loss of the SET domain, though it is one of the better matches within the large zinc finger family. Excluding the zinc finger domain, ZNF343, ZNF133 and ZNF169 provide much higher blastp scores, as they also do just comparing the zinc finger arrays. The juxtaposition of ZNF596 and PRDM9a is likely coincidental rather than a consequence of inhomogeneous recombination between zinc fingers bringing PRDM9 to this site.
The fourth PRDM9 locus of interest, called here PRDM9b, is still not mapped to any bovine chromosome. It resides in contig DAAA02065087 in the UMD3.1 assembly and is temporarily assigned to chr Un.004.649 at Baylor assembly. Here the reading frame in exon two can be restored if a run of 5 A's is corrected to 6 A's. That is done here in the reference sequences because this is typically just sequencing error. The protein has a full set of domains KRAB SSXRD SET C2H2 with a moderate zinc finger array of five. Synteny cannot be determined in chr Un features which can simply pool unrelated unplaceable contigs into a manageable unit. Flanking dna in DAAA02065087map to several places in the cow genome, suggesting this feature has copy number attributes, perhaps of telomeric repeat type. PRDM9b is not a recent feature because it differs at a considerable number of amino acids from other PRDM9 in the cow genome. These substitutions avoid highly conserved residues, not consistent with early pseudogenization. PRDM9b is capable of histone marking but it is not clear whether that has functional significance to meiosis.
Yet another locus in the Baylor 4.0 assembly, called PRDM9c here, could not initially be placed on a cow chromosome. While such features are often assembly artefacts, this one is supported by a transcript from 4-cell embryos (GO353654) consistent with a role in or after meiosis. In UMD3.1, this gene has been placed on chr X. Despite a very large contig, no zinc fingers occur in any reading frame, suggesting that the gene was transferred here without the last exon (or it subsequently got deleted). In any event, the penultimate exon does not have a phase 1 splice donor in expected position and so terminates at the next stop codon downstream. The protein retains the KRAB, SSXRD and SET domains but does not possess the ability to scan or bind dna. It has accrued various amino acid substitutions relative to other bovine that rule out recent establishment.
Finally, two additional genes, denoted PRDM9d and PRDM9e here, are located as a parallel tandem pair in a higher quality region of bovine chr X. These are 96% identical as proteins, consistent with one being derived fairly recently from the other. Synteny here will not be informative until other ruminant genomes become available.
Overall the situation in cow is very different from primates and rodents. Results there about the function of single-copy autosomal PRDM9 gnes in meiosis markup can scarcely be carried over to a species with five seemingly intact genes, three of which are on chr X (which intriguingly has the very limited pseudoautosomal region on chr Y where it can cross over).
The cow situation cannot be limited to the Hereford breed used for the genome project because the PRDM9 are too diverged from one another outside the zinc finger region. Indeed there is some suggestion from non-NCBI sheep genome that it too has many of these copies. However other cetartiodactyl genomes (dolphin, pig and alpaca) and other laurasiatheres (panda, dog, cat, shrew, bats) do not show these copies, suggesting that this complexity could be limited to pecoran ruminants. All-vs-all blastp percent identities are consistent with this, though rates of evolution in this gene family are hardly typical.This cannot be resolved with cow genome alone -- there is no good candidate still present for parent gene to all these copies. These results are summarized in the table below:
Gene #ZNF Status Chr Synteny cDNA Accession 9a_bosTau 9b_bosTau 9e_bosTau 9a_oviAri 9a_turTru 7_ailMel PRDM7 - pseudo 18 GAS8 no none -- -- -- -- -- -- PRDM9a 7 ok 1 ZNF596 yes NW_003053109 100% 85% 81% 82% 76% 72% PRDM9b 5 ok ? not det no DAAA02065087 81% 100% 78% 79% 72% 68% PRDM9c 0 ok X not det yes XM_002699750 80% 80% 82% 83% 74% 73% PRDM9d 9 ok X --- no none 80% 78% 96% 93% 73% 67% PRDM9e 9 ok X --- no none 81% 78% 100% 93% 73% 68%
Human PRDM9 variation
A great deal of attention -- and rightly so -- has been expended on cataloging variation in the zinc finger array at the level of both individuals and populations. While not the whole story of PRDM9 functionality by any means, this region is the primary determinant of recombination hotspot locations in meiotic dna. These sites greatly influence observed haplotypes and so the zinc finger array and its changing specificity over time must be understood to make reliable inferences about recent human evolutionary history and indeed speciation.
The zinc finger array is roughly analogous to tRNA. Both bind trinucleotides, the former in double-stranded dna and the latter in single-stranded messenger rna. Both are somewhat fuzzy in binding specificity, the zinc fingers only partly specifying a sequence (eg CCNCCNTNNCCNC) and tRNA accepting wobble codons. Both require an array, these are covalently joined and consecutive in the zinc finger array but are discrete and sequentially acting in tRNAs.
However this analogy only goes so far: the anticodons of tRNA have been fixed for billions of years whereas the four amino acid 'anticodons' of PRDM9 zinc fingers must undergo very rapid but highly restrictive mutation to keep up with an ever-changing recognition site (which obliterates itself with gene conversion, often the outcome of double-stranded break repair instead of recombination). Further, while all tRNAs recognize at least one codon, only a fraction of the zinc fingers in the human PRDM9 array can be utilized -- 13 fingers specify 39 nucleotides whereas observed sites are far shorter, some 13-17 base pairs. What selective pressure then maintains the unused fingers?
That is but one of many remaining questions about PRDM9. Expression in some mammals is not restricted to germ line cells, suggesting other functionalities in the regulation of gene expression. The PRDM9 locus on chr5 itself does not contain a notable recombination hotspot (relative to its own zinc finger array) so gene conversion here cannot explain its mutational frequency, focus on the four determinative residues, and restricted compositional outcome (to nine of twenty amino acids).
Selectional pressure on this gene is highly unusual in that an amino acid substitution in a germline cell yielding a zinc finger that cannot recognize a meiotic target is eliminated right away because recombination is essential to the meiotic process, meaning that no correctly divided haploid cell is available for fertilization. Other regions of the same protein evolve much more conventionally, with human PRDM9 diverging overall from other primates at unremarkable rates.
The zinc finger array varies not only pointwise but also in number of repeats, from 13 or fewer to 20 or more, in contrast to many other stable 'polydactylic' zinc finger proteins. The mutational mechanism by which repeat numbers contract and expand has not been established but is presumably replication slippage, as in other unrelated proteins (such as the octapeptide repeat region in human PRNP). It is unclear what happens to individual zinc finger utilization after an expansion or contraction.
Note in males, recombination must occur in the two short pseudoautosomal regions of homology between chrX and chrY where few basepairs are available (relative to much longer autosomal chromosomes) for the recognition sequence to occur randomly with reasonable probability. Thus in humans PAR1 on the short-arm ends of chrX and chrY is 2.6 mbp whereas as PAR2 on the long arms ends only comprises 320 kbp. By comparison, the shortest human chromosome, chr22, has 50 million bases to host recombination recognition sites (16x as much). Thus the PARs may provide the do-or-die selectional bottleneck driving zinc finger array evolution.
Given that small surveys in moderately inbred populations (such as Iceland) already find considerable variation in both number and sequence particulars of PRDM9 zinc finger arrays, it seems inevitable that many individuals must be heterozygous, sometimes radically so. However these would not necessarily be reported from sequencing projects where commonly only one allele is determined. It is not known whether both alleles in a heterozygous individual would be expressed and participate on an equal footing in meiosis in the same dividing cell. If so, the repertoire of recognizable sites would be expanded, with complications for understanding haplotype evolution if common.
One last immense complication is that human and mouse do not speak for the rest of mammals. There, multiple copies are present in some major lineages, in some cases with zinc finger arrays too short to determine an adequately restrictive suite of recombination sites. Here the possibility must be considered that paralogous copies can act in tandem with short arrays acting in concert to define adequate length sites. The pseudoautosomal regions are by no means strictly conserved phylogenetically. Here adequate data may well be available from horse and cattle breeders but it has not surfaced to date.
The role of CpG mutations
Human PRDM9 has 39 CpG sites in its coding exons, potentially methylated on the C, subject to spontaneous deamination to uracil and misrepair, and so mutational hotspots. After attempted dna repair, the resulting change can be either CpA or TpG. These changes alter the encoded amino acid at nonsynonymous sites. Some 28 of the CpG sites of PRDM9 are at arginine CGn codons (of which the protein has 90 overall).
These always result in a substitution: G -> A misrepair yields histidine for CGT and CGC and glutamine for CGG and CGA; C -> T misrepair leads to cysteine for CGT and CGC and tryptophan and stop codon for CGG and CGA. These changes indeed occur in reported human and mammal sequences where they are perhaps best viewed as cSNPs in an individual rather than representing the species as a whole. The display below shows wildtype human PRDM9 in the top lines and the effects of G -> A and C -> T in the next.
In terms of upstream CpG islands that would protect against methylation of CpG in coding regions, PRDM9 has none. While three occur somewhat near the start of PRDM7, these do not extend into coding exons and may not even be associated with this gene. The composite snapshot below from chr5 and chr16 of the UCSC human genome browser displays these CpG islands relative to the two genes. Thus CpG cytidines would be methylated in coding regions of both PRDM7 and PRDM9, rendering them susceptible to hotspot mutations.
In the terminal zinc finger array of the human PRDM9 reference sequence, position -1 is sensitive to the CpG hotspot effect. However rapid rapid evolution in the zinc finger array, which is overwhelmingly concentrated in the four dna-recognizing residues, cannot be explained by the CpG effect. On the other hand, the common alteration of the terminal partial finger YVCREDE* to Y*CREDE* in some species likely is a CpG effect but one that is insufficient for loss of function.
PRDM9_homSapWT MSPEKSQEESPEEDTERTERKPMVKDAFKDISIYFTKEEWAEMGDWEKTRYRNVKRNYNALITIGLRATRPAFMCHRRQAIKLQVDDTEDSDEEWTPRQQVKPPWMALRVEQRKHQKGMPKASFSNESSLKELSRTANLLNASGSEQAQKPVSPSGEASTSGQHSRLKLELRKKETERKM
PRDM9_homSapCA ...................Q.............................H...................Q......Q...................................H...................................................................
PRDM9_homSapTG ...................W.............................C...................*......*...................................C........V..........................................................
PRDM9_homSapWT YSLRERKGHAYKEVSEPQDDDYLYCEMCQNFFIDSCAAHGPPTFVKDSAVDKGHPNRSALSLPPGLRIGPSGIPQAGLGVWNEASDLPLGLHFGPYEGRITEDEEAANNGYSWLITKGRNCYEYVDGKDKSWANWMRYVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRVIRPGCELLVWYGDE
PRDM9_homSapCA ...Q...........K........................................H.........................................Q....K......................................Q.....................Q...............
PRDM9_homSapTG ...*............L.......................................C..............................L..........*...........................................W.....................*...............
PRDM9_homSapWT YGQELGIKWGSKWKKELMAGREPKPEIHPCPSCCLAFSSQKFLSQHVERNHSSQNFPGPSARKLLQPENPCPGDQNQEQQYPDPHSRNDKTKGQEIKERSKLLNKRTWQREISRAFSSPPKGQMGSCRVGKRIMEEESRTGQKVNPGNTGKLFVGVGISRIAK
PRDM9_homSapCA .S..............................................H.....................................H............................................................................
PRDM9_homSapTG ................................................C.....................................C............................................................................
........-1..23..6.......... ........-1..23..6.......... ........-1..23..6.......... ........-1..23..6..........
VKYGECGQGSVKSDVITHQRTHTGEKL YVCRECGRGSRQSVLLTHQRRHTGEKP YVCRECGRGRDKSHLLRHQRTHTGEKP
........................... .......Q..Q................ .......Q.HN................
........................... .......W..W................ .......W.C.................
YVCRECGRGSWKSHLLIHQRIHTGEKP YVCRECGRGSWQSVLLTHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGRDKSNLLSHQRTHTGEKP
.I.....Q................... .......Q................... .......Q...................
.......W................... .......W................... .......W...................
YVCRECGRGSWQSVLLTHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGSWQSVLLTHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGSNKSHLLRHQRTHTGEKP
.......Q................... .......Q................... .......Q...................
.......W................... .......W................... .......W...................
YVCRECGRGSRQSVLLTHQRRHTGEKP YVCRECGRGSNKSHLLRHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGRNKSHLLRHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGSDRSSLCYHQRTHTGEKP YVCREDE
.......Q..Q................ .......Q................... .......Q.H................. .I.....Q..N................ .I.....
.......W..W................ .......W................... .......W.C................. .......W................... .......
A weblogo based on alignment of placental mammal PRDM7 and PRDM9 genes (with pseudogenes excluded) illustrates the location of expected CpG mutations relative to conserved residues. These will be relatively high frequency loss-of-function alleles (not affecting health per se if only reproductive meiosis is affected).
In the initial KRAB domain, the potentially affected arginines are not especially well-conserved. However, at the first site, neither histidine nor cysteine is part of the reduced alphabet ans so these changes are unlikely to be tolerated in meiotic functioning. At the second and third sites, glutamine does occur secondarily in some species (cow, sheep and muntjac) and murid rodents, respectively. These changes are thus borderline for adverse effects on functionality.
Sequence analysis of human variation
The PRDM9 terminal zinc finger array varies extensively in human, with significant consequences for hotspot recognition motif, distribution of recombination location options along the chromosomes, population history (linkage disequilibrium), and chromosomal rearrangement diseases. No other species -- notably other great apes -- has been surveyed to any extent for individual variation (with the exception of mouse PRDM7 where hybrid sterility was first mapped).
For these species, we have only the sequence of the animal selected for genome sequencing and so have no idea whether human variation is unique or typical. With high priority chimp, Genbank contains only an uncurated mistaken gene prediction XM_517829 and an array fragment GU166820 with a disturbing number of differences to chimp reference genome. Gorilla is worse. Mouse has considerable variation in its zinc finger array but the strains involved are highly inbred and not necessarily representative of wild mouse diversity.
Cheap short reads mapped to human reference as SNPs prove highly unsatisfactory for genes like PRDM9 where individuals differ not only at pointwise sites but also in wholesale repeat number. Several labs have reported novel repeat multiples but found an hour of resequencing too tedious; others assumed all possible arrays had already been reported and forced reads into one of these pre-existing classes; others left their discoveries as article graphics, behind firewall or in supplemental, not troubling themselves with GenBank entries, with laudable exceptions. Even if certain arrays are rare, they provide invaluable information on the genetic mechanisms by which repeat number variation arises.
It appears that few individual human genome or exome projects really gathered enough data to allow ab initio assembly of the zinc finger repeat array, or even when they did, walked away from that exercise, deposited a mess of indels and base miscalls at the Short Read Archive and then claimed SNPs relative to human reference, contaminating that resource with error.
This is very unfortunate in the case of both basal and ancient human dna, which might record intermediate or population-specific stages in the evolution of human PRDM9. Extracting accurate bushman, paleo-eskimo, neanderthal, and denisova PRDM9 zinc finger arrays requires starting from scratch from raw read data. This may however be impossible due to inadequate coverage and confusion of short reads with PRDM7 and even within PRDM9, not to mention other closely related zinc finger proteins.
Here PSU provides an excellent display of reads (along with quality scores) reported by the various projects. The final exon of PRDM9 can be viewed (noting PSU uses hg18 coordinates) at chr5:23562098-23562523 for the early region and chr5:23562524-23563636 for the terminal zinc finger array. Viewing the display to dense mode shows the extent of tiling: it does not appear that adequate coverage was obtained in the critical cases. Here it cannot be assumed that the zinc finger array of bushman (who represent the earliest diverging living relative of Europeans) will closely resemble extensively sequenced West African variants (Yoriba). The best that can currently be done with bushman genome is VKYGECGQGFSVKSDVITHQRTHTGEKL YVCRECGRGFSWKSHLLIHQRIH ... YHQRTHTGEKP YVCREDE* which matches hg19 human reference sequence without shedding any light on internal repeat length or sequence variation.
Although the zinc finger array conveniently resides in a single exon, that exon is almost never sequenced in its entirety. It has never been sequenced as a byproduct of an expression project. Consequently we have no idea its early zinc finger covaries with the terminal array nor any understanding of the constraints acting on the long bridging domain.
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
PRDM9_homSap EPKPEIHPCPSCCLAFSSQKFLSQHVERNHSSQNFPGPSARKLLQPENPCPGDQNQEQQYPDPHSRNDKTKGQEIKERSKLLNKRTWQREISRAFSSPPKGQMGSCRVGKRIMEEESRTGQKVNPGNTGKLFVGVGISRIAKVKYGECGQGFSVKSDVITHQRTHTGEKL
PRDM9_panTro ...............................................................R................................................................A........................D.............G.P
PRDM9_gorGor .........................................T.....................R.........................................................................................................P
PRDM9_ponAbe .......................................................H....S..R.C.......................................................................................D.............GRS
PRDM9_nomLeu ...A......................A.H.............F.................S..R.C...............................S..V...........I..-.............Q...........E............................
PRDM9_macMul ...............................T.........R.F....L.S.........S..R.C.....................PK................S...E.M....Y........E...........................D.....I.........P
PRDM9_papHam ...............................T...R.....R......L.S.........S..R.C....................R.K................S...E.M...........S.E.I.........................D....VI.........P
PRDM7_calJac .S.....................H.............T.T............K.KE....F..CNS........T........I......MA....N........S..EE.M.............VD...............A..........DM...TG.........P
PRDM7_micMur ............S.............KHT....IS.RT.G..H................HS....C...A.D..V...P.PFH.K.Q..G...........K.....E........P......G..D.D..CAAG.....SR....DS..S..D..N..I.........P
PRDM7_otoGar ............S....T..........T.P..ISQ.T.G..N.R.QT...R.E.....HS..N..........V..M..TSH.K.Q.SR...I..C........S.E.E.MI...P.PD...G..D.E.FC.AI...G.V...NR..V.S..N..N-LR.........P
A terrible error was made early on in human PRDM9 variant nomenclature. It is completely unacceptable for PRDM9 to have a private system for naming zinc fingers that stands in conflict with dozens of previously established crystallographic structures, SwissProt, SCOP and PFAM practice, and nomenclature for the other 842 zinc fingers encoded in the human genome.
Wrong as it is, the current nomenclature will not be easy to displace. However this site uses a nomenclature consistent with physical structure, comparative genomics and historical precedent throughout and only provides a partial translation table to the numerous misguided motif naming systems.
The mistake arose because the first and last zinc fingers in primate PRDM9 are mildly anomalous. However it is exceedingly common even for internal zinc fingers to depart from canonical form, even to admit different spacings and substitutions in the C2H2 ligands, as well depart in length and cap domain. Zinc finger arrays commonly terminate in fragmentary motifs that often continue for a while in another reading frame (ie, represent non-3n indels with run-on to the next encountered stop codon).
Even when each zinc finger is letter-perfect, only a small subset seem to function in dna recognition -- thus 15 zinc fingers in a PRDM9 variant could theoretically recognize a 45 bp dna sequence but a look at meiotic events show that 17 bp seems the upper limit for specificity, meaning no more than 6-7 motifs are utilized in vivo. Nomenclature must acknowledge all zinc fingers whether they are anomalous or not (or functional or not).
Some 7,000 of the overall ten thousand zinc fingers end in a structurally distinct cap unit, typically TGEKP. This was shown long ago to lock the zinc finger down after scanning and has found the recognition sequence. Proteins with a single zinc finger still have this motif. It occurs at the end -- not the beginning -- of the main zinc binding region. Proline is no accident here: as a cyclic imino acid, it is structurally terminating for helix and sheet.
In summary, zinc fingers begin 5 residues before the second zinc cysteine, not at the second cysteine as in the 'ABCD...' nomenclature. Human PRDM9 begins with a full length zinc finger, but with a lysine at position 2 replacing the usual branched aliphatic, a tyrosine at position 3 replacing the first cysteine and a leucine replacing the terminal proline: VKYGECGQGFSVKSDVITHQRTHTGEKL. These oddities became stably established in the theran ancestor 135 myr ago (though departures -- and even the expected residues -- are seen in some species). Otherwise, the first zinc finger is quite conventional. The terminal leucine surprisingly is seen in all reported human variants. While the first zinc finger assuredly has the zinc finger fold and likely binds zinc to some extent, it likely does not function directly in specific dna motif recognition. Its role may more that of a macro cap, facilitating the lineup of downstream zinc fingers.
Similarly, the terminal YVCREDE* fragment, with its anomalous charged aspartate and glutamate in place of cysteine and glycine, is not zinc binding or part of a dna recognizing motif but simply a partial end cap. It has persisted (imperfectly) since the boreoeutheran ancestor so evidently provides significant value. In many laurasiatheres it is YCRECE or even YRCREG. Even a canonical hexapeptide cannot reach across the preceding TGEKP cap to displace zinc binding residues of the last full repeat, nor can the six residues circle around to displace the first five residues of first repeat. Instead, these residues form the start of an additional fold, enough to that keep the repeat array from unraveling.
Below the available diversity at GenBank is shown, with the 0th GEKL repeat removed because it has no variation. Also the longest allele has its last two repeats removed to shorten the display width. The terminal fragment is also not shown. Redundant sequences have been largely removed from the set of 42. The alignment is shown at the protein level because synonymous dna variation is largely irrelevant to function.
If all 42 human variant zinc finger array alleles at GenBank are collected, parsed into their zinc fingers and aligned for their differences relative to the genomic reference sequence, 25 variant fingers emerge at varying frequencies of occurrences. These are provided below, ordered by subgroup. The full sequence, allele name of the original investigators and representative accession are also given.
As previously observed, variation at the amino acid level is overwhelmingly concentrated at that handful of internal positions recognizing dna bases in the major groove. Furthermore, the amino acid substitutions are strongly concentrated within only 9 of the 20 available amino acids. These observations raise the question of how ordinary random mutational processes could possibly have produced these results. Perhaps variation elsewhere results in failed meiosis, causing these to disappear immediately, leaving only the observed variation.
Note in the table below (whose underlying data is here) that threonine appears as a very common alternative to isoleucine outside the critical region (between the two zinc-binding histidines): YVCRECGRGFSWKSHLLIHQRIHTGEKP. This is actually an oddity of the first GEKP repeat: T is found here in all other primates (ie ancestrally), not I. As bushmen also have I here, this allele was fixed prior to their divergence at 70,000 years.
Human Variation in 507 Zinc Fingers in 42 PRDM9 Variants
Difference to NM refSeq Freq Full length zinc finger Accession Allele Great Ape Zinc Finger Variation
YVCRECGRGFSWKSHLLIHQRIHTGEKP 39 YVCRECGRGFSWKSHLLIHQRIHTGEKP NM_020227 ref YVCRECGRGFSWKSHLLIHQRIHTGEKP homSap
......................R..... 1 YVCRECGRGFSWKSHLLIHQRIRTGEKP FJ899869 7 .................S...T...... 1 panTro
............Q.V..T...T...... 100 YVCRECGRGFSWQSVLLTHQRTHTGEKP NM_020227 ref ...........V..S..S...T...... 6 panTro
............Q.V..S...T...... 22 YVCRECGRGFSWQSVLLSHQRTHTGEKP GU216222 A ...........V..S..S.RTT...... 1 panTro
............Q.V..R...T...... 13 YVCRECGRGFSWQSVLLRHQRTHTGEKP GU183919 CH3 ...........VQ.N..S...T.....L 1 panTro
......R.....Q.V..T...T...... 1 YVCRECRRGFSWQSVLLTHQRTHTGEKP HM211000 L18 ...........QQ.N..S...T...... 1 panTro
............Q.VP.T...T...... 1 YVCRECGRGFSWQSVPLTHQRTHTGEKP FJ899895 18a ...........RQ.A......T...... 1 panTro
...........N.....R...T...... 65 YVCRECGRGFSNKSHLLRHQRTHTGEKP NM_020227 ref ......E....QQ....R...T...... 1 panTro
..........RN.....R...T...... 39 YVCRECGRGFRNKSHLLRHQRTHTGEKP NM_020227 ref ...........QQ....R...T...... 2 panTro
..........RK.....R...T...... 1 YVCRECGRGFRKKSHLLRHQRTHTGEKP GU183915 AA2 ...........QQ....S...T...... 2 panTro
..........RD.....S...T...... 14 YVCRECGRGFRDKSHLLSHQRTHTGEKP GU216229 I ...........KQ....S...T...... 2 panTro
..........RD.....R...T...... 27 YVCRECGRGFRDKSHLLRHQRTHTGEKP NM_020227 ref ...........RQ.V......T...... 1 ponAbe
..........RD..N..S...T...... 48 YVCRECGRGFRDKSNLLSHQRTHTGEKP NM_020227 ref ...........RR.V......T...... 1 ponAbe
..........RD..P..S...T...... 1 YVCRECGRGFRDKSPLLSHQRTHTGEKP GU183915 AA2 ...........QQ.V......T...... 1 ponAbe
..........RD..N..S...T...D.. 4 YVCRECGRGFRDKSNLLSHQRTHTGDKP GU183915 AA2 ...........RR.V......T...... 1 ponAbe
..........RDE.N..S...T...... 2 YVCRECGRGFRDESNLLSHQRTHTGEKP HM211006 24L ..............V..R...T...... 1 ponAbe
..........RDQ....S...T...... 1 YVCRECGRGFRDQSHLLSHQRTHTGEKP GU183919 CH3 ...........QQ.VVF....T...... 1 ponAbe
...........RQ.V..T...T...... 2 YVCRECGRGFSRQSVLLTHQRTHTGEKP FJ899905 10b ...........G..V.FR...T...... 1 ponAbe
...........RQ.V..T...R...... 79 YVCRECGRGFSRQSVLLTHQRRHTGEKP NM_020227 ref ...........D..GVCY...T...... 1 ponAbe
...........RQ.V..T...G...... 2 YVCRECGRGFSRQSVLLTHQRGHTGEKP FJ899872 10 ...........V..N..S...T..E..L 1 ponAbe
...........RQ.V..S...T...... 1 YVCRECGRGFSRQSVLLSHQRTHTGEKP GU216228 H ...........D..S..R...T...... 3 nomLeu
...........NQ.V..T...T...... 1 YVCRECGRGFSNQSVLLTHQRTHTGEKP GU183916 AA11 ...........K..N..S...T...... 1 nomLeu
...........DQ.V..T...T...... 1 YVCRECGRGFSDQSVLLTHQRTHTGEKP GU183916 AA11 ...........V..N..S...T...... 1 nomLeu
...........DR.S.CY...T...... 37 YVCRECGRGFSDRSSLCYHQRTHTGEKP HM210983 L1 ...........Q..S..S...T...... 3 nomLeu
...........DR.S.CY...T..MSKS 5 YVCRECGRGFSDRSSLCYHQRTHTMSKS GU183916 AA11 .L.........V..S..S...T...... 1 nomLeu
507
When the 42 variants are aligned at the dna level, synonymous variation might be anticipated more or less evenly across the repeat array under the assumption that natural selection acts here only at amino acid level. However this is not the case as shown in the graphic below. For example, the GEKL repeat has no variation whatsoever despite numerous 4N codons. Elsewhere, synonymous variation is again highly concentrated at residues important to meiotic repeat recognition. This suggests a novel mutational mechanism exists that focuses change at the key regions, at a rate far above the genomic average. Conceivably the dna itself might have additional hairpin structure that exposes the critical regions to enhanced mutation. Such a speculative structure would fit with replication slippage varying the number of array repeats. This mechanism can also sweep out variation. Alternatively, the observed distribution of synonymous variation could arise via hypothetical mRNA editing in conjunction with a retroposon-like or copy-editing mechanism. A third option envisions another protein recognizing the dna encoding the repeats and acting upon them to provide variation.
Among the 843 human genetic loci encoding zinc fingers proteins, the arrays most closely resembling PRDM9 in length, structure and amino acid composition are ZNF133, HKR1, ZNF343, ZNF589, ZNF169, ZNF596. While the functions of these proteins are largely unknown, the first two have a KRAB domain, a spacer, early zinc finger in the terminal phase 2 exon, and a zinc finger array similar in size to human. The next two are similar but lack the spacer, with the KRAB domain encroaching into the final exon. The final two have only the KRAB domain and terminal array. Some 290 human gene products encode a KRAB domain.
Here ZNF133 and the misnamed HKR1 are the best candidates for donating (via inhomogeneous recombination) the zinc finger array to the nascent PRDM7 which was already a chimer of KRAB, SSXRD and PR(SET) domains. The relationships here might instead go the other way (domain loss in PRDM) but different intronation of the KRAB domain is incompatible with that scenario. While none of the six ZNF is capable of histone methylation, KRAB domains are capable of recruiting SETDB1, a H3K9 methylase, partnering with the TIF1ß co-repressor protein (encoded by TRIM28), which interacts with many KRAB domains).
Phylogenetic variation in the zinc finger arrays of these proteins is potentially quite informative, the question being whether their variation too is focused on the four amino acid positions providing dna binding specificity in PRDM7/9. This next sections examine each protein separately for mutational variation in the zinc fingers over placental mammal evolutionary time.
Here the 46-species genomic alignment at UCSC serves as initial source of zinc finger arrays, which are then tested by blat back into individual species and then parsed into separate fasta files for each protein finger (the formats needed by the Multalin2 variable width differential aligner and weblogo tool).
ZNF133
Human ZNF133 is a conventional KRAB-zinc finger array. The array is a better model of PRDM9 than any of the other 14 PRDM* loci in terms of repeat character and length. Rodents cannot be used here as a model system as the mouse syntenic counterpart is a known pseudogene -- as is rat but not guinea pig or rabbit -- and ZNF133 too does not readily track back into marsupials or earlier vertebrates.
As with PRDM7/9, the C-terminal run-off of ZNF133 is subject to frameshifts. However elephant and human are still 86% identical in their last exon, with zinc finger arrays even higher. Armadillo, another mammal diverging from human at 101 myr, is 91% identical in this region and has exactly the same number of zinc fingers (14.7). This suggests that the dna binding target is strongly conserved, just the opposite of PRDM7/9. However this conservation in ZNF133 weakens markedly in the distal 3 repeats.
The 11 conserved zinc fingers in ZNF133 are long enough to specify nearly unique dna sites in a 3 gbp genome, even if not all fingers take part in a given site recognition. Note the SGEKP lockdown cap departs from canonical form in repeat 5, 7, 12, and 13 perhaps impacting binding site prediction. Human variation in repeat numbers has not been studied but it appears from phylogenetic considerations to be far less common than in PRDM7/9.
Alignment of human ZNF133 zinc finger array to orthologs in Primates, Glires, Laurasiatheres, Xenarthra and Afrotheres
z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z z
homSap VNCGECGLSFSKMTNLLSHQRIHSGEKP YVCGVCEKGFSLKKSLARHQKAHSGEKP IVCRECGRGFNRKSTLIIHERTHSGEKP YMCSECGRGFSQKSNLIIHQRTHSGEKP YVCRECGKGFSQKSAVVRHQRTHLEEKT
calJac ............................ ............................ ............................ ............................ ............................
oryCun ........G...LA.............. ............................ ............................ ...T........................ ............................
equCab ........G................... ............................ ............................ ............................ ............................
canFam ...R....G................... ............................ ............................ ...................R........ ............................
dasNov I..A....G................... ............................ ............................ ............................ .......................S....
proCap ...E....G................... ............................ ............................ ........R................... .......................S....
homSap IVCSDCGLGFSDRSNLISHQRTHSGEKP YACKECGRCFRQRTTLVNHQRTHSKEKP YVCGVCGHSFSQNSTLISHRRTHTGEKP YVCGVCGRGFSLKSHLNRHQNIHSGEKP IVCKDCGRGFSQQSNLIRHQRTHSGEKP
calJac ............................ ............................ ............................ ............................ ............................
oryCun ...G........................ ............................ ............................ .....................T...... ...Q......................R.
equCab ............................ ............................ ............................ .........................D.. ............................
canFam ...N........................ ............................ ............................ .........................D.. ............................
dasNov ............................ ............................ ............................ ................I........D.. ............................
proCap ............................ ...G........................ ............................ ................T........D.. ............................
homSap MVCGECGRGFSQKSNLVAHQRTHSGERP YVCRECGRGFSHQAGLIRHKRKHSREKP YMCRQCGLGFGNKSALITHKRAHSEEKP CVCRECGQGFLQKSHLTLHQMTHTGEKP YVCKTCGRGFSLKSHLSRHRKTTS VHHRLPVQPDPEPCAGQPSDSLYSL
calJac ...A......................K. ............................ ............................ ..........I............N.... ....M..Q..............K. ......L..G...R....A...C..
oryCun ...Q............L.........K. ............................ .T.........S.........T...... .GGGQ...S.S......S..L..K.... H......Q...Q.........IKA ...KP.LH..S.AYS...PGP....
equCab ...E............I.........K. ............................ .T........S.........W......L ..........I.....V......Q...L .......Q...Q........RMK. ..Q.P.PH.AS.A.S..S..P.H..
canFam ...E......................K. ............................ ..........S......I...V...... ........D.I.....L......Q.... ....M.DK...H........RMK. ..YK..LP....A....S..L.H..
dasNov ...E............I.........K. ...................R........ .T........S...T......L...... ........S.I.R...I....I.KE... ...R...Q...Q.......SRMKC ...KPLL...S.DYS..S..P....
proCap ...ED...........I.........K. ............................ .A....R...N...T..A..QL...D.L .......ED.M.....LV.....K.... ..SR.H.Q..NQ......Y.RIK. ...KS.F.S.L.T.S..S.VPV...
The ubiquitously expressed ZNF133 has been established by experiment to be a transcriptional repressor, recognizing specific sites in dsDNA. Despite the presence of the KRAB domain (which usually has this task), the zinc finger array alone contributes to transcriptional repression, with this effect mediated by another gene product, PIAS1, which binds the main array and recruits histone deacylases. The early zinc finger is not necessary for the PIAS1 effect and though conserved, its role remains obscure. PIAS1 may also have a role in PRDM9 and recombination.
For ZNF133, the weblogo below based on 413 repeats from 32 placentals illustrates that quite different selectional pressures have been operative here than in PRDM7/9. First, variation is not concentrated at the four special amino acid positions (purple boxes between CxxC HxxxH) but instead is distributed (though unevenly) among the non-C2H2 positions. Some of this occurs at residues primarily concerned with the zinc binding fold and not target macromolecule interactions. This establishes structural variation in the fold can be tolerated, ie PRDM7/9 is the real oddity for not exhibiting it.
(to be continued shortly)
Domain by domain structure/function
PRDM7 and PRDM9 are chimeric proteins comprised of 6 recognizable domains joined by linker regions. While multi-domain proteins are common in the overall human proteome, this particular combination occurs nowhere else. However some of the domains here occur in other combinations in other proteins, notable in the vast heterogeneous family of zinc finger proteins (gene names ZNFxxx).
KRAB_A Kruppel SSXRD zinc knuckle PR or SET domain early zinc finger terminal zinc finger array
Because the inter-domain linkers are evolving chaotically in terms of little amino acid property conservation and sometimes length, they cannot plausibly be under significant selective pressure, nor can they assume a stable structural fold. However this does not imply that the domains that they link do not have significant physical interactions important to the global tertiary protein structure. To date, only the isolated domains have been studied crystalographically (with the exception of the knuckle-PR combination).
While the domain folds individually are quite ancient and do not reflect de novo innovation in vertebrates from random dna strings, their assembly into PRDM7/9 is fairly recent, about 150 million years ago. Prior to this, a proto-PRDM7 containing the last 4 domains arose and persisted for 300 million years, giving rise to several gene duplicates, all with vaguely understood function related to transcriptional regulation.
The following sections consider what is known about each domain in turn primarily from the perspective of comparative genomics. As of July 2011, 51 land vertebrate genomes are available, providing a rich history of how PRDM7 has been evolving in various branches of the phylogenetic tree.
Reciprocal translocation: origin of the SSX1-PRDM chimera
Upon blastp of the first 6 exons of any PRDM7/9 protein against GenBank restricted to human, SSX1 emerges as the only full length non-self match. Comparison of its 6 exons establishes further that their intron phasing is an exact match. Since this is impossibly coincidental, it follows that PRDM7 (the immediate parent of PRDM9 in primates) arose as a chimera of ancestors to these two proteins prior to marsupial divergence. The percent identity has dropped from the initial perfect agreement to 32% today, without however loss of KRAB_A and SSXRD domain recognizability in either gene family. No other proteins in the human genome -- in particular no zinc finger proteins -- contain these 6 exons though the KRAB domain alone is widespread.
>SSX1_homSap >PRDM9_homSap 0 MNGDDTFAKRPRDDAKASEKRSK 0 0 MSPEKSQEESPEEDTERTERKPM 0 0 AFDDIATYFSKKEWKKMKYSEKISYVYMKRNYKAMTKL 1 0 VKDAFKDISIYFTKEEWAEMGDWEKTRYRNVKRNYNALITI 1 2 GFKVTLPPFMCNKQATDFQGNDFDNDHNRRIQ 1 2 GLRATRPAFMCHRRQAIKLQVDDTEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1 2 VEHPQMTFGRLHRIIPK 0 2 VKPPWMALRVEQRKHQK 0 0 IMPKKPAEDENDSKGVSEASGPQNDGKQLHPPGKANISEKINKRS 1 0 GMPKASFSNESSLKELSRTANLLNASGSEQAQKPVSPSGEASTSGQHSRLKL 1 2 GPKRGKHAWTHRLRERKQLVIYEEISDPEEDDE* 2 ELRKKETERKMYSLRERKGHAYKEVSEPQDDDYL 1 PRDM9 MSPEKSQEESPEEDTERTERKPMVKDAFKDISIYFTKEEWAEMGDWEKTRYRNVKRNYNALITIGLRATRPAFMCHRRQAIKLQVDDTEDSDEEWTPRQQ M+ + + + P +D + +E++ K AF DI+ YF+K+EW +M EK Y +KRNY A+ +G + T P FMC+ +QA Q +D D + R Q SSX1 MNGDDTFAKRPRDDAKASEKRSK---AFDDIATYFSKKEWKKMKYSEKISYVYMKRNYKAMTKLGFKVTLPPFMCN-KQATDFQGNDF---DNDHNRRIQ PRDM9 VKPPWMALRVEQRKHQKGMPKASFSNESSLKELSRTANLLNASGSEQAQKPVSPSGEASTSGQHSRLKLELRKKETERKMYSLRERKGHA-YKEVSEPQDDDYL 1 V+ P M R K MPK +E+ K +S ASG + K + P G+A+ S + ++ ++ + LRERK Y+E+S+P++DD SSX1 VEHPQMTFGRLHRIIPKIMPKKPAEDENDSKGVSE------ASGPQNDGKQLHPPGKANISEKINK-RSGPKRGKHAW-THRLRERKQLVIYEEISDPEEDDE*
This chimera arose subsequent to the duplication of proto-PRMD7 and its divergence to PRDM11, its nearest PRDM relative which has leading exons unrelated to SSX1. Indeed none of the other 14 PRDM proteins have a KRAB or SSXRD domain. The SSX1 gene itself, then and now, lies in a tandem array and so did not disappear as a standalone gene family as only one copy was used up in forming the hybrid protein. For viability, the event was likely a reciprocal translocation, accounting for the SSX array and PRDM7 being on different chromosomes today.
The SSX1-group genes occurs in the human reference genome as 11 features in two nearby clusters both on chromosome X. Some of these may be pseudogenes. The degree of similarity suggests recent gene duplication and/or gene conversion. The array is notorious for reciprocal translocations involving the one of 24 human synaptotagmins, the SYT4 gene on chromosome 18. These translocations fuse early exons of SYT4 with distal exons of an SSX gene, usually SSX1 or SSX2 but sometimes SSX4. The event takes place within intron 4 of the SSX genes and preserves reading frame, allowing for a chimeric protein with diseasterous regulatory properties to emerge -- nearly all cases of synovial sarcomas arise from repeated occurrence of this event.
SSX1b + chrX:47967088-47980069 similar to SSX1 SSX5 - chrX:48045656-48056199 synovial sarcoma X breakpoint 5 SSX1a + chrX:48114797-48126879 synovial sarcoma X breakpoint 1 SSX9 - chrX:48154885-48165614 synovial sarcoma X breakpoint 9 SSX3 - chrX:48205863-48216142 synovial sarcoma X breakpoint 3 SSX4 + chrX:48242968-48252785 synovial sarcoma X breakpoint 4 SSX4B - chrX:48261524-48271344 synovial sarcoma X breakpoint 4B SSX8 + chrX:52651985-52662998 similar to SSX8 SSX7 - chrX:52673111-52683950 synovial sarcoma X breakpoint 7 SSX2a - chrX:52725946-52736249 synovial sarcoma X breakpoint 2 SSX2b + chrX:52780308-52790617 synovial sarcoma X breakpoint 2
Possibly the SSX1 array has long been predisposed to translocation events. It might seem very difficult to establish the structure of the ancestral array at the time of PRDM chimera formation -- contemporary marsupial has barely related genes on different chromosomes; elephant and dog too lack a multi-gene array. However rhesus but not marmoset has a chr X cluster, so that aspect is restricted to old world primates. A single SSX1 gene can be recovered from elephant but is already quite diverged from human. Marsupials have no evident SSX1 genes today.
This gene fusion of SSX1 and PRDM brought together a negative regulatory domain for transcription with a histone methylase and dna site recognition domain. This new combination succeeded in replacing whatever prior mechanism existed for meiotic breakpoint pairing and recombination.
>SSX1_loxAfr 0 VNRDSSLAKSSKEDTQKPEKESK 0 0 AFKDILKYFSKEEWAKLGYSKKVTYVYMKRNYDTMTNL 1 2 GLRATLPPFMDPNRLATKSQLDESDEEQNPGTQ 1 2 DEPPQMASSVRESKHLM 0 0 MKPKKPSKEENGSKVVPGTAGLMRTSGPEQAQKQPCPPGKANTSGQQSKQTP 1 2 VPGKEETKVWACRLRERKNLVAYEEISDPEEED*
The zinc knuckle preceding the PR (SET) domain
A 2011 crystallographic study establishes that a short motif YC..C..........C..HGP found in 6 members of the human PRDM gene family binds zinc via the 3 cysteines and a histidine. The fold most closely resembles the previously known RanBP2 zinc finger domain which occurs in some 21 human proteins, notably nucleoporins NUP153, NUP358, NPL4, EWS, TLS, RBP56, RBM5, RBM10, TEX13A, RANDB2 and ZRANB2. Not all these domains are necessarily homologous because the fold is small and zinc fingers seem to have evolved numerous times. Such fingers can bind other proteins, ssRNA and likely DNA. Their function in PRDM genes is completely unknown but the aromatic residue preceding the first cysteine may contribute to a pi-bonding base stack with guanines.
The domain begins at a phase 2 exon, meaning that the first codon letter is borrowed from the preceding exon splice donor. A dozen earlier residues from this exon are also used but do not exhibit any conservation outside their orthology class. In most cases the knuckle domain exon also contains a downstream PR(SET) domain but at variable intervening lengths (distances shown are to conserved FGP in center of PR(SET) domain. The function of these intervening residues are unknown.
exon 6 splice exon 7 SET gene name IPLNQHTSDPNN 1 2 RCDMCADNRNGECPMHGPLHSLRRLVG .49. PRDM6_homSap PDPPRPFDPHDL 1 2 WCEECNNAHASVCPKHGPLHPIPNRPV .16. PRDM10_homSap MAEDGSEEIMFI 1 2 WCEDCSQYHDSECPELGPVVMVKDSFV .99. PRDM15_homSap GSKENMATLFTI 1 2 WCTLCDRAYPSDCPEHGPVTFVPDTPI .36. PRDM4_homSap IVPKSFQQVDFW 1 2 FCESCQEYFVDECPNHGPPVFVSDTPV .42. PRDM11_homSap KEVSEPQDDDYL 1 2 YCEMCQNFFIDSCAAHGPPTFVKDSAV .42. PRDM9_homSap KEISEPQDDDYL 1 2 YCEMCQNFFIDSCAAHGPPTFVKDSAV .42. PRDM7_homSap QEIWDPQDDDYL 1 2 YCEECQTFFLETCAVHGPPKFVQDSVM .42. PRDM7_monDom NENYRPEDDDYL 1 2 YCEICQTFFLEKCVLHGPPVFVQDLPV .42. PRDM7_ornAna EEQDDTFNDQPF 1 2 YCEMCQQHFIDQCETHGPPSFTCDSPA .42. PRDM7_danRer TEEEELRDEEYF 1 2 FCEECKSFFIEECELHGPPLFIPDTPA .42. PRDM7_salSal IKEEEADVKDFL 1 2 YCEVCKSVFFSKCEVHGPALFIADSPV .42. PRDM7_ictPun YVCRECGRGFSWQSVLLTHQRTHTGEKP comparison to longer zinc finger in main array of PRDM7/9
Structural alignment of all PRDM proteins
To determine the evolutionary relationship of the 16 human PRDM genes, it is useful (given the great divergence in primary sequence) to consider rare genomic events such as intron gain/loss and indels. Only 7 of the 16 contain the knuckle region. Of these PDRM11 is the most closely related to PRMD9.
This is fortunate because the 3D structure of PRDM11 was recently determined (PDB: 3RAY) from before the knuckle region on into the final exon, thus allowing threading of PRDM9 (whose structure has not been studied). The dozen-odd conserved patches in these widely diverged paralogs find their explanation in the atomic details of this structure. Note the PRA(SET) domain and zinc fingers are all that can currently modeled as the KRAB, SSXRD and final exon have no counterparts at PDB.
The knuckle region apparently represents a one-time domain acquisition relative to a knuckle-less ancestral state. The date of this event relative to species phylogeny and the source of the domain are unclear (it is very unlikely to have evolved in situ). Similarly, the internal phase 00 intron is ancestral even though it breaks up a coherent structural domain. Note the final 12 intron is also ancestral -- the PR(SET) domain never occurs without it even though zinc fingers are not always found in the next exon. However the later 21 intron is a newer acquired feature specific to PRDM9 and its closest associates, post-dating acquisition of the knuckle domain and predating duplication and divergence of the PRDM7/9 group. This again follows from gene tree and parsimony considerations.
Crystallographic coverage is excessive yet highly unsatisfactory -- the knuckle-PR(SET) domain is covered by 6 different structures, yet none of them are exactly what is needed (PRDM11 3RAY; PRDM4 2L9Z/3DB5; PRDM10 3IXH; PRDM1 3DAL; PRDM2 3JV0; PRDM12 3EP0). There is no coverage of the preceding KRAB or SSXRD domain or the following early knuckle. However on the knuckle-PR(SET) domain, all these structures could likely be superimposed simultaneously on the near-universal domains identified below. PRDM7/9 would then follow this fold trace as well, though it could be modeled directly from just PRDM11. The intervening regions between conserved anchors can be modeled for PRDM7/9 only to the extent that local conservation in length and residue can be found to a determined structure. For example, IFYRTCRVI in PRDM9 can be modeled by the PRDM11 structure since its internal residues contain three matches and no gaps, IFYRACRDI.
Humans have 51 genes encoding SET domains, with the PRDM group most diverged from the canonical structures. It is difficult enough to meaningfully align the PRDM and even more so to include all 51 of these lysine methylases. When that is done, most of the conserved patches below emerge as universal motifs yet others are restricted to the PRDM family. All of these proteins would likely bind S-adenosyl methionine and have a lysine pocket in addition superimposable global folds (neither relatable to the 45 human arginine methyltransferases).
gapping: uncertain between conserved markers iM: initial methionine, protein thus too short for further comparison knuckle: shortened zinc finger motif underlining: magenta coloring shows non-informative idiosyncratic introns C2H2: terminal zinc finger region following universal phase 12 intron PRDM15: duplicated diverged exon removed 21 SWPASGHVHTQAGQGMRGYEDRDRADPQQLPEAVPAGLVRRLSGQQLPCRSTLTWGRLCHLVAQGR 0: indel unifying PRDM9/7/11, cannot be resolved as insertion or deletion 7: near-universal motif NWMrYV split by phase 21 intron gained by PRDM9/7/11/4 1: arginine supporting PRDM6 as outgroup to the knuckle subgroup 8: inexplicable repositioning of 6 residues to previous exon in PRDM4 2: near-universal motif SLP 9: near-universal motif EQNL 3: near-universal motif GF 10: near-universal motif IFY 4: indel unifying PRDM9/7/11, resolvable as an insertion 11: near-universal motif ELLVWY 5: near-universal motif FGP 12: possible synapormorphy grouping first 9 genes 6: near-universal motif WLI split by universal phase 00 intron PRDM16: CVDANQAGAG insertion removed from ISEDLGSEKFCVDANQAGAGSWLKYIRVA PRDM3: inexplicably has official gene name MECOM text-pdf version here
Applicable 3D structural determinations: .... PRDM9 YCEMCQNFFIDSCAAHGPPTFVKDSAVDKGHPNRSALSLPPGLRIGPSGI.PQAGLGVWNEASDLPLGLHFGPYEGRIT.....EDEEAANNGYSWLITKG.RNCYEYVD.......GKDKSWANWMRYVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHR..QIFYRTCRVIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKKELMAGR 3RAY PRDM11 FCESCQEYFVDECPNHGPPVFVSDTPVPVGIPDRAALTIPQGMEVVKDTS...GESDVRCVNEVIPKGHIFGPYEGQIS......TQDKSAGFFSWLIVDK.NNRYKSID.......GSDETKANWMRYVVISREEREQNLLAFQHSE..RIYFRACRDIRPGEWLRVWYSEDYMKRLHSMSQETIHRNLAR 2L9Z PRDM4 WCTLCDRAYPSDCPEHGPVTFVPDTPIE....SRARLSLPKQLVLRQSIV..GAEVGVWTG.ETIPVRTCFGPLIGQQSHSMEVAEWTDKAVNHIWKIYHN.GVLEFCII.......TTDENECNWMMFVRKARNREEQNLVAYPHDG..KIFFCTSQDIPPENELLFYYSRDYAQQI.............. 3IXH PRDM10 WCEECNNAHASVCPKHGPLHPIPNRPVL....TRARASLPLVLYIDRFLG......GVFSK.RRIPKRTQFGPVEGPLV.....RGSELKDCYIHLKVSLDKGDRKERDLHEDLWFELSDETLCNWMMFVRPAQNHLEQNLVAYQYGH..HVYYTTIKNVEPKQELKVWYAASYAEFVNQKIHDISEEERK. 3DAL PRDM1 DGGTSVQAEASLPRNLLFKYATN.SEEVIGVMSK.EYIPKGTRFGPLIGEIY..TNDTVPKNANRKYFWRIYSR.GELHHFID.......GFNEEKSNWMRYVNPAHSPREQNLAACQNGM..NIYFYTIKPIPANQELLVWYCRDFAERLHYPYPGELTMMNL. 3JV0 PRDM2 LAEVPEHVLRGLPEEVR.LFPSAVDKTRIGVWAT.KPILKGKKFGPFVGDKK.....KRSQVKNNVYMWEVYYP.NLGWMCID.......ATDPEKGNWLRYVNWACSGEEQNLFPLEINR..AIYYKTLKPIAPGEELLVWYNGEDNPEIAAAIEEERASARSK 3EP0 PRDM12 SGEVQKLSSLVLPAEVIIAQSSIPGEGL.GIFSK.TWIKAGTEMGPFTGRVI..APEHVDICKNNNLMWEVFNEDGTVRYFID.......ASQEDHRSWMTYIKCARNEQEQNLEV.VQIGT.SIFYKAIEMIPPDQELLVWYGNSHNTFLGIPGVPGLEEDQKK
Phylogenetic variability of the knuckle-PR(SET) domain for PRDM7/9, shown below, is complicated by the various gene duplications of PRDM7. Much less variability occurs between the universally conserved patches in the other five genes with a comparable domain, namely PRDM11, PRDM4, PRDM10, PRDM15 and PRDM6. These genes did not experience duplications during placental evolution. The fact that the entire domain is strongly conserved -- with vary different amino acids in each protein -- implies strong selective pressure acts along the entire domain in these five proteins so the 3D structure is not floppy (indeterminate random coil) between the universally conserved patches, and that whatever functions these genes have remained constant during placental evolution.
Note knuckle region in PRDM7/9 has moderate variability. Assuming on analogy with the terminal array zinc fingers that the residues between the second and third zinc ligands contain the residues that provide recognition specificity, these are QNFFIDS. This region has little phylogenetic variability in PRDM7/9. However overall PRDM11, PRDM4, PRDM10, PRDM15 and PRDM6 have even less variability. These regions could bind dna, single stranded rna or another protein involved in regulation. Those these partners may differ, the type of macromolecule will likely be the same because of underlying homology and implausibility of type change. The phylogenetic alignment of non-pseudogenes in the PRDM7/9 group is quite conservative from calJac (new world monkey Callithrix) to human:
PRDM9_homSap YCEMCQNFFIDSCAAHGPPTFVKDSAVDKGHPNRSALSLPPGLRIGPSGIPQAGLGVWNEASDLPLGLHFGPYEGRITEDEEAANNGYSWLITKGRNCYEYVDGKDKSWANWMRYVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRVIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKKELMAGR PRDM9_panTro .......................................................R.......P.....S.....Q.........S.............................E............S......S.......................................... PRDM9_gorGor ...................I.....................................................K........................................................................................................ PRDM9_ponAbe ................................................................................K......................................W.......................................................P.. PRDM9_nomLeu .....................I...T.G...........................................................................................W.......................................................P.. PRDM9_macMul .....................I.....E..................................................Q................................................................................................... PRDM9_papHam ...........................N....................................................K................................................................................................. PRDM7_homSap .....................................................................................S......................S..................................................................... PRDM7_ponAbe .....................................T........................................K................................................................................................... PRDM7_calJac ...I.............................HA.........................................V.......SS............................................................................................ PRDM7_micMur ...K.......................................K.R................E............QV........S....................D..............E...................Q.............................E..TIRQ PRDM7_otoGar ...K.......N..V.........T..E.......V....S..G.RT.......F.........Q..........QV........S....................E.QG...........E....................................................T..Q PRDM7_tupBel ...K.........S.....I..........SL...V.........A.....E.......A.T.............Q.........S....................E.C..............................................E................S.WQ.E PRDM9_oryCun ...K.....L....V....I...............V...............E.......................Q...E.....S....................R.............N............K.......Q..K..........................E..T... PRDM7_oryCun ...K.....L....V....I...............V...............E.......................Q...E.....S....................R.............N............K.......Q..K..........................E..T... PRDM7_ochPri ..........E...V..S..............H..V....S..........E........TT.............QV..E...T.S...........R........P.Q...........N.....................AV.Q.........................E..T... PRDM7_ratNor ...K.........PN....V.....V..R....H.V...............E.............V.......K.Q.........S..................Q.E.Q.........................K............R.....................M..GFT... PRDM7_musMus ...K.........PN....L.....M..R....H.V.........S.....E.............V.........Q.........S..................Q.E.Q.........................K..................................M..GFT... PRDM7_musMol ...K.........PN....L.....M..R....H.V.........S.....E.............V.........Q.........S..................Q.E.Q.........................K..................................M..GFT... PRDM7_dipOrd ...Q......N..TV....I..R.NV.....YD..V.........RQ.S..E........E..............Q.....D...S....M........V........Q...........Y.......................KA.........................R..T... PRDM7_speTri ..DK.....M...PV......I...V.N.D.S.H.T....L.......S..E.........T...........R.Q.........S....................E.Q.................................................................S... PRDM9_bosTau ..QE.........D.............E...A...V.T.....S.KL....E..........H............Q..D.K..I.S...........S........T.L...........HY...........G.......Q.V...............EK....CE.RG.SMFA... PRDM9_oviAri ..QE......N..D.............E...A.....T.....S.RL....E..........H............Q..D.K..V.S....................T.L....................L..QG.......Q.V................D....RD.SG.S..A... PRDM9_munMun ...E......N.............C..E...A.....T..H..S.RL....D.......KV...A........K.Q..DN.....S..A.................T..........................G.......Q.V................DF...RN.RG.S..A... PRDM7_turTru ...K.............A.........E.........T.....S.R.....E.......................Q.........S....................T..............E.....................V..............S.....P...G..SQ.V... PRDM7_lamPac ...K.................................T.......R.....E.........H.............QV........S..........K..........Y...............................................E................S.WQ.E PRDM7_susScr ...K.................................T.......R.....E.........H.............QV........S.........................................................V..............................T..I PRDM7_felCat ...K..........V.........N..G.........T.......R..S..E...............T.......Q.........S....................N................................................................S..ST.K PRDM7_ailMel ...K..........V...............Q......T.......R.............................Q.........S....................N..............E.................................................S..A..K PRDM7_pteVam ...K.............S.I.....E..IR.......T.............E................L......QV........S.....QG.............E.R..............................................................R..T... PRDM7_myoLuc ...K..........V................A.....T.............E........EC...V...Y.....Q.....AI..S....................T.Q..................................V.K.........E...............T.PV... PRDM7_equCab ...N...............I.................T..L....R.....E.......................Q.........S....................I....................................V...........................R..T... PRDM7_sorAra ...N......NK.S...S.I....N..A...S.....T..H..........E....I..................Q..N......S..................V.E.L............Y....................I.K..........................S..T.DK PRDM9_loxAfr ...K.......T..V..A.M.....P..R....H...T..........S..K..........E............QV...K....S.........K..........E..............E....................T.Q.D.....................R.....TS.. PRDM7_choHof ...K.....FEN........LL.....GQ.R.KH...V......L......E.......................QV......T.S......................C.................................A...............................T.EK PRDM9_homSap YCEMCQNFFIDSCAAHGPPTFVKDSAVDKGHPNRSALSLPPGLRIGPSGIPQAGLGVWNEASDLPLGLHFGPYEGRITEDEEAANNGYSWLITKGRNCYEYVDGKDKSWANWMRYVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRVIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKKELMAGR
Central PR(SET) domain descended from PRDM11
Various additional sequences are relevant to understanding the curated placental mammal PRDM7/9 set. For example, the neanderthal genome despite being very far from satisfactory coverage can provide a PRDM9 sequence derived from the human reference sequence using non-synonymous SNPs reported in the corresponding UCSC browser track. The changes reported in the zinc finger domain (R HDL S R) may be enough to have created somewhat of a species barrier, though this involves comparing a fossil sequence to a contemporary human (which are today themselves quite variable). Similarly, the bushman genome sequence might yield an intermediate outgroup, though that assembly (like so many others) remains elusive.
Terminal sequences for 9 additional species of murid rodents have been determined but these have limited value for comparative genomics because they do not even cover the entire terminal exon and their syntenic contexts (and thus homological relationships) were not established. The single individual sequenced may not be representative of the overall population in the zinc finger region (based on the extensive diversity observed in human), diminishing their utility for predicting species barriers. These genes are most likely PRDM7 orthologs only secondarily related to the catarrhine primate PRDM9 set, ie descended from the unique locus present in stem euarchontoglires whereas the latter duplicated from a stem old world monkey PRDM7. It is worth noting that the reported sequences are very orderly and lack the overall chaos of frameshifts and stop codons so often seen in this gene family. The protein accessions are here.
A zebrafish protein put forward as an ortholog to placental mammal PRDM9 seems implausible given that birds, lizard and frog lack notable homologs. It lacks close counterparts in other species of fish with determined genomes and is not syntenic to mammalian gene locations. Thus it might represent an independent gene shuffle that resulted in a similar concatenation of domains (parallel evolution).
The protein lacks the KRAB and SSXRD domains but contains a standard knuckle, PR(SET), early ZNF finger and ZNF repeat domain (all in exons phased identically to human). Although backblast restricted exons 3-5 to the human proteome has best matches to PRDM9, PRDM7 and the closely related PRDM11 (suggesting orthology of this region), the pre-zinc finger part of exon 6 does not give a clear signal despite its early C2H2 domain, perhaps because of few conserved residues after it. The same could be said for the pre-zinc finger of PRDM9 -- it is apparently just a fast evolving linker region not under selection for amino acid sequence.
While blastp of the zinc finger array is always a problematic exercise, here it gives closer resemblance to other zinc finger genes, notably ZNF658 and ZNF 585, than to any member of the PRDM family. The phase 12 intron here is moderately diagnostic in conjunction with the early zinc finger. The zebrafish terminal zinc finger array, while disorderly, does have several zinc fingers ending in the GEKP-like lockdown cap which supports a relationship with similar caps in PRDM7/9. Genes related to the zebrafish feature are found in salmon, trout, catfish and minnow but not stickleback, fugu, tetraodon or medaka. Transcripts are exceedingly common in contrast to mammals. The missing KRAB and SSXRD domains are believed critical in recruiting other essential proteins to the hotspot in the only systems with experimental data (mouse and human) so this gene cannot fulfill the same functional role.
Thus only central PR(SET) exons are established as directly relevant to the history of PRDM7/9, ie that it was present in the common ancestor of mammals and fish. The terminal exon could represent orthology with extreme relative divergence but the evidence favors a chimeric origin with a different zinc finger terminal exon. The zebrafish gene is thus only a partially verifiable member of the PRDM family, one lacking a convincingly orthologous terminal exon as well as the final fusion with SSX1 as in PRDM7/9. Early diverging tetrapods need re-examination to see if they too have a gene with central PR(SET) exons of PRDM7/9 in a gene with a following phase 12 exon.
Absence in frog, lizard and bird genomes would require persistence through the common ancestor but multiple independent loss events in the descendent lineages. Here frog still has a knuckle-PR(SET) domain most like that of PRDM7/9 but it is attached to a long BED domain and most resembles the human protein ZBED1 family overall.
Even more attractive is the hypothesis that nearest neighbor PRDM11 -- which is highly conserved and effortlessly located in all tetrapods including frog, birds, lizard and platypus -- gave rise to PRDM7/9 via gene duplication. The duplicated gene subsequently neofunctionalized by reciprocal translocation with SSXRD and a ZNF gene to acquire its current N- and C-termini. PRDM11 has hardly changed since the parenting event. Best-blast (of ancestral, consensus, or any individual species) to human proteins is far and away PRDM7/9. This scenario explains -- without multiple gene loss events -- why PRDM7/9 cannot be located in early diverging tetrapods.
Reported PRDM9 orthologs in early diverging bilatera such as Lottia, Capitella and Nematostella can be dismissed as independent occurrences of common ancient domain combinations. None of these domains are mammalian innovations -- PR(SET) traces back to bacterial methylases and zinc fingers also have a long and complex history. Without conservation of all mammalian domains, exon phasing, syntenic chromosomal location and demonstration of descent from a single gene in the last common ancestor, there is no basis for calling such genes orthologous nor assuming they function similarly in meiosis or illuminate mammalian PRDM7/9 evolution. Widespread expression in testes is not supportive as it conflicts with the very restrictive mammalian expression pattern. How could such a fundamental capacity be lost (and replaced by a non-homologous system) so many times in so many other lineages -- all of which have obligatory meiosis?
>PRDM7_danRer Danio rerio (zebrafish) Q6P2A1 transcript BC064665 no KRAB SSXRD or exon 5 but knuckle SET early ZNf C2H2 array 0 MSLSP 1 2 DLPPSEEQNLEIQGSATNCYSVVIIEEQDDTFNDQPF 1 2 YCEMCQQHFIDQCETHGPPSFTCDSPAALGTPQRALLTLPQGLVIGRSSISHAGLGVFNQGQTVPLGMHFGPFDGEEISEEKALDSANSWV 0 0 ICRGNNQYSYIDAEKDTHSNWMK 2 1 FVVCSRSETEQNLVAFQQNGRILFRCCRPISPGQEFRVWYAEEYAQGLGAIWDKIWDNKCISQ 1 2 GSTEEQATQNCPCPFCHYSFPTLVYLHAHVKRTHPNEYAQFTQTHPLESEAHTPITEVEQCLVASDEALSTQTQPVTESPQEQISTQNGQPIHQTENSDEPDASDIYTAAGEISDEI HACVDCGRSFLRSCHLKRHQRTIHSKEKP YCCSQCKKCFSQATGLKRHQHTHQEQEKNIESPDRPSDI YPCTKCTLSFVAKINLHQHLKRHHHGEYLRLVESGSLTAETEEDHT EVCFDKQDPNYEPPSRGRKSTKNSLKGRGCPKKVAVGRPRGRPPKNKNLEVEVQKIS PICTNCEQSFSDLETLKTHQCPRRDDEGDNVEHPQEASQ YICGECIRAFSNLDLLKAHECIQQGEGS YCCPHCDLYFNRMCNLRRHERTIHSKEKP YCCTVCLKSFTQSSGLKRHQQSHLRRKSHRQSSALFTAAI FPCAYCPFSFTDERYLYKHIRRHHPEMSLKYLSFQEGGVLSVEKP HSCSQCCKSFSTIKGFKNHSCFKQGEKV YLCPDCGKAFSWFNSLKQHQRIHTGEKP YTCSQCGKSFVHSGQLNVHLRTHTGEKP FLCSQCGESFRQSGDLRRHEQKHSGVRP CQCPDCGKSFSRPQSLKAHQQLHVGTKL FPCTQCGKSFTRRYHLTRHHQKMHS* 0 >ZBED1_xenTro 0 MQAAEEACAQLEDELL 1 2 FCEDCRLYFRDSCPTHGAPTFILDTPVPENVPSRALLSLPEGLVVKERPQGGFGVWCTIPVIPRGCIFGPYEGDVIMDRSDCTVYSWA 0 0 VRENGSYFYIDASDDSKSSWMR 2 1 YVACASTEEEHNLTVFQYRGKIYYRASQVIPTGTELLVWIGEEYARTLGLKL 1 2 GEHFKYEFGEKELLMKLFQDLQLKPVDSISNHVSSQSQYMCNDMVTPVMQAHRTSYPLNNIGHTSSVFPLLEGTQNLVSLGRAQSRYWTFFGFQGDAYGRIIDKTKIICKLCGVRLSYSGNTTNLRQHLIYKHRRQYNDL
>PRDM11_conSeq consensus of 30 tetrapod PRDM11 orthologs 2 FCESCQEYFVDECPNHGPPVFVSDTPVPVGIPDRAALTIPQGMEVVKEASGENDVRCINEVIPKGHIFGPYEGQISTQDKSAGFFSWL 0 0 IVDKNNRYKSIDGSDETKANWMR 2 1 YVVISREEREQNLLAFQHSERIYFRACRDIRPGERLRVWYSEDYMKRLHSMSQETIHRNLAR 1 PRDM9_homSap YL Y..M..NF.I.S.AA....T..K.SA.DK.H.N.S..SL.P.LRIGPSGIPQAGLGVW..AL.L.LH......R.TEDEEA.NNY... .TKGR.C.EYV..K.KSW..... ..NCA.DDE....V...YHRQ.FY.T..V....CE.L...GDE.GQE.GIKWGSKWKKE.MA PRDM11_homSap FW FCESCQEYFVDECPNHGPPVFVSDTPVPVGIPDRAALTIPQGMEVVKDTSGESDVRCVNEVIPKGHIFGPYEGQISTQDKSAGFFSWL IVDKNNRYKSIDGSDETKANWMR YVVISREEREQNLLAFQHSERIYFRACRDIRPGEWLRVWYSEDYMKRLHSMSQETIHRNLAR PRDM11_panTro .. ........................................................................................ ....................... .............................................................. PRDM11_rheMac .. .........................................................I.............................. ....................... .............................................................. PRDM11_calJac .. ........................................................................................ ....................... ....................C......................................... PRDM11_otoGar .. ............................M..................EA...N....I.............................. ....................... ..A...............................R........................... PRDM11_musMus .. ................................................AG.......I.............................. ....................... ..................................R........................... PRDM11_ratNor .. ..............T................................EVG.......I...V.......................... ....................... ..................................R........................... PRDM11_cavPor .. .............................................I.EAG.......I.............................. ...............D......- ..................................R........................... PRDM11_speTri .. ...............................................EA........IS............................. ....................... ..........R.......G...............R......Q...R................ PRDM11_oryCun .. ..........................................L...QEA........I.D.....R.........AA........... .....S................. ........Q.........N.H..........A..R......G.................... PRDM11_ochPri .. ............................M..A...............EA........LSD............................ ....................... ....................H.........Q...R........................... PRDM11_bosTau .. ...............................................EA...N....I.......R...................... ....................... ........S.........................R........................... PRDM11_equCab .. ...............................................EA...N....I.......................T...... ....................... ..................................R........................... PRDM11_canFam .. ...............................................EA...N....I.............................. ....................... ..................................R......................H.... PRDM11_myoLuc .. ..............K....M..........L.................AN..N....I.............................. ....................... ....................H.......................................T. PRDM11_pteVam .. ................................................A...N...SI.............................. ................S...... ....................H.............R........................... PRDM11_eriEur .. ..............K...........................V....EA........I.............................. ......H.........S...... ....................H.............R........................... PRDM11_loxAfr .. ...............................................EA...N....IS............................. ..........V............ .........................V........R......Q.................... PRDM11_echTel .. ............................M..................EG...N....IS....T-..LR......Y.RN......... ....................... ....C...............H.............R.....GQ..................T. PRDM11_dasNov .. ...............................................EA...N....I.............................. ....................... .........................S........Q...............V........... PRDM11_macEug .. ............................M...........P......EA..QN....M.............................. .............T...Q..... ..I..........M......K....V........R.....................Q...T. PRDM11_monDom .. ............................M...........P......EA..Q.....M.............................. ......H......T......... .............M......K....V........R.....................Q...T. PRDM11_ornAna .. ........................................P.I....EA...N....M.............................. .............T......... .I.......................V........R.........................T. PRDM11_galGal .. ........................................P.I....EP...N....M..................S........... .............T......... ..I..........M....................K.....................N...TT PRDM11_taeGut .. ........................................P......EP...N....M..................S..R........ .............T......... ..I..........M................H...K....................MN.SFTS PRDM11_anoCar .. ...................M.L..A...I.........V.P......EAN..R.....G.I....R.Y.....KL.S........... .............T...TS.... ..A..........M...........T........R.....................N...T. PRDM11_xenTro .. ..............S....IL.P..L..I.M.E....SV.C.I.....S...R.....G.I....R.Y.....KL.S........... .............T...TS.... .............M......K....T....Q...K.....................N...TQ
Structural considerations in C2H2 zinc fingers
High resolution structures of C2H2 zinc finger domains have been available for decades. As the name suggests, the divalent zinc atom locks the two cysteines and two histidines into a rigid geometry providing a core conformation that a small peptide of 28 residues could not otherwise stably assume. Note in the unbound state, finger tips must retain flexibility while the domain ensemble scans its genome for specific dna sequences appropriate to its function. Each finger binds a trinucleotide -- in effect making a zinc finger the protein counterpart to tRNA anticodon. However overall binding is not a simple read-off code because adjacent fingers alter each other's specificities in subtle ways.
The linker region TGEKP plays a key role when the correct DNA sequence is encountered, snap-locking its finger down onto its target by capping the C-terminus of its alpha helix. A hydrogen bond between the first threonine and middle glutamate is key to this binding-induced conformational shift. From comparative genomics, it appears that a serine in first position can also form this hydrogen bond. The role of the glycine is to stay out of the way; the lysine counterbalances the negative charge of the glutamate; the proline terminates any helical propensity, allowing a fresh start in the adjacent finger.
While this motif is immensely conserved within C2H2 zinc finger of PDRM9 homologs, exceptions do occur. It is important to understand these because these loss of dna lock-down could loosen or even eliminate trinucleotide binding specificity. Such steps might represent initial stages of pseudogenization. However many exceptions occur within the first or last fingers. It is also common for fragmentary and imperfect motifs to end the protein, sometimes continuing on in another reading frame past the current stop codon.
Note in aligning zinc finger motifs, the breaks should always be put at the end of the linker region. It is completely illogical to break at the first cysteine as some authors do because capping by the linker region is specific to its zinc finger, not the following one.
Predicting dna binding sites of zinc finger domains
Supplemental information
The sections below store data used above. This includes curated sequences from all available mammals for PRDM7 and PRDM9 and additional their partial paralogs in the PRDM gene family. These latter have extensive comparative genomics alignments readily available elsewhere (UCSC genome browser, under GeneSorter feature and ProteinFasta feature in gene details page) so that is not repeated here.
While this topic has a long history in the peer-reviewed scientific literature, only the most recent articles are provided here because their reference sections satisfactorly summarize pre-2005 studies. Instead, the focus here is identifying free full text access to the recent articles, preferably as html which better supports copying snippets of text. The journal, google, and PubMed all provide forward citations to still other articles that cite the articles provided here.
Curated reference sequences
The sequences below have largely been compiled from genome projects -- only rarely do validating transcripts exist at GenBank. Sequences with a single frameshift or other glitch have been edited to allow full length proteins on the theory that the error either reflects an aberrant atypical individual chosen for sequencing or sequencing error in low coverage projects within a difficult region. However such sequences may instead reflect early stages of pseudogenization. Other sequences are in fact clearly pseudogenes; here recognizable exons have been collected to allow rough dating of loss of function.
In the case of more intensively studied species such as human, the number of C2H2 repeats varies widely. Only the reference sequence representative is shown here. This variation likely occurs in all species with the individual animal chosen for sequencing not necessarily the most common allele. Many clades have independent histories of gene amplification and gene loss, making both orthologous and functional comparisons problematic at substantial divergences.
The reference sequences below are also available as here as tab-delimited pdf text that will paste cleanly into rows and columns of a spreadsheet which allows sorting to conveniently select data subsets.
Other useful sequences such as PRDM11, PRDM4 and zinc finger semi-homologs having similar exon and domain structures, are provide in the subsequent section along with syntenic markers such as GAS8.
>PRDM9_homSap Homo sapiens (human) genome Prim gene 13 CDH12 chr5 10 exon size 18,301 bp KRAB SSXRD SET C2H2
0 MSPEKSQEESPEEDTERTERKPM 0
0 VKDAFKDISIYFTKEEWAEMGDWEKTRYRNVKRNYNALITI 1
2 GLRATRPAFMCHRRQAIKLQVDDTEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 VKPPWMALRVEQRKHQK 0
0 GMPKASFSNESSLKELSRTANLLNASGSEQAQKPVSPSGEASTSGQHSRLKL 1
2 ELRKKETERKMYSLRERKGHAYKEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 YCEMCQNFFIDSCAAHGPPTFVKDSAVDKGHPNRSALSLPPGLRIGPSGIPQAGLGVWNEASDLPLGLHFGPYEGRITEDEEAANNGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDKSWANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRVIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKKELMAGR 1
2 EPKPEIHPCPSCCLAFSSQKFLSQHVERNHSSQNFPGPSARKLLQPENPCPGDQNQEQQYPDPHSRNDKTKGQEIKERSKLLNKRTWQREISRAFSSPPKGQMGSCRVGKRIMEEESRTGQKVNPGNTGKLFVGVGISRIAK
VKYGECGQGFSVKSDVITHQRTHTGEKL
YVCRECGRGFSWKSHLLIHQRIHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSWQSVLLTHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSRQSVLLTHQRRHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSRQSVLLTHQRRHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSWQSVLLTHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSWQSVLLTHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSNKSHLLRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFRDKSHLLRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFRDKSNLLSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSNKSHLLRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFRNKSHLLRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSDRSSLCYHQRTHTGEKP
YVCREDE.....................
>PRDM9_panTro Pan troglodytes (chimp) genome Prim gene 19 CDH12 chr5 frag assembly glitch in mid C2H2
0 MSPERSQEESPEGDTERTERKPM 0
0 VKDAFKDISIYFTKEEWAEMGDWgKTRYRiVKMNYNALITi 1
2 GLRATRPAFMCHRRQAIKLQVDDTEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 VKPPWMAFRGEQSKHQK 0
0 GMPKASFNNESSLkELSGmPNLLNTSgSEQAQKPVSPPGEASTSGQHSRLKL 1
2 ELRRKETvGKMYSLRERKGHAYKEISEPQDDDYL 1
2 yCEMCQNFFIDSCAAHGPPTFVKDSAVDKGHPNRSALSLPPGLRIGPSGIPQAGLRVWNEASDPPLGLHSGPYEGQITEDEEAANSGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDKSwANWMR 2
1 YENCARDDEEQNLVSFQYHRQSFYRTCRVIRPGCELLVWYGDE GQELGIKWGSKWKKELMAGR 1
2 EPKPEIHPCPSCCLAFSSQKFLSQHVERNHSSQNFPGPSARKLLQPENPCPGDQNQEQQYPDPRSRNDKTKGQEIKERSKLLNKRTWQREISRAFSSPPKGQMGSCRVGKRIMEEESRTGQKVNPGNTAKLFVGVGISRIAK
VKYGECGQGFSDKSDVITHQRTHTGGKP
YVCRECGRGFSWKSHLLSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSVKSSLLSHRTTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSVKSSLLSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSQQSNLLSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSVKSSLLSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSVKSSLLSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSKQSHLLSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSVQSNLLSHQRTHTGEKL
YVCRECGRGFSQQSHLLRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRecgrgfsqqshLLSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSVKSSLLSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSKQSHLLSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSQQSHLLSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSQQSHLLRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSVKSSLLSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSVKSSLLSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECERGFSQQSHLLRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSRQSALLIHQRTHTGEKP
VCREDE......................
>PRDM9_gorGor Gorilla gorilla (gorilla) CABD02290264 Prim gene -- cdh12 chr5 several contigs needed, most of ZNF domain missing
0 MSPERSQEESPEEDTERTERKPM 0
0 VKDAFKDISIYFTKEEWAEMGDWEKTRYRNVKRNYNALITI 1
2 GLRATRPAFMCHRRQAIKLQVDDTEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 VKPPCMALRVEQRKHQK 0
0 GMPKASFSNESSLKELSRTANLLNASGSEQAQKPVSPPGEASTSGQHSRLKL 1
2 ELRKKETEGKMYSLRERKGHAYKEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 yCEMCQNFFIDSCAAHGPPIFVKDSAVDKGHPNRSALSLPPGLRIGPSGIPQAGLGVWNEASDLPLGLHFGPYKGRITEDEEAANNGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDKSWANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRVIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKKELMAGR 1
2 EPKPEIHPCPSCCLAFSSQKFLSQHVERNHSSQNFPGPSARTLLQPENPCPGDQNQEQQYPDPRSRNDKTKGQEIKERSKLLNKRTWQREISRAFSSPPKGQMGSCRVGKRIMEEESR TGQKVNPGNTGKLFVGVGISRIAK
VKYGECGQGFSVKSDVITHQRTHTGEKP
YVC.........................
>PRDM9_ponAbe Pongo abelii (orangutan) genome Prim gene 10 CDH12 chr5 frameshift extra a penultimate ZNF
0 MSPERSQEESPkGDTERTERKPM 0
0 VKDAFKDISIYFTKEEWTEMGDWEKTRYRNVKRNYKTLITI 1
2 GLRATRPAFMCHRRQAIKLQVDDTEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 VKPPWMAFRGEQSKHQK 0
0 GMPKASFNNESSLKELSGTQNLLNTSGSEQAQKPVSPPGEASTSGQHSTLKI 1
2 ELRRKETEGKTYSLRERKGHAYKEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 YCEMCQNFFIDSCAAHGPPTFVKDSAVDKGHPNRSALSLPPGLRIGPSGIPQAGLGVWNEASDLPLGLHFGPYEGRITEDKEAANNGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDKSWANWMR 2
1 YVNCAWDDEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRVIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKKELMPGR 1
2 EPKPEIHPCPSCCLAFSSQKFLSQHVERNHSSQNFPGPSARKLLQPENPCPGDQNHEQQYSDPRSCNDKTKGQEIKERSKLLNKRTWQREISRAFSSPPKGQMGSCRVGKRIMEEESRTGQKVNPGNTGKLFVGVGISRIAK
VKYGECGQGFSDKSDVITHQRTHTGGRS
YVCRECGRGFSRQSVLLIHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSRRSVLLIHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSQQSVLLIHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSRRSVLLIHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSWKSVLLRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSQQSVVFIHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSGKSVLFRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSDKSGVCYHQRTHTRGEA
YVCRECGRGFSVKSNLLSHQRTHTEEKL
YVCREDE.....................
>PRDM9_nomLeu Nomascus leucogenys (gibbon) ADFV01015315 Prim gene 10 cdh12 ADFV01015317 ADFV01015319 no synteny CpG stop exon 6 in 6/6 traces VCRKDE* in altered reading frame
0 MSPERSQEESPEEDTERTEQKPT 0
0 VKDAFKDISIYFTKEEWAEMGDWEKTRYRNVKRNYNALITI 1
2 GLRATRPAFMCHRRQAIKLQVDDTEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 VKPPWMALRMEQRKHQK 0
0 GMPKASFSNESSLKELSGAANLLNASGSEQAQKPVSPPGEASTSGQHSRLKL 1
2 ELRRKETEGKMYSL*ERKGHAYKEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 YCEMCQNFFTDSCAAHGPPTFIKDSTVGKGHPNRSALSLPPGLRIGPSGIPQAGLGVWNEASDLPLGLHFGPYEGRITEDEEAANNGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDKSWANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCQVIRPGCEPLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKKELTAER 1
2 EPKAEIHPCPSCCLAFSSQKFLSQHVARHHSSQNFPGPSARKFLQPENPCPGDQNQEQQYSDPRSCNDKTKGQEIKERSKLLNKRTWQREISRAFSSSPKVQMGSCRVGKRIIEESRTGQKVNPGNTGQLFVGVGISRIAE
VKYGECGQGFSVKSDVITHQRTHTGEKL
YLCRECGRGFSVKSSLLSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSKKSNLLSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSDKSSLLRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSQKSSLLSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSQKSSLLSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSDKSSLLRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSQKSSLLSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSVKSNLLSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSDKSSLLRHQRTHTGEKP
>PRDM9_macMul Macaca mulatta (rhesus) genome Prim gene 9 CDH12 chr6 exon 4 lost to Ns
0 MSPERSQEESPEEDTERTERKPT 0
0 VKDAFKDISIYFTKEEWAEMGDWEKTRYRNVKRNYNALITI 1
2 GLRATRPAFMCHRRQAIKLQVDDTEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 0
0 GMPKASFNNESSLKEVSGMANLLNTSGSEQAQKPVSPPGEARTSGQHSRLKL 1
2 ELRRKETEGKMYSLRERKGHAYKEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 YCEMCQNFFIDSCAAHGPPTFIKDSAVEKGHPNRSALSLPPGLRIGPSGIPQAGLGVWNEASDLPLGLHFGPYEGRITQDEEAANNGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDKSWANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRVIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKKELMAGR 1
2 EPKPEIHPCPSCCLAFSSQKFLSQHVERNHSTQNFPGPSARRLFQPENLCSGDQNQEQQYSDPRSCNDKTKGQEIKERSKLLNKRTWPKEISRAFSSPPKGQMGSSRVGERMMEEEYRTGQKVNPENTGKLFVGVGISRIAK
VKYGECGQGFSDKSDVIIHQRTHTGEKP
YLCRECGRGFSQKSSLRRHQRTHTGEKP
YLCRECGRGFRDNSSLRYHQRTHTGEKP
YLCRECGRGFSNNSGLCYHQRTHTGEKP
YLCRECGRGFSDNSSLHRHQRTHTGEKP
YLCRECGRGFSNNSGLRYHQRTHTGEKP
YLCRECGRGFSNNSGLRHHQRTHTGEKP
YLCRECGRGFSQKANLLRHQRTHTGEKP
YLCRECGRGFSQKADLLSHQRTHTGEKP
VCRKDE......................
>PRDM9_papHam Papio hamadryas (baboon) genome Prim gene 11 cdh12 contigs scattered
0 0
0 1
2 1
2 VKPPWMAFRVEQSKHQK 0
0 EMPKTSFSNESSLKELSGTPNLLSTSGSEQAQKPASPPGEASTSGQHSRLKL 1
2 ELRRKEAEGKMYSLRERKGHAYKEVSELQDDDYL 1
2 ycEMCQNFFIDSCAAHGPPTFVKDSAVNKGHPNRSALSLPPGLRIGPSGIPQAGLGVWNEASDLPLGLHFGPYEGRITEDKEAANNGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDKSWANWMR 2
1 1
2 EPKPEIHPCPSCCLAFSSQKFLSQHVERNHSTQNFRGPSARRLLQPENLCSGDQNQEQQYSDPRSCNDKTKGQEIKERSKLLNKRTRQKEISRAFSSPPKGQMGSSRVGERMMEEESRTGQKVSPENIGKLFVGVGISRIAK
VKYGECGQGFSDKSDVVIHQRTHTGEKP
YLCRECGRGFRDNSSLRCHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSQKSHLLSHQRTHTGEKP
YLCRECGRGFRDNSSLRCHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSQKSHLLSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFRDNSSLCCHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSDNSGLRCHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSQKSHLLSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSDNSGLRCHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSQKSHLLSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRSVGGALAGRQTSSVTR
>PRDM7_homSap Homo sapiens (human) genome Prim gene 3 GAS8+ chr16 TUBB3+ DEFB+ AFG3L1+ DBNDD1- GAS8+ PRDM7- 92% id
0 MSPERSQEESPEGDTERTERKPM 0
0 VKDAFKDISIYFTKEEWAEMGDWEKTRYRNVKMNYNALITV 1
2 GLRATRPAFMCHRRQAIKLQVDDTEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 VKPPWMAFRGEQSKHQK 0
0 GMPKASFNNESSLRELSGTPNLLNTSDSEQAQKPVSPPGEASTSGQHSRLKL 1
2 ELRRKETEGKMYSLRERKGHAYKEISEPQDDDYL 1
2 YCEMCQNFFIDSCAAHGPPTFVKDSAVDKGHPNRSALSLPPGLRIGPSGIPQAGLGVWNEASDLPLGLHFGPYEGRITEDEEAANSGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDKSSANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRVIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKKELMAGR 1
2 EPKPEIHPCPSCCLAFSSQKFLSQHVERNHSSQNFPGPSARKLLQPENPCPGDQNQERQYSDPRCCNDKTKGQEIKERSKLLNKRTWQREISRAFSSPPKGQMGSSRVGERMMEEESRTGQKVNPGNTGKLFVGVGISRIAK
VKYGECGQGFSDKSDVITHQRTHTGGKP
YVCRECGRgFSRKSDLLSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECERGFSRKSVLLIHQRTHRGDAP
VCRKDE......................
>PRDM7_panTro Pan troglodytes (chimp) genome Prim pseu 2 GAS8+ chr16
0 MSPERSQEESPEEDTERTERKPM 0
0 VKDAFKDISIYFTKEEWAEMGDWEKTRYRNVKRNYNALITI 1
2 GLRATRPAFMCHRRQAIKLQVDDTEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 VKPPLMALRVEQRKHQK 0
0 GMPKASFSNESSLKELSRTANLLNASGSEQAQKPVSPPGEASTSGQHSRLKL 1
2 ELKKKETEGKMYSLRERKGHAYKEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 YCEMCQNFFIDSCAAHGPPTFVKDSAVDKGHPNRSALSLPPGLRIGPSGIPQAGLGVWNEASDLPLGLHFGPYKGRITEDEEAANNGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDKSWANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRVIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKKELMAGR 1
2 EPKPEIHPCPSCCLAFSSQKFLSQHVERNHSSQNFPGPSARKLQPENP PGDQNQERQYSDPRCCNDKTKGQEVKERSKLLNKWTWQREISRAFSSLPKGQMGSSRVGERMMEEESRTGQKVNPGNTGKLFVGVGISRIAK
VKYGECGQGFSVKSDVITHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGQGFSRKSVLLIHQRTHRGEKP
VCRKDE......................
>PRDM7_gorGor Gorilla gorilla (gorilla) genome Prim pseu 3 GAS8+ chr15730 numerous frameshifts in terminal ZNF domain
0 MSPERSQEESPEGDTERTERKPM 0
0 VKDAFKDISIYFTKEEWAEMGDWEKTRYRNVKRNYNALITI 1
2 GLRATQPVFMCHRRQAIKLQVDDTEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 0
0 GMPKASFNNESSLKELSGTPNLLNTSGSEQAQKPVSPPGEASTSGQHSRRKL 1
2 ELRRKETEGKMYSLRERKGHAYKEISKPQDDDYL 1
2 yCEMCQNFFIDSCAAHGPPTFVKDSAVDKRHPNRSALSLPPGLRIGPSGIPQAGLGVWNEASDLPLGLHFGPYEGRITEDKEAANSGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDKSWANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVALQYHRQIFYRTCRVIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKKELTAGR 1
2 EPKPEIHPCPSCCLAFSSQKFLSQHVERNHSSQNFPGPSARKLLQPENPCPGDQNQERQYSDPRCCNDKTKGQEIKERSKLLNKRTWQREISRAFSSPPKGQMGSSRVGERMMEEESRTGQKVNPGNTGKLFVGVGISRIAK
VKYGECGQGFSWKSNLLRHQRTHTGGKP
YVCRECGRGFSWKSDLLSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSWKSNLLSHQRTHTGEKP
>PRDM7_ponAbe Pongo abelii (orangutan) genome Prim gene 4 GAS8+ chr16
0 MSPERSQEESPEDDTERTERKPT 0
0 VKDAFKDISIYFTKEEWAEMGDWEKTRYRNVKRNYNALITI 1
2 GLRATRPAFMCHRRQAIKLQVDDTEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 VKPPWMALRVEQRKHQK 0
0 GMPKASFNNESSLKELSETANLLNASGSEQAQKPVSPPGEASTSGQHSRLKL 1
2 ELRSKETEGNTYSLRERKGHAYKEISEPQDDDYL 1
2 yCEMCQNFFIDSCAAHGPPTFVKDSAVDKGHPNRSALTLPPGLRIGPSGIPQAGLGVWNEASDLPLGLHFGPYEGRITKDEEAANNGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDKSWANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRVIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKKELMAGR 1
2 EPKPEIHPCPSCCLAFSSQKFLSQHVERNHSSQNFPGPSARHLLQAENPCPGDQNQEQQYSDPDCCNDKTKGQEIKERSKLLNKRTWQREISRAFSSSAKGQMGSSRVGERMMEEESGTGQKVNPGNTGKLFVGVGISRIAK
VKYGECGQGFSVKSDVITHQRTHTGEKP
YICRESGRGFTQKSGLLSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGWGFSQKSNLLRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSRKSVLLIHQRTHTGEKP
VCRKDE......................
>PRDM7_nomLeu Nomascus leucogenys (gibbon) ADFV01125891 Prim pseu 5 gas8+ synteny implied by non-coding
0 0
0 1
2 1
2 IKSPWMAVRVEQSKHQK 0
0 GMPKASFNNESGLKELSGTQNLLNTSG EQARKPVSPPGEASTSGQHSRQKL 1
2 ELRRKETEGKMYSL ERKGHAYKEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 yCEMCQNFFTDSCAAHGPPTFVKDSAVDKGHPNHSALSLPPGLRIGPSGIPQAGLGVWNEASDLPLGLHFGPYEGRITEDEEAANNGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDKS ANWMK 2
1 YVNCARDHEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCQVIRPGCEPLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKKELTAER 1
2 EPKPEIHPCPSCCLVFTSQKFLSQHVECNHSSQNFPGPSARKLLQRENPCPGDQNQEQQYSDSRSCNDKTKGQEIKERSKL NKRIWQRKISRAFSSLPKGQMGSSRVGERMMEEESRTGQKVNPGNTGKLFVGVGISRIAK
VKYGECGQGFSDKSDVIAHQGTHTGGKS
.ICRECGWGFSQESHLLIHQRTHTGEKL
YVCRECGQGFSQKSDLLSHQRTHTGEKP
YVRRECGRGFSQKSNLLSHQRTHTEEKP
YVCRECGWGFSQKSHLLIHQRTHTGKKP
VCRKDE......................
>PRDM7_macMul Macaca mulatta (rhesus) genome Prim pseu 2 GAS8+ chr20 frameshifts exon 5 and 10, exon 10 a to aa restores frame
0 0
0 1
2 1
2 VKPPWMAFRVEQSKHQK 0
0 EMPKTSFNNESSLKELSGTPNLLSTSDSE AQKPASPPGEASTSGQHSRLKL 1
2 ELRRKETEGKMYSLRERKRHAYKEASELQHDDYL 1
2 YCEMCQNFFIDSCAAHGPPTFVKDNAVNKGHPNRSALSLPPGLRIGPSGIPQAGLGVWNEASDLPLGLHFGPCEGRITEDKEAANSGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDKSWAKWMR 2
1 1
2 EPKPEIYPCPSCCLAFSSQKFLSQHVERNHSSQNFPGPSARKLLQSENPCPGDQNQEQQYSDPSSCNDKTKGQEIKERSKLLNKRTWQREILRAFTSPPKGQMGSSRVGERMMEEEFRTGQKANPGNTGKLFVGVEISRIAK
VKYGECGQGFSGKSDVITHQRTHTEGKP
YVCRGCGRRFSQKSSLLRHQRTHTGEKP
VCKKNE......................
>PRDM7_papHam Papio hamadryas (baboon) genome Prim pseu 2 gas8+ contigs scattered
0 MSPERSQEESPEEDTERTEWKPM 0
0 VKDAFKDISIYFTKEEWAEMGDWEKTRYRNVKRNYNALITI 1
2 GLRATRPAFMCHRRQAIKLQVDDTEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 VKPPWMAVRVEQSKHQK 0
0 GMPKASFNNESSLKEVSGMANLLNTSGSEQAQKPVSPPGEARTSGQHSRLKL 1
2 ELRRKETEGKMYSLRERKGHAYKEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 YCEMCQNFFIDSCAAHGPPTFIKDSAVEKGHPNRSALSLPPGLRIGPSGIPQAGLGVWNEASDLPLGLHFGPYEGRITQDEEAANNGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDKSWANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRVIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKKELMAGR 1
2 EPKPEIYPCPSCCLAFSSQKFLSQHVERNHSSQNFPGPSARKLLQSENPCPGDQNQEQQYSDPSSCNDKTKGQEIKERSKLLNKRTRQRQILRAFTSPPKGQMGSSRVGERMMKEEFRTGQKANPGNTGKLFVGVEISRIAK
VKYGECGQGFSDKSDVVIHQRTHTREKP
YVYRgCGQGFSIKSNLLRHQRIHTGEKP
>PRDM7_calJac Callithrix jacchus (marmoset) genome Prim gene 12 GAS8+ chr20 one frameshift in repeat area chr20 terminus
0 MSPERSQEESPEGDTGRTEQKPM 0
0 VKDAFKDISMYFSKEEWAEMGDWEKTRYRNMKRNYNALITI 1
2 GLRATRPAFMCHRRQAIKLQVDDTEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 VKPPGMAFRVGQSKHQK 0
0 GMPKASFGNESSLKKLSGTANVLNTSGPEQAQKPVSPPGEASTSGQHSRLKL 1
2 ELRRKDTEEKMYSLRERKGLAYKEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 yCEICQNFFIDSCAAHGPPTFVKDSAVDKGHPNHAALSLPPGLRIGPSGIPQAGLGVWNEASDLPLGLHFGPYEGRVTEDEEAASSGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDKSWANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRVIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKKELMAGR 1
2 ESKPEIHPCPSCCLAFSSQKFLSHHVERNHSSQNFPGTSTRKLLQPENPCPGKQKEEQQYFDPCNSNDKTKGQETKERSKLLNIRTWQREMARAFSNPPKGQMGSSRVEERMMEEESRTGQKVNPVDTGKLFVGVGISRIAK
AKYGECGQGFSDMSDVTGHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSQKSALLSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSQKSHLLSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCTECGRGFSQKSVLLSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCTECGRGFSRKSNLLSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSRKSALLSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRKCGRGFSQKSNLLSHQGTHTGEKP
YVCTECGRGFSQKSHLLSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRKCGRGFSQKSNLLSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSFKSALLRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSRKSHLLSHQGTHIGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSRKSNLLSHQRIHTGEKP
YVRREDE.....................
>PRDM7_tarSyr Tarsius syrichta (tarsier) ABRT011082008 Prim pseu -- gas8+ double frameshift in exon 5, ABRT010499286
0 0
0 1
2 GLRAPRPAFMCHRKRAIKPLVDDTEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 0
0 GMPRAPLSIVSSLKELSEMANLLNTSDSEQAWKPVSPSREASTSEQHSRKKL 1
2 EFRKKEIEVNMYSLRERKDCAYKEVNEPQDDDYL 1
2 YCEQCQNFFIDSCATHGIPTFINDSAVDKGHPNRSALSLPPGLRIGPSGIPQAGLGVWNEASELPLGLHFGPYEGQITDDEEAANSGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDKSWANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRIIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKKELMAGR 1
2
>PRDM7_micMur Microcebus murinus (lemur) ABDC01433247 Prim gene 8 gas8+ weak coverage last exons corrected for two frameshifts
0 MSPEKSQEESPEEDTERTERKPM 0
0 vKDAFKDISIYFTKEEWAEMGDWEKTRYRNVKRNYNALITI 1
2 GLRATRPAFMCHRRQAIKLQVDDTEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 VKPPWMALRVEQRKHQK 0
0 GMPKASFSNESSLKELSRTANLLNASGSEQAQKPVSPSGEASTSGQHSRLKL 1
2 ELRKKETERKMYSLRERKGHAYKEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 YCEKCQNFFIDSCAAHGPPTFVKDSAVDKGHPNRSALSLPPGLKIRPSGIPQAGLGVWNEASELPLGLHFGPYEGQVTEDEEAANSGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDDSWANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDEEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCQVIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKEELTIRQ 1
2 EPKPEIHPCPSCSLAFSSQKFLSQHVKHTHSSQISPRTSGRKHLQPENPCPGDQNQEQQHSDPHSCNDKAKDQEVKERPKPFHKKTQQRGISRAFSSPPKGKMGSCREGKRIMEEEPRTGQKVGPGDTDKLCAAGGISRISR
VKYGDSGQSFSDKSNVIIHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSQKSDLLKHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSQKSHLLRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSQKSDLLIHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSCKSHLLIHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSCKSSLLIHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSRKSDLLIHQRTHTGEKP
CVCRKGE
>PRDM7_otoGar Otolemur garnettii (galago) genome Prim gene 7 GAS8+ good coverage
0 MSPEKSQEESPEEDTERTERKPM 0
0 VKDAFKDISIYFTKEEWAEMGDWEKTRYRNVKRNYNALITI 1
2 GLRATRPAFMCHRRQAIKLQVDDTEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 VKHPWMAFRMEQSKRQK 0
0 ILKKCMLSFNMHLKELSGPASLPNISGSEQHQKHMSSPREASTSGQHSGRKS 1
2 DLRIKEIEVRMYSLRERKGHAYKEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 yCEKCQNFFIDNCAVHGPPTFVKDTAVEKGHPNRSVLSLPSGLGIRTSGIPQAGFGVWNEASDLQLGLHFGPYEGQVTEDEEAANSGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDESQGNWMR 2
1 YVNCARDEEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRVIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKKELTAGQ 1
2 EPKPEIHPCPSCSLAFSTQKFLSQHVERTHPSQISQGTSGRKNLRPQTPCPRDENQEQQHSDPNSRNDKTKGQEVKEMSKTSHKKTQQSRISRIFSCPPKGQMGSSREGERMIEEEPRPDQKVGPGDTEKFCVAIGISGIVK
VKNRECVQSFSNKS
NLRHQRTHTGEKP
YMCRDCGRGFSHKSSLFRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRDCGRGFSLKANLLTHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRDCGQGFSQKAHLLRHQRTHTGEKP
YMCRDCGQGFSRKAYLLTHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRDCGQGFSQKAHLLTHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRDCGRGFSHKSSLFRHQRTHTGEKP
YICRDCG
>PRDM7_tupBel Tupaia belangeri (tree_shrew) AAPY01316756 noDet
0 MRRYKSPEESPEGDAGRTEWKPT 0
0 VKDAFKDISVYFSKEEWAQMGEWEKIRYRNVKRNYTTLIAI 1
2 GLRAPRPAFMCHRKLAVKPHMDDAEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 0
0 1
2 KMYSLRERKCGTYKEVHEPQDDDYL 1
2 yCEKCQNFFIDSCSAHGPPIFVKDSAVDKGSLNRSVLSLPPGLRIAPSGIPEAGLGVWNAATDLPLGLHFGPYEGQITEDEEAANSGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDESCANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRVIRPGCELLVWYGEEYGQELGIKWGSKWKKSLWQGE 1
2 EPRPEIHPCLSCSLAFSSQKFLNQHVEHNHSCQRSLRTS
QSSLIRHQRTHTGEKP
YLCGECGRGFSRQSHLIIHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSLQSNLIIHQRTHTGEKP
YGCRECGRGFSQQSSLIRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSRHSSLIIHQRTHTGEKP
YLCGECGRGFSRQSHLIIHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSQQPQLIIHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFRCQSHLIIHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSQQPHLIIHQRTHTGEKP*VCRKGE
>PRDM9_oryCun Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) genome Glir gene 8 other Un0161 exon 2 ttt to tt restores frame; ZNF717+ DCAF4+ YAP1+ PRDM9- qTer
0 MSAAAPAEPSPGADAGQARGKPE 0
0 VQDAFRDISIYFSKEEWAEMGEWEKIRYRNVKRNYCALVAI 1
2 GLRAPRPAFMCHRRLAVRARADDTEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 VKPPWMAFRTEHSKHQK 0
0 GMPRLPVNNESSLKELSGTANLLKTTGSEEDQKPSFPPKETRTSGQHSTRKL 1
2 GLRRKNIEVKMYSFRKRKSQAYKECSEPQDDDYL 1
2 YCEKCQNFFLDSCAVHGPPIFVKDSAVDKGHPNRSVLSLPPGLRIGPSGIPEAGLGVWNEASDLPLGLHFGPYEGQITEEEEAANSGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDRSWANWMR 2
1 YVNCARNDEEQNLVAFQYHKQIFYRTCQVIKPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKEELTAGR 1
2 EPKPEIHPCPSCSLAFSSHKFLSQHMERSHSSQIFPGAPARNHLQPANPCPGKEHQKLSDPQSWNDKNEGQDVKEKSRFSSKRTRQKAISRSFSSLPKGQVETSREGERMIEEEPRIGQELNPEDTGKSSVGAGLSRIAG
VKYRDCRQGLSDKSHLINGQRAHTGEKP
YACRECERGFTVKSNLISHQRTHTGEKP
YACRECGRGFTVKSALTTHQRTHTGEKP
YACRECGRGFTVKSHLISHQRTHTGEKP
YACRECGRGFTVKSALITHQRTHTGEKP
YACRECGQGFTVKSNLISHQRTHTGEKP
YACRECGRGFTQKSHLINHLRAHTGEKP
YACRECGRGFTVKSDLISHQRTHTGEKP
YACRVDE.....................
>PRDM7_oryCun Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) genome Glir gene 4 other synteny novel
0 0
0 1
2 GLRAPRPAFMCHRRLAVRARADDTEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 VKPPWMAFRTEHSKHQK 0
0 GMPRLPVNNESSLKELSGIANLLNTTGSEEDQKPSFPPKETRTSGQHSTRKL 1
2 GLRRKNIEVKMYSFRKRKSQAYKECSEPQDDDYL 1
2 YCEKCQNFFLDSCAVHGPPIFVKDSAVDKGHPNRSVLSLPPGLRIGPSGIPEAGLGVWNEASDLPLGLHFGPYEGQITEEEEAANSGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDRSWANWMR 2
1 YVNCARNDEEQNLVAFQYHKQIFYRTCQVIKPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKEELTAGR 1
2 EPKPEIHPCPSCSLAFSSHKFLSQHMECSHSSQIFPGAPARNHLQPANPCPGKEHQKLSDPQSWNDKNEGQDVKEKSRFSSKRTRQKAISRSFSSLPKGQVETSREGERMIEEEPRIGQELNPEDTGKSSVGAGLSRIAG
VKYRDCRQGLSDKSHLINGQRAHTGEKP
YACRECGQSFTVKSNLISHQRTHTGEKP
YACRECGRGFTQKSHLIRHQRTHTGEKP
YACRECGQSFTWKSNLISHQRTHTGEKP
YACRVDE.....................
>PRDM7_ochPri Ochotona princeps (pika) AAYZ01312269 Glir gene -- noDet dubious fragment, no orthologous terminal exon
0 0
0 1
2 1
2 0
0 1
2 1
2 yCEMCQNFFIESCAVHGSPTFVKD GHPHRSVLSLPSGLRIGPSGIPEAGLGVWNETTDLPLGLHFGPYEGQVTEEEEATNSGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNRYEYVDGKDPSQANWMR 2
1 YVNCARNDEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRAVRQGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKEELTAGR 1
2
>PRDM7_ratNor Rattus norvegicus (rat) P0C6Y7 Glir gene 10 PDCD2 chr1 FM103467 single transcript from body fat
0 MNTNKPEENSTEGDAGKLEWKPK 0
0 VKDEFKDISIYFSKEEWAEMGEWEKIRYRNVKRNYKMLISI 1
2 GLRAPRPAFMCYQRQAIKPQINDNEDSDEEWTPKQQ 1
2 VSSPWVPFRVKHSKQQK 0
0 ETPRMPLSDKSSVKEVFGIENLLNTSGSEHAQKPVCSPEEGNTSGQHFGKKL 1
2 KLRRKNVEVNRYRLRERKDLAYEEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 YCEKCQNFFIDSCPNHGPPVFVKDSVVDRGHPNHSVLSLPPGLRIGPSGIPEAGLGVWNEASDLPVGLHFGPYKGQITEDEEAANSGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGQDESQANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHRKIFYRTCRVIRPGRELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKMKKGFTAGR 1
2 ELRTEIHPCFLCSLAFSSQKFLTQHVEWNHRTEIFPGASARINPKPGDPCPDQLQEHFDSQNKNDKASNEVKRKSKPRHKWTRQRISTAFSSTLKEQMRSEESKRTVEEELRTGQTTNIEDTAKSFIASETS
RIERQCGQCFSDKSNVSEHQRTHTGEKP
YICRECGRGFSQKSDLIKHQRTHTEEKP
YICRECGRGFTQKSDLIKHQRTHTEEKP
YICRECGRGFTQKSDLIKHQRTHTGEKP
YICRECGRGFTQKSDLIKHQRTHTEEKP
YICRECGRGFTQKSSLIRHQRTHTGEKP
YICRECGLGFTQKSNLIRHLRTHTGEKP
YICRECGLGFTRKSNLIQHQRTHTGEKP
YICRECGQGLTWKSSLIQHQRTHTGEKP
YICRECGRGFTWKSSLIQHQRTHTVEK.
>PRDM7_musMus Mus musculus (mouse) Q96EQ9 Glir gene 12 PDCD2 chr17 CN723438 eight transcripts, four from retina
0 MNTNKLEENSPEEDTGKFEWKPK 0
0 VKDEFKDISIYFSKEEWAEMGEWEKIRYRNVKRNYKMLISI 1
2 GLRAPRPAFMCYQRQAMKPQINDSEDSDEEWTPKQQ 1
2 VSPPWVPFRVKHSKQQK 0
0 ESSRMPFSGESNVKEGSGIENLLNTSGSEHVQKPVSSLEEGNTSGQHSGKKL 1
2 KLRKKNVEVKMYRLRERKGLAYEEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 YCEKCQNFFIDSCPNHGPPLFVKDSMVDRGHPNHSVLSLPPGLRISPSGIPEAGLGVWNEASDLPVGLHFGPYEGQITEDEEAANSGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGQDESQANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHRKIFYRTCRVIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKMKKGFTAGR 1
2 ELRTEIHPCLLCSLAFSSQKFLTQHMEWNHRTEIFPGTSARINPKPGDPCSDQLQEQHVDSQNKNDKASNEVKRKSKPRQRISTTFPSTLKEQMRSEESKRTVEELRTGQTTNTEDTVKSFIASEIS
SIERQCGQYFSDKSNVNEHQKTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTQNSHLIQHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTQKSDLIKHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTQKSDLIKHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTQKSVLIKHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTQKSVLIKHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTAKSVLIQHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTAKSNLIQHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTAKSVLIQHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTAKSVLIQHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTQKSNLIKHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGWGFTQKSDLIQHQRTHTREK.
>PRDM7_musMol Mus molossinus (wild_mouse) GU216230 Glir gene 11 noDet full length deposit
0 MNTNKLEENSPEEDTGKFEWKPK 0
0 VKDEFKDISIYFSKEEWAEMGEWEKIRYRNVKRNYKMLISI 1
2 GLRAPRPAFMCYQRQAMKPQINDSEDSDEEWTPKQQ 1
2 VSPPWVPFRVKHSKQQK 0
0 ESSRMPFSGESNVKEGSGIENLLNTSGSEHVQKPVSSLEEGNTSGQHSGKKL 1
2 KLRKKNVEVKMYRLRERKGLAYKEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 YCEKCQNFFIDSCPNHGPPLFVKDSMVDRGHPNHSVLSLPPGLRISPSGIPEAGLGVWNEASDLPVGLHFGPYEGQITEDEEAANSGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGQDESQANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHRKIFYRTCRVIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKMKKGFTAGR 1
2 ELRTEIHPCLLCSLAFSSQKFLTQHMEWNHRTEIFPGTSARINPKPGDPCSDQLQEQHVDSQNKNDKASNEVKRKSKPRQRISTTFPSTLKEQMRSEESKRTVEELRTGQTTNTEDTVKSFIASEIS
SIERQCGQYFSDKSNVNEHQKTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTAKSNLIQHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTQKSVLIQHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTQKSDLIKHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTAKSNLIQHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTEKSSLIKHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGWGFTAKSNLIQHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTQKSSLIKHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTAKSNLIQHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGWGFTQKSNLIKHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGWGFTQKSDLIQHQRTHTR.EK
>PRDM7_criGri Cricetulus griseus (hamster) AFTD01086355 no out-of-frame continuation
0 MSCTRNTNKQEGNSPAGDAERLEWKPK 0
0 VKDEFKDISIYFSKEEWAEMGEWEKIRYRNVKRNYKMLISI 1
2 GLKAPRPAFMCYQRQAFKPQMDDSEDSDEEWTPKQQ 1
2 GSPPWVPFRVKHTKKQK 0
0 ETQRIPLNKESNVKEVSGSENLLSTSGSEHVQKTVFSPGEGNASGQHTGQKP 1
2 ELRRKNVEVKMYSLRERKDLAYEEVNEPQDDDYL 1
2 YCEKCQNFFINSCPSHGPPIFVKDSMVDRGHPNCSVLSLPPGLRIGPSGIPEAGLGVWNEASDLPVGLHFGPYKGQITDDEEAANSGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGQEESQANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRVINPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIQWGRKNKKGFATGR 1
2 ELRTEIHPCLLCSLAFSSPKFLSQHVQWNHRTQIFPGASSTINSKPGDPHPDQLQEQQHFNSHNKNDKARSLEVKGKSKPMHKWTRQISTAFPSTLKGHMRSEENKKTMEVLRTGQKTNTEDTIKSFIGSEIS
RIERKCGQYFSDKSNVNEHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTQKSHLIRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTQKSNLIRHQRTHTGERP CVCLFKKDKKASVNKTTPQQSQKDKCSL* 0
>PRDM7_dipOrd Dipodomys ordii (kangaroo_rat) genome Glir gene -- noDet dubious fragment, no orthologous terminal exon
0 0
0 1
2 GLKAPRPVFMCHRRQAIKPQVDDTDDSDEEWTPGRQ 1
2 0
0 1
2 elRTKEVKMRMYSLRERKSYAYEEISEPQDDDYL 1
2 yCEQCQNFFINSCTVHGPPIFVRDNVVDKGHYDRSVLSLPPGLRIRQSSIPEAGLGVWNEESDLPLGLHFGPYEGQITEDEDAANSGYSWM 0
0 ITKGRNCYVYVDGKDKSQANWMR 2
1 YVNCARYDEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRVIKAGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKRELTAgr 1
2
>PRDM7_speTri Spermophilus tridecemlineatus (squirrel) AAQQ01308561 Glir gene -- noDet plus exon by exon traces
0 0
0 1
2 GFRAPRPAFMCHQRQTIKLQMDDTEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 0
0 LKPEVLLSNESSLKELSGTANLLNTSGSEQVQKPVSPLREASASRQHSRRKL 1
2 ELRTKEVEVKMYSLRERKGHAYKEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 yCDKCQNFFMDSCPVHGPPTFIKDSVVNKDHSNHSTLSLPLGLRIGPSSIPEAGLGVWNEATDLPLGLHFGPYRGQITEDEEAANSGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDESQANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRVIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKKELSAGR 1
2 EPKPEIHPCPSCSLAFSSQKFLSQHVDRSHPSQIFPGTSMRKKLIPGDSSPRDQLQEQQHPDPHGWNDKARGQEVQGSLKPTHKGTRQRGISSPPKGQMGRSEESERMMEDDLKADQEINPEDTDKILVGVEMSRI
-
>PRDM9a_bosTau Bos taurus (cattle) NW_003053109 Laur gene 7 noDet chr1
0 MSQNRSPEERTKGDAGRTEWKLT 0
0 AKDAFKDISIYFSKEEWAEMGEWEKTGYRNVKRNYEVLIAI 1
2 GLRATQPAFMHHRRQVIKPQGDDTEDSDEEWTPQHQ 1
2 GKPSRKAFRMEHRKHQK 0
0 GKSRGPLSKVSSLKKLQGAAKLLNTSGSKWAQKPANPPRETRTLEQHSRQKV 1
2 ELRRKETDMKRYSLRERKGHVYQEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 YCQECQNFFIDSCDAHGPPTFVKDSAVEKGHANRSVLTLPPGLSIKLSGIPEAGLGVWNEASHLPLGLHFGPYEGQITDDKEAINSGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNSYEYVDGKDTSLaNWMR 2
1 YVNCARHYEEQNLVAFQYHGQIFYRTCQVVRPGCELLVWYGDEYGEKLGIKCESRGKSMFAAGr 1
2 ESKPKIHPCASCSLAFSSQKFLSQHVQHNHPSQTLLRPSARDYLQPEDPCPGSQNQQQRYSDPHSPSDKPEGREVKDRPQPLLKSIRLKRISRASSYSPRGQMGASGVHERITEEPSTSQKPNPEDTGKLFMGAGVSGIIK
VKYGECGQGSKDRSSLITNQRTHTGEKP
YVCGECGQSFNQKSTLITHQRTHTGEKP
YVCGECGRSFNQKSTLITHQRTHTGEKP
YVCGECGRSFSQKSTLIKHQRTHTGEKP
YVCGECGQSFNQKSTLITHQRTHTGEKP
YVCGECGQSFNQKSTLITHQRTHTGEKP
YVCGECGRSFSRKSTLITHQRTHRGEKL
CLQGV......................
>PRDM9b_bosTau Bos taurus (cattle) DAAA02065087 Laur gene 5 noDet chrU aaaaa fixed to aaaaaa in exon 2 KRAB SSXRD SET C2H2
0 MSPNRSPENSTEGDAGRTEWKPM 0
0 AKDAFKDISIYFTKEEWAEMGEWEKIQYRNVKRNYEALIAI 1
2 GFRATQPGFMHHGRQVLKSQVDDTEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 GKPSGMAFRGEPSKHPK 0
0 RLSRGPLNKVSSLKKLPGAAKLLKKSGSKQAQKPVPPPREARTPGKHPRHKV 1
2 ELRRKETEVKRYSVRERKGHVYQEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 YCEECQNFFIDSCAAHGPPTFVKDSAVEKGHANRSALTLPPGLSIRPSGIPEAGLGVWNEASDLPLGLHFGPYEGQIIYNEEDSNSGYCWL 0
0 VTKGRNSYEYVDGKDTSLANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVALQYHGQIFYRTCRVVRPGCELLVWYGDEYGEELGIKQDKRGKSKLSAQR 1
2 AKMHPCASCSLAFSSQKFLSQHVQRNHPSQTLLRPSARDHLQPEDPCPGNQNQQQRYSDPHSPSDKPEGRKAKDRPQPLLKSIKLKRISRASSYSPRGQVGRSGVHERITEEPSTSQKLNPEDTGKLFMGAGVSGIIK
VKYRECGQGSKDRSSLITHERTHRAEAL
CLRRVWAKLQSEVPLLVMHQRTHTGEKL
YVCGECGKSFSQKSPLIRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCGECGKSFSQKSPLIRHQRTHTGKKP
YVCRECGRSFSDKSH.HTPEYTHRGEAL
HLRGVWA.....................
>PRDM9c_bosTau Bos taurus (cattle) XM_002699750 Laur gene -- noDet chrX GO353654 4-cell embryo transcript no zinc downstream despite 43k bp
0 MSPNRSPENSTEGDAGRTEWKPM 0
0 AKDAFKDISIYFTKEEWAEMGEWEKIRYRNVKRNYEALIAI 1
2 GFRATQPGFMHHRRQVLKPQVDDTEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 GKPSGMAFRGERSKHQK 0
0 RLSRGPLNKVSSLKKLPGAAKLLKKSGSKQAQKPVPPPREARTPGKHPRHKV 1
2 ELRRKETKVKRYSVRERKGHVYQEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 YCEECQNFFIDSCAAHGPPTFVKDSAVEKGHANRSALTLPPGLSIRPSGIPEAGLGVWNEASDLPLGLHFGPYEGQIIYNEEDSHSGYCWL 0
0 VTKGRNSYEYVDGKDTSLANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVALQYHGQIFYRTCRVVRPGCELLVWYGDEYGEELGIKQDKRGKSKLSAQR 1
2
>PRDM9d_bosTau Bos taurus (cattle) genome Laur gene 9 noDet chrX proximal tandem
0 MRPNTSPEESTERDAGRTEWKPT 0
0 AKDAFKDISVYFSKEEWEEMGEWEKIRYRNVKRNYEALIAI 1
2 GFRATRPAFMHHRRQVIKLQADDTEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 GKLSSMAFRVEHNKHQN 0
0 TMSRAPLSKEFSLKELPGAAKLLKTSGSKQAQKLVPPPGKARTPGQHPRQKV 1
2 ELRRKETEVKRYSLRERKGHVYQEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 YCEECQSFFIDSCAAHGPPIFVKDCAVEKGHANRSALTLPPGLSIRESSIPEAGLGVWNEVSDLPLGLHFGPYEGQITDDEEAANSGYSWL 0
0 ITKRRNCYEYVDGKDTSLANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVALQYHGQIFYRTCQVVRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQDLGIKRESSRKSELAGPR 1
2 EPKPKIYPCASCCLSFSSQKFLSQHVQRNHPSQILLRPSIGDHLQPEDPCPGSQNQQQRYSDPHSLSDKPEGREPKERPHPLLKGPKLCIRPKRISTASSYPPKGQMGGSEVHERMTEEPSTSQKLNPEDTGKLFMEAGVSGIVR
VNYGDHEQGSKDRSSLITHEKIHTGEKP
YVCKECGKSFNGRSDLTKHKRTHTGEKP
YACGECGRSFSFKKNLITHKRTHTREKP
YVCRECGRSFNEKSRLTIHKRTHTGEKP
YVCGDCGQSFSLKSVLITHQRTHTGEKP
YVCGECGRSFNEKSRLTIHKRTHTGEKP
YVCGDCGQSFSLKSVLITHQRTHTGEKP
YVCGECGQSFNEKSRLTIHKRTHTGEKP
YACGDCGQSFSLKSVLITHQRTHTGEKP
YVCMECE.....................
>PRDM9e_bosTau Bos taurus (cattle) genome Laur gene 9 noDet chrX distal tandem
0 MRPNRSPEESTEGDAGRTEWKPM 0
0 AKDAFKDISIYFSKEEWEEMGEWEKIRYRNVKRNYEVLITI 1
2 GFRAARPAFMHHRRQVIKPQVNDIKDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 GKPFSMAFRVEHSKHQK 0
0 GMSRAPLSKESSLKELPGAAKLLKTSGCKQAQKLVPPPRKARTPEQHPRQKV 1
2 ERRRKETGVKRYSLREREGLVYQEVSEPLDDDYL 1
2 YCEECQSFFIDICAAHRPPTFVKDCAVEKGHANCSALTLPPGLSIRLSGIPEAGLGVWNEASDLPLGLHFGPYEGQITDDKEAAHSRYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDTSLANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVALQYQGQIFYRTCQVVRPGCELLVWYGDEYGWDLSIKQDSRGKNKLAAGR 1
2 EPKPKIYPCASCCLSFSSQKFLSQHVQRNHPSQILLRPSIGDHLQPEDPCPGSQNEQQRYSDPHSLSDKPEGREPKERPHPLLKGPKLCIRLKRISTASSYPPKGQMGGSEVHERMTEEPSTSQKLNPEDTGKLFMEAGVSGIVR
VKYGEHEQDSKDKSSLITHEKIHTGEKP
YVCTECGKSFNWKSDLTKHKRTHSEEKP
YACGECGRSFSFKKNLIIHQRTHTGEKP
YVCGECGRSFSEKSNLTKHKRTHTGEKP
YACGECGQSFSFKKNLITHQRTHTGEKP
YVCGECGRSFSEKSRLTTHKRTHTGEKP
YVCGDCGQSFSLKSVLITHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRSFSVISNLIRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECEQSFREKSNLVRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCMECE.....................
>PRDM9e_oviAri Ovis aries (sheep) genome Laur pseu -- noDet chr 18 cow has PDRM7 pseudogene; sheep GAS8 is on sheep chr14
0 0
0 1
2 GLRAP PPFMYHRRQVIKPQVDDIEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 0
0 1
2 ELRRKETEMKIYSLQKRKGHMYQEVSDPQDDNYL 1
2 ycEKCQNF INSCAAHGPPTFVKDCVVEKGHASCSALtLSPGLSIRPSGIPEAGLRVWNEASDLPLGLHFGPYKGQITDDEEVANSRYFWL 0
0 2
1 YVNCAQDDEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFS TCWVVRPGCELLVWYRDEYGQELSIK GSRHKSELTVRR 1
2
>PRDM9d_oviAri Ovis aries (sheep) genome Laur gene -- noDet chr1 near end chr1
0 0
0 1
2 GLRATRLAFMHHCRQVIKPQVDDIEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 0
0 1
2 1
2 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDTSLANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVALQYQGQIFYRTCQVVRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQDLGIKRDSSGKSELAAGR 1
2
>PRDM9c_oviAri Ovis aries (sheep) genome Laur pseu 4 noDet chr5 middle of 108,514,869 bp
0 0
0 1
2 GLRATRLAFMHHCRQVIKPQVDDIEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 0
0 GMSKALVSNKSSLKEMPGASKLLKTRGPKQAQIPVPAPREPSTSEQHPRQKV 1
2 1
2 HGLPTLVKDCAVEKGHANHSALSLSPGSSIRPSGIPEAGLGVWNKVSDLLLGLHFGSYVGQITDDEEAAKSGYSWL 0
0 2
1 YVNGAQD KEQNLVAFLTHRQIFY TCRVVRPGCELLVWYRDTYSQELSIKCGSRWKSELTASR 1
2 PMCSCSLAFSSQKFLSQHVKCNHPSQILLKTSARDRLQPEDPCPGNPNQQQQYSDLHSWSDKPESRESKEKPQPLLKSIRLRRISRASSYSSRGQMGGFRVHKRMREEPSTGKEVSPEDAGKLFMGEGVSRIMR
VKYGDCG
GSKDRSSLMTHQRTHTGENP
YVCREYE.SFSEKSSLIKHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECWQSFGRKSTLITHQRMHTREKP
CVCRECGRSFSKKSTLITHQRTHTGQKP
>PRDM9b_oviAri Ovis aries (sheep) genome Laur pseu 2 noDet chrX not tandem: 62 mbp separation
0 MSPNRSPENSTEGDAGRTEWKPM 0
0 AKDAFKDISIYFTKEEWAEMGEWEKIRYRNVKRNYEALIAI 1
2 GFRATQPAFMHHHRQVIKPQVDDTEDSEEEWTPRQQ 1
2 GKPSGMAFRGERSKHQK 0
0 RLSRGPLNKVSSLKKLPGAAKLLKKTGSKQAQKPVPPPREARTPGQHPRHKV 1
2 ELRRKETEVKRYSLRERKGHVYQEVSELQDDDYL 1
2 yCEECQNFFIDSCAAHGPPTFVKDSAVEKGHANRSALTLPPGLSIRPSGIPEAGLGVWNEASDLPLGLHFGPYEGQVIYNEEASHSGYSWL 0
0 VTKGRNSYEYVDGKDTSLANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVALQYHGQIFYRTCQVVRPGCELLVWYGDEYGEELGIKQDSRGKSKLSAQR 1
2 ELKPKIHPCASCSPAFSSQKFLSQYVQPNHPSQILLRPSARDHLQPEDPCPGNQNEQQ YSDPHSPSDKPEGCKAKERPPWLLKSMSVRISMASSYSPKGQMRGSETHYRMTEEPSTSQKLNPEDIGKLFMGTGVSGIIK
IKYEECGQVSKDRSSLITHEGTHTREQS
YVCRECGQSFSVKSSLIRLQRTHTGEKP
Y...........................
>PRDM9a_oviAri Ovis aries (sheep) genome Laur gene 9 noDet chrX not tandem
0 MSPNRSPENSTEGDAGRTEWKPM 0
0 AKDAFKDISIYFTKEEWAEMGEWEKIRYRNVKRNYEALIAI 1
2 GFRATQPAFMHHHRQVIKPQVDDTEDSEEEWTPRQQ 1
2 GKPSGMAFRGERSKHQK 0
0 GMSRGPLSKVSSLKKLPGTTKLLKTSGSKQAQKPVPSSREARTSG HTRQKV 1
2 ELGRKETDMKRYSLRERKGHVYQEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 yCQECQNFFINSCDAHGPPTFVKDSAVEKGHANRSALTLPPGLSIRLSGIPEAGLGVWNEASHLPLGLHFGPYEGQITDDKEAVNSGYSWL 0
0 2
1 YVNCARHYEEQNLVAFQYHGQIFYRTCQVVRPGCELLVWYGDEYGEKLGIRCESRGKSMLAAGR 1
2 EPKPKIHPCASCSLSFSSQKFLSQHVQRSHPSQILLRPSPRDHLQPEDPCPGKQNQQQRYSDPHSPSDKPEGQEPKERPHPLLKGPKLCIRLKRISTASSYTPKGQMGGSEVHEKMTEEPSTSQKLNPENTGKLFMEAGVSGIVR
VKYGEHEQGSKDKSSLITHERIHTGEKP
YVCKECGKSFNGRSNLTRHKRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGQSFSLKSILITHQRTHTGEKP
YVCGECGQSFSEKSNLTRHKRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGQSFSLKSILITHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRSFSVKSNLTRHKMTHTGEKP
YVCGECGQSFSQKPHLIKHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRSFSAMSNLIRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRSFSAMSNLIRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCREC......................
>PRDM9d_munMun Muntiacus muntjak (muntjac) AC216498 Laur gene 4 noDet frameshift exon 9 no syntenic loci; identities: 92%b 89%a 90%c
0 MRPNRSQEESTEGNAGRTERKPT 0
0 GKDAFKDISVYFSKEEWEEMGEWEKIRYRNMKRNYEALIAI 1
2 GFRATQPTFMHHRRQVIKSQVDDTEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 GKPSSMAFRVEHSKNQK 0
0 RMSRAPLSNESGLKELPGAAKSLKTSDSKQARNPVPHHRKARTPGQLPRQKV 1
2 ELRRKETGVKRYSLRERKGHVYQEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 YCEECQNFFINSCAAHGPpTFVKDCAVEKGHANRSALTLPHGLSIRLSGIPDAGLGVWNKVSDLALGLHFGPYKGQITDNEEAANSGYAWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDTSWANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHGQIFYRTCQVVRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQDFGIKRNSRGKSELAAGR 1
2 EPKPKIHPCASCSLTFSSQKFLSQHIQCSHPPQTLLRPSERDLLQPEDPCPGNQNQQQRYSDPHSPSDKPEGHEAKDRPQPLLKSIRLKRISRASSCSPRGQMGGSGVHERMTEEPSTSQKLNPGDTGTLLTGAGVSGIMK
VKYGECGQGSKDRSSLSTHERTHTGEKP
YVCRECGQSFSGKPVLIRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCMECGRSFSAKSVLMTHHRTHTGEKP
YICRECGQSFSQKIHLIRHQRIHTGE.P
SVFRECE.....................
>PRDM9c_munMun Muntiacus muntjak (muntjac) AC154919 Laur gene 15 noDet no syntenic loci AC204173 99% identical
0 MRPNRSPEESTEGDAGRTEQKPT 0
0 AKDAFKDISVYFSKEEWEEMGDWEKIRYRNMKRNYEVLIAI 1
2 GFRATRPDFMHHRRQVIKPQVDDTEDSDEEWAPRQQ 1
2 GKPSSVAFRVEHSKHQK 0
0 RMSRAPLSNESGLKELPGAAKPLKTSGSKQAQNPVPHHRKARTPGQLPRQKV 1
2 ELRRKETGVKRYSLRERKGHVYQEVSKPQDDDYL 1
2 YCEKCQNFFIDSCAAHGPPTFVKDCAVEKGHANRSLLTLPPGLSIRLSGIPDAGLGVWNEASDLPLGLHFGPYEGQITDDEEAANSGYAWL 0
0 ITKGRDCYQYVDGKDTSWANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHGQIFYQTCQVVRPGCELLVWCGDEYGQDLGIKRNSRGKSELVAGR 1
2 EPKPKIHPCASCSLAFSSQKFLSQHIQRSHPSQTLLRPSERDLLQPEDPCPGNQNQRFSDPHRPSDRPQPLLKSIRLKRISRASSYSPRGQMGGSGVHELMTEEPSTSHKLNPEDTGTLLMGAGVSGIMR
VTYGECGQGSKDRSSLTTHERTYTGEKP
YVCGECGRSFCQKAHLITHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGQSFSRNSLLIRHQRIHTGEKP
YVCGECGRSFRDKSNLISHRRTHTGEKP
YVCGECGQSFSDKSNLIRHQRTHAGEKP
YVCGECGRSFNRKSHLITHQRTHTGEKP
YACRECGQSFSQKSILITHQRTHTGEKP
YACRECG.SFSQKSILITHQRTHTGEKP
YVCGECGRSFSQKSLLITHQRTHTGEKP
YVCMECGRSFSQKTHLITHQRTHTGEKP
YVCGECGRSFSQKSLLITHQRTHTGEKP
YVCGECGRSFSQKSLLITHQRTHTGEKP
YICMECGRSFSQKTHLITHQRTHTGEKP
YVCGKCGQSFSDKSNLISHKRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRSFNRKSLLITHQRTHT.E.P
YVCRECE.....................
>PRDM9b_munMun Muntiacus muntjak (muntjac) AC218859 Laur gene 13 noDet no syntenic loci
0 MRPNTSPEESTEGDAGRTERKPT 0
0 AKDAFKDISVYFSKEEWEEMGDWEKSRYRNMKRNYEVLIAI 1
2 GFRATRPDFMHHRRQVIKPQVDDTEDSDEEWAPRQQ 1
2 GKPSSMAFRVEHSKHQK 0
0 RMSRAPLSNESGLKELPGAAKPLKTSGSKQAQNPVPHHRKARTPGQLPRQKV 1
2 ELRRKETGVKRYSLRERKGHVYQEVSKPQDDDYL 1
2 YCEECQNFFIDSCAAHGPPTFVKDCAVEKGHANRSALTLPPGLSIRLSGIPDAGLGVWNETSDLPLGLHFGPYEGQITDDEEAANSGYAWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYQYVDGKDTSWANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHGQIFYRTCQVIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQDLGIKRNSRGKSELATGR 1
2 EPKPKIHPCASCSLAFSSQKFLSQHIQRSHPSQTLLRPSERDLLQPEDPCPGSQNQRYSDPHSPSDKPEGQEAKDRPQQLLKSIRLKRISRASSYSPGGQMGGSGVHERMTEEPSTSQKLNPEDTGTLLTGAGVSGIMR
VTYGECWKGSKDRSSLTTHERTHTGEKP
YVCGECGQSFHHGSVLIRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCGECGRSFSQKSVLIRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCGECGRSFSQKSVLIRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCGECGRSFSQKAHLITHQRTHTGEKP
YVCGECGRSFSQKTHLISHKRTHTGEKP
YVCGECGRSFCQKSALIRHQRAHTGEKP
YVCGECGRSFIQKSDFIRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGQSYSDKTVLITHERTHTGEKP
YVCGECGRSYSDKTVLITHERTHTGEKP
YVCGECGRSFLWKSALIRHQRTHTGEKP
YACGDCGRSFNQKSNFIRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCGECWRSFSQKSSSSDTRGHTQGRRP
VCRECG..SFSQKSHLISHQRTHTEEKP
YVCRECE.....................
>PRDM9a_munMun Muntiacus muntjak (muntjac) AC225653 Laur gene 7 noDet unordered contigs htgs; no synteny tag stop instead of aag K
0 MRPNRSPEESTEGDAGRTEQKPT 0
0 AKDAFKDISVYFSKEEWEEMGEWEKIRYRNVKRNYEALIAI 1
2 GFRATRPDFMHHCRQVIKPQVDDTEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 GKPSSMAFRVKHSKHQK 0
0 GMSRAPLIKESSLKELLGAAKLMKTSGSKQAQNPVPHPRKARTPGQHPRQKV 1
2 ELTRKETGVKRYSLRERKGHVYQEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 YCEECQNFFIDSCAAHGLPTFVKDCAVEKGHANRSALTLPPGLSIRLSGIPDAGLGVWNEESDLPLGLHFGPYEGQITDDEEAANSGYAWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYQYVDGKDTSWANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHGQIFYRTCQVIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQDLGIKRNSRGKSELAAGR 1
2 EPKPKIHPCASCSLAFTSQKFLSQHIQRSHPAQTLLRPSERNLLQPEHPCPGSQNQRYSDPHSLSDKPEGQEAKDRPQPLLKSIRLKRISRASSYSPGGQMGGSGVHERMKDEPSTSQKLNPEDTGTLLTGAGVSGIMR
VTYGECGKGSKDRSSLTTHERTHTGEKP
YACRECGRSFRQKSDFITHQRTHTGEKP
YVCGQCGRSFGRKFALIRHQRIHTGEKP
YVCRECGQSFSQKTHLSSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCGECGRSFSQKSVLIRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCQECGRSFSDKSNLISHKRTHMGEKP
YVCRECGRSFIRKSVLIRHQRTHTGE.P
YVCRECE.....................
>PRDM7_bosTau Bos taurus (cattle) genome Laur pseu -- GAS8+ missing C2H2
0 MSPNRSPEESIEGDTGRTEWKPT 0
0 AKDAFKDISIYFCKEEWAQMG WEKIRYRNVKRNYEALITL 1
2 1
2 0
0 1
2 1
2 0
0 2
1 1
2
>PRDM7_turTru Tursiops truncatus (dolphin) ABRN01441536 Laur gene 9 gas8+ no useful synteny
0 MSTDRWPEDSTEGDAGRTAWKPT 0
0 VKDAFKDISIYFSKEEWTEMGEWEKIRYRNVKKNYEALVTL 1
2 GLRAPRPAFMCHRRQAIKAQVGDPEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 VKPSWVAFRVEHSKHQK 0
0 AVPPVPLSNESSLKKLPGAAQLQKASGPAQAQSPAPPPGAASTSAWHTRQKL 1
2 ERRAKQIEVKMYSLRERKGHVYQEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 yCEKCQNFFIDSCAAHGAPTFVKDSAVEKGHPNRSALTLPPGLSIRPSGIPEAGLGVWNEASDLPLGLHFGPYEGQITEDEEAANSGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDTSWANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDEEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRVVRPGCELLVWYGDEYSQELGIPWGSGWKSQLVaGR 1
2 DPKPKIQPCGSCSLAFSSQKILSQHVECSHPSQVLPRTSARDRVQPEDPCPGYQNRQQQYSDPHSWSNKPECQEVKERSKPLLKRIRLGRISRAFSSSPKGQMGSSRAHERMMEAGPSTGQKVNPEATGKLLIGAGVSRVVK
VKYRSSGQGSKDRSSLTKHQRTHTGEKP
YVCGECGRDFSLKSDLIRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCGECGRDFSLKSGLISHQRTHTGEKP
YVCGECGRDFSQKSGLIRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCGECGRDFSLKSGLISHQRTHTGEKP
YVCGECGRDFSQKSGLIRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCGECGRDFSLKSGLITHQRTHTGEKP
YVCGECGRDFSQKSNLITHQRTHTGEKP
YVCGECGRDFSRKSSYI...........
>PRDM7_lamPac Lama pacos (llama) scaffolds traces
0 0
0 TFKDISIYFSKEEWTEMGEWEKIRYRNVKRNYEALITI 1
2 GLRAPRPAFMCHRRKAIKPQVDDTEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 0
0 GMPRGPLSNQSSLKELSGTAKPLKTSGSGQAQKPFPPLGEASTSGRHSRQKL 1
2 ELRRKESQVKMYSLRERKGHAYQEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 0
0 ITKGRKCYEYVDGKDKYWANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRVIRPGCELLVWYGEEYGQELGIKWGSKWKKSLWQGE 1
2 EPKIYLCPSCSLAFSSQKFLSQHVKHNHPSQILPRTAAGRHLEPEDPCPGNQNEQQQHSDQHSWNDKPEGQEAKERSKPFLKRIRLRRISGAFSYSHKGQMGNSRVHDRMIEEEPSTGQKVNPKDTGKLFTWAGVSRTVE
VNYGEYGQGCKDTSHLTTHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTRKSNLTIHQREHTTGEK
>PRDM7_susScr Sus scrofa (pig) FP476134 Laur gene 9 GAS8+ unordered HTGS not wgs misassembly or inversion; not in genome browser
0 MRPDRRPEESPDPAAGSTERKAA 0
0 ATDAFKDISIYFSKEEWTEMGEWEKIRYRNVKRNYEALTTI 1
2 GLRAPRPAFMCHRRQAIKPQVDDTEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 VKPCRVAFRVEHNKHQK 0
0 SDSRVPLSNKSSLKELLTTAEVPETSGSEQAQEPVSPPGEASTSRRRSGQEL 1
2 ARRRKDTEARMYSLRERKGHAYQEVGEPQDDDYL 1
2 yCEKCQNFFIDSCAAHGPPTFVKDSAVDKGHPNRSALTLPPGLRIRPSGIPEAGLGVWNEAHDLPLGLHFGPYEGQVTEDEEAANSGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDKSWANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRVVRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKKELTAGI 1
2 EPKPKIHPCPSCSLAFSSQRFLSQHVERSHPSQSLPRASARRGLQPEGPCPDNQQQQQPYPDPHSWDGTSESQDVKEGSKPFLERRRLRKTSRASSYAPEGQMRSSRVRERMTEEEPSAGQKVNPEDTGTLFTVAGES
GILRVENRGYGPDSGLTRHPRTHTGEKP
HVCSECGRGFSVKSHLIRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSVKSHLIRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSVKSSLITHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSVKSHLIRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSEKSSLVTHQRTHTGEKP
FVCRECGRGFSVKSSLVTHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSVKSNFITHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSEKSSLVTHQRTHTGEKP
YVCREGE.....................
>PRDM7_canFam Canis familiaris (dog) genome Laur pseu 5 GAS8+ frameshift fixed to 6 ZNF; synteny MNS1 K1F1B intervening CDH3 oddity
0 0
0 1
2 1
2 VKPSWVAFRMEQSKHQK 0
0 GIPRVPLSNKSSLKELSETAKLLNTSSPEQGQKSVSLPGKASTSGHHTRQKL 1
2 ELRRKDVEVKMYSLQERKGLAYQEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 yCEK QTFFIDSCTVHGPPTFVKDSEVDKGQPNHSALTLPPGLRIRTSSIPQAGLGVWN ASDLPLGLHFGPYKGQITEDEEAANSGYSCL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDkSWANWMR 2
1 YMNCARDDEEQS LVAFQYHRQIFYRTPGHQASCELLVWYGDEYSQELGIKWGSKWKSELTAGK 1
2 EPNPEIHPCPSCSL AFSSQKFLSQHLEHNHPSQILPRISVREHFRPKDPCPGCQNQQQQQHSDPQRWNDRAKGQEGKERFKPLPKSIRQRRISRAFSTPCKGQTTCEGIVKEEPSAGSQKLNPEDTGKLFKGVGMTRIIR
VKYRGCGRGFNDRSHLSRHQRTHTGENP
YVCRECGRGFIHRTNLIIHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGtGFIQRSNLSIHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTQRSTLNEHQRTHTEEKP
YVCRECGRSFTRRSTLITHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRSFT.................
KRSTWDPWVAQRFGACLWP.........
>PRDM7_felCat Felis catus (cat) genome Laur gene 11 GAS8+ two contigs GAS8 implied by downstream CAD1
0 MEPSPASESARGQPGGPGTTSPLRFPEQSAERGSRKARWKPT 0
0 AKDAFKDISIYFSKEEWTEMGDWEKIRYRNVKRNYEALMTI 1
2 gLRAPRPAFMCHRRQAIKPQVDVTEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 VKPSWVASRVDQNKQHK 0
0 GTHRVPLSKESSLKDFSETAKLLNTSGSEQGQKPVSLPGEASTSGHHSRRKL 1
2 ELRRKEIGVKMYSLRERKGFAYQEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 yCEKCQNFFIDSCAVHGPPTFVKDNAVGKGHPNRSALTLPPGLRIRPSSIPEAGLGVWNEASDLPLGTHFGPYEGQITEDEEAANSGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDNSWANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRVIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKSELSTGK 1
2 EPQPDIHRCPSCSLAFSSQKFLSQHVECKHSSQSLPQISARKHFQPENPCPGDQNQQQQQHSDPHSWNDKAKCQEVKERSRPLLKSIKQRRISRAFSTPCKGQMGSSRVCEGMVEEGPSMGQNLNSEDTGKLFMGVGMSRIVR
IKNRGCEQGFNDRSHFSRHQRTHKEEKP
SVCNEFRRDFSHKSALITHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTQRSNLFRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTQRSDLFTHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTRRSNLFTHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTRRSHLFTHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTQRSNLFTHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTQRSDLFRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTQRSHLFTHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTQRSNLFRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTWRSNLFTHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRKDGQGFTNKLHLSYQRT
NVATTHSIPQL
>PRDM7_ailMel Ailuropoda melanoleuca (panda) GL193502 Laur gene 6 GAS8+ first three exons from different contig ACTA01106867
0 MGPLPASESEQSLPGGPSTMSLNTSPEETPERDSGRTGWKPT 0
0 AKDAFKDISIYFSKEEWTEMGDWEKIRYRNVKRNYEALITI 1
2 GLRAPRPAFMCHRRQAIKPQVDDTEDSDEEWTPRRQ 1
2 VRPSWVAFRMEQSKHQR 0
0 GIPRAPLRNESSLKELSETAKLLNTSGSELGQKPVSLPGEASTSGHDSLQKL 1
2 GFRRKDVEVKMYSLRERKSLAYQEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 yCEKCQNFFIDSCAVHGPPTFVKDSAVDKGQPNRSALTLPPGLRIRPSGIPQAGLGVWNEASDLPLGLHFGPYEGQITEDEEAANSGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDNSWANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDEEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRVIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKSELAAGK 1
2 EPKPEIHPCPSCSLAFSSQKFLSQHLEHNHPSQILSRKSASEHFQQEDPCPGHQNQQQQQHSDPHRWNDKAKGQEVKERFKPLLKSIRQRRISRAFSSPCKGQTRSSTVCEGMVEEEPSAGQKLNPEETGKLFMGVGMSGIIR
VKYRGCGRDFSDRSHQSGHQRRHQKKP
SVCKKVKREFSHKSVLITHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTQRSNLIRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTQRSNLIRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTQRSSLIRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTLRPNLIGHQRTHTEALP
INYISTTKEQM
>PRDM7_musPut Mustela putorius (ferret) AEYP01035076 AEYP01035077 terminates early in C2H2
0 MRPRTASESEQGLPGGPSTGSVSGPPEETPERDSGRTGRKPP 0
0 AQDAFKDISVYFSKEEWTEMGDWEKIRYRNVKRNYEALITI 1
2 GLRAPRPAFMCHRRQATIPRVDDTEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 VRPSWVAFKMEQSKHQK 0
0 GVPRAPLSNESSLKELSETAKLLNTSGSEHDQKPVSHPGEASTSGHHSLRKL 1
2 ELRRKDVEVKMYSLRERKSLAYQEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 YCEKCQNFFIDSCAVHGPPTFVKDSAVDKGQPNRSALTLPPGLRIRPSGIPQAGLGVWNEASDLPLGLHFGPYEGQITEDEEAANSGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDNSWANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYRRQIFYRTCRVIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKSELTAEK 1
2 EPKPEIHPCPSCTLAFSSQKFLSQHLERNHPSQILPRISAGEHFQPEDPCPGEQNHQQQQHSDPQNWNDKAKGQDVKESFKPLLESIRQRKNSRAFPIPCEGQTGYEGIVEEEPSTGQKLNPEETGKLFMGVGMSRIIR
VKYRGSGQGFDDRSHLSRHQRTHKEEKP
SVGKEPRREFIHKSVLVTHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTQRSHLIRHQR
>PRDM9_pteVam Pteropus vampyrus (bat) ABRP01232219 Laur pseu 15 noDet frameshift ttt to tttt fixed in last zinc finger; no blastx synteny
0 0
0 1
2 1
2 vQPSWVAFGVEQSKHQK 0
0 AMPRVPLSNESSLKELSVIANPLKASGSEQNQQPVFPPGKASASRQHSRRKL 1
2 eLRRKGVEVKMDSLRERMGRVYQEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 yCEKCQNFFIDSCAAHGSPIFVKDSEVDIGHPNHSALTLPPGLRIGPSGIPEAGLGVWNEASNLPLGLLFGPYEGQVTEDEEAANSKYSwM 0
0 spKGETAEYV DGKDESRANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEDQNLVAFQFRRQIFYRTCRVIMPGCELLVWYGDEYGQGLGIKWGSKWKREFTAGR 1
2 EPKPEIHPCPSCSLAFSSRKFLSQHMKRSHPSQSLPGISARKHLQSKEPHPEDQSQQQQQQQHTDPCSWNDKAEGQEVKERSKPMLERNGQRKISRAFSKPPKGQMGSPRECERMMEAEPSTSQKVNPENTGKSSVGVGASRIVR
VKYGGCGHGFDDGSHFIRHQRTHSGEKP
FVCRECERGFNEKSSLTMHQRTHSGEKP
FVCREC.EGFSVKSSLIRHQRTYSGEKP
FVCRECEQGFNEKSSLTMHQRTHSGEKP
FFCRECEGFSVK.SSLIRHQRTHSGQKP
FVCRECKRGFTQKSHLITHQRTHSGEKP
FCRECER.GFTQKSHLIKHQRTHSGEKP
FVCRECA.....................
>PRDM7_pteVam Pteropus vampyrus (bat) ABRP01250178 Laur gene 7 GAS8+ 4 distal exons of GAS8+-; unique F sweep in zinc finger; 15 ZNF dotplot no CAD1
0 MRPDRSPEEAPEGDTRRTGCKPK 0
0 AKDAFKDISIYFSKEEWTEMGDWEKIRYRNVKRNYDALQAI 1
2 GLRAPRPAFMCRRRQAIKPQVDDSEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 0
0 AMPRVPLSNEPSLKELSVIANLLKASGSEQDQKPVFPPGKASASRQHSRQKL 1
2 GLRRKGVEVKMYSLRERTGRVYQEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 yCEKCQNFFIDSCAAHGSPIFVKDSEVDIRHPNRSALTLPPGLRIGPSGIPEAGLGVWNEASDLPLGLLFGPYEGQVTEDEEAANSGYSWL 0
0 QGKGRNCYEYVDGKDESRANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRVIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKRELTAGR 1
2 EPKPAIHPCPSCSLAFSGQKFLSQHMKRSHPSQSLPGISARKHLQSKEPHPEDQSQQQHNDPRSWNDKAEGQEVKERSKPLLERNRQRKIFRAFSKPPKGQMGSPREYERMMEAEPSTSQKVNPENTGKSSVGVGASRIVI
VKYGGCEHGFDDGSHLIMHQRTHSGEKP
FVCRECERGFSKKSNLITHQRTHSGEKP
FVCRECERGFTRKSSLITHQRTHSGEKP
FVCRECERGFTQKSHLITHQRTHSGEKP
FVCRECERGFSEKSSLIKHQRTHSGEKP
FVCRECERGFTRKSSLITHQRTHSGEKP
FVCRECERGFTQKSSLIKHQRTHSGEKP
FVCRECERGFTQKSSLIKHQRTHSGEKP
FVCRECERGFTQKSSLIKHQRTHSGEKP
FVCRECERGFTQKSSLITHQRTHSGEKP
FVCRECERGFTQKSHLITHQRTHSGEKP
FVCRECERGFSKKSNLITHQRTHSGEKP
FVCRECERGFTRKSLLITHQRTHSGEKP
FVFRECERGFTQKSSLITHQRTHSGEKP
FVCRECERGFTRKSYLITHQRTHSGEKP
FVGRECE.....................
>PRDM7_myoLuc Myotis lucifugus (bat) AAPE02062260 Laur gene 6 gas8+ TGA stop codon; CpG hotspot for R CGA; SXXRD implies missing KRAB no CAD1
0 0
0 1
2 1
2 0
0 AKSRAPLSNESSLKELSGTANLLTTSGSEQTQKTVPPPGEASTSGQHPRSKL 1
2 dLRRKEIEVKMYSLRERKCRVYQEISEPQDDDYL 1
2 YCEKCQNFFIDSCAVHGPPTFVKDSAVDKGHANRSALTLPPGLRIGPSGIPEAGLGVWNEECDLPVGLHYGPYEGQITEDEAIANSGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDTSQANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRVVRKGCELLVWYGEEYGQELGIKWGSKWKTEPVAGR 1
2 EPKPEIHPCPSCSVAFSSQTFLSQHGKRNHPSEILPGAPAGNHLQSEEPGPERQNQQQQQQTGPHGWNDKAEGQEVKGRSKPLLKRIRQRGTSRASFKPPNRHMGSSSERERIREEEPSTGQNVNHKNTGKLFVGVKRSKSVT
IKHGGCGQGFNDGSHIDTHQRTHSGEKP
YICRECGGFTHKSDL.IRHQRTHSQENP
YVCRECGRGFRDRSTLITHQRTHSGEKP
YVCRECGRGLTEKSTLITHQRTHSGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTRKSTLITHQRTHSGEKP
YVCRECGRGSRVKSNLIRHQRTHSGEK
SGVCIEGE....................
>PRDM7_equCab Equus caballus (horse) genome Laur gene 4 GAS8+ missing front exons, pre-terminal stop GAS8+- flanked right by EMR2-
0 0
0 1
2 1
2 VKPSWVAFRVEQSKQQK 0
0 RMRTAPLSNESRLKELSGTAKLLKTSSSEQVQKPVSPLGEASSSEQHSRRKL 1
2 ELRRKEVGVKMYSLRERKGHAYQEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 yCENCQNFFIDSCAAHGPPIFVKDSAVDKGHPNRSALTLPLGLRIRPSGIPEAGLGVWNEASDLPLGLHFGPYEGQITEDEEAANSGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDISWANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRVVRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKRELTAGR 1
2 EPKLEIHPCPSCSLAFSSQKFLSQHVERNHPSQILPGTSARNHLQPEDPSPGDQNQQQQHSDPHSWKDKAHSQEVKERSKPLLKKIRQRRIPRAFSYPPKGQMENFRMRERIMEEKPSIGRKVNPEDTGKLFLEMRMSRNVR
VQYGGCGRGFNDRASLIKHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECEQGFTQKSSLIAHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECEQGFSEKSHLIRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECEQGFSVKSNLIRHQRTHTGEKL
.FCREGK.....................
>PRDM7_sorAra Sorex araneus (shrew) AALT01000095 Laur gene 8 noDet no useful synteny; upstream spectrin, IgG; GAS8 contig has no sign of pseudogene
0 MSLNRPAEMNTQGKARKLMLKPM 0
0 SKDAFKDISMYFSKEEWAEMGDWEKIRHRNVKRNYEELISI 1
2 GLRAARPAFMSHRRQAIKTQLDDTEESDEEWTPNQQ 1
2 VKSLRVAFRAEQSKHQK 0
0 GRSRTPISNESSSKELSGTRTLLNTKCTKQAQKPLFPPGEASTSGHYSKPKL 1
2 ELRRKEPEVKMYSLRERKGRAYQEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 YCENCQNFFINKCSAHGSPIFVKDNAVAKGHSNRSALTLPHGLRIGPSGIPEAGLGIWNEASDLPLGLHFGPYEGQITNDEEAANSGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGVDESLANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDYEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRIIKPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKSELTADK 1
2 EPKPEIYPCPCCSLAFSNQKFLSRHVEHSHPSLILPGTSARTHPKSVNFCPGDQNQWQQHSDACNDKPDEPWNDKLENHKSKGRSKPLPKRMGQKRISTAFPNLRSSKMGSSNKHETIMDKINTGQKENPKDTYRVFAGIGMPRIIR
DKHVTLRRSFTNRSSPLTHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSQKSHLLTHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTDRSSLLTHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSLKSSLLRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSLKSSLLTHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFTDRSSLLTHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSLKSSLLTHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSRKSSLLRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCES.......................
>PRDM9a_loxAfr Loxodonta africana (elephant) genome Afro gene 12 noDet chr 153 novel synteny THEG+ MIER2+ PPAP2C PRDM9- ZNF699-
0 MSPARAAKKNPRGDVGSAGRTPT 0
0 aKDTFRDISIYFSKEEWAEMGEWEKFRYRNVKRNYEALVTI 1
2 GLRAPRPAFMCHRRQAIKAQVDNTEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 VKPPSVASRAEQSRHQK 0
0 GTPKALLGNESSLKEVSGTAILLNTTGSEQAQKPVSSPGEASTSDQPSRWKL 1
2 EPRRNEVEVKMYNLRERKGLEYQEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 yCEKCQNFFIDTCAVHGAPMFVKDSPVDRGHPNHSALTLPPGLRIGPSSIPKAGLGVWNEASELPLGLHFGPYEGQVTEDKEAANSGYSWL 0
0 ITKGKNCYEYVDGKDESWANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDEEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRTIQPDCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSRWKKELTSGR 1
2 EPKPEIHPCPSCRLAFSSQKFLSQHMKHSHPSPPFPGTPERKYLQPEDPRPGGRRQQRSEQHMWSDKAEDPEAGDGSRLVFERTRRGCISKACSSLPKGQIGSSREGNRMMETKPSPGQKANPEDAEKLFLGVGTSRIAK
VRCGECGQGFSQKSVLIRHQKTHSGEKP
YVCGECGRGFSVKSVLIKHQRTHSGEKP
YVCGECGRGFSVKSVLITHQRTHSGEKP
YVCGECGRGFSVKSVLITHQRTHSGEKP
YVCGECGRGFSQKSDLIKHQRTHSGEKP
YSCRECGRGFSRKSVLITHQRTHSGEKP
YVCGECGRGFSQKSNLITHQRTHSGEKP
YVCGECGRGFSRKSVLITHQRTHSGEKP
YVCGECGRGFSQKSNLITHQRTHSGEKP
YVCGECGRGFSQKSDLITHQRTHSGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSRKSNLITHQRTHSGEKP
YVCRECRRGFSVKSALI...........
GHGRRKCSKSAEPLHFPRVSRDQK....
>PRDM9b_loxAfr Loxodonta africana (elephant) genome Afro pseu 3 noDet approx seq after frameshift correction
0 0
0 1
2 1
2 0
0 GTPKVLLSNESSLKEVSGTAILLSTMGSEQAQKPVSSPGEASTSDQPSRRKQ 1
2 EPRRKEVEVNMYSLRERKGLVYQEVGEPQDDDYL 1
2 yCEKCQNFFIHTCAVHGAPMFVKDSHVDRGHLNHSALTLPPGLRIGPSSIPEAGLRVR EVSEQLLGLHIGPYEGQVTEDkEAAHSGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYKYVDGKDDPWANRMR 2
1 YVNCIQD KEQNLVAFQYHRQIFHWTCCTIRPGCELLVWYGDNYSQELGIKWGSR KKEL 1
2 EPKPEIHPCPSCPLAISSQKFLDQHTKHSHPSPPFPGTPERKHLQPEDPHPGGRRQQHSEQHLNDKAEDPETGDGSKPVFERARLVGGGAGGVSKVCSSLPKGQMGSSREGNRMMETEGQKVNPEDTEKLFLGVGISRLAK
VRCGEYGQGFSQKSVLIRHQRTYSGEEH
YVCGECGRGFSWKSQLTRHQRSHSWEKP
YVCRECGGFSVKSTLI............
GTGEGNAATIHLHLPS............
>PRDM7_loxAfr Loxodonta africana (elephant) genome Afro pseu 5 GAS8+ scaffold_57 several frameshifts; ZNF540 opposite strand upstream of N-terminus
0 0
0 1
2 GLRASHPAFTCHCMQAIKAQMDDTEDSNEEQTPRQq 1
2 VRPSWVAFRMEQSKHQR 0
0 GMLRVPRSNESSLKNLSGTSIMLSRAGSEQAQKLVLPPGKASTSDEHSRQKP 1
2 EHRRKGVEVKMYSF ERKGLVYQEIS PQDDDYL 1
2 YCEKCQNFFIDTCESHGVPTFVKNSTTDSGHPNHLALTPSSGLRTRPSSIPKAWLRLWNKAFELLLGLPFSPCEGQVIEDEAVDNSGYSWL 0
0 2
1 YVNGTQDEKEQNLVFFQYHRQIFYQTCYAVWPGCQLLVWYRDECGQELGIKWDNRGKKEFe 1
2 EPKPEAHPCPSCPLAFSSEKFLSQHMKHNHPSQSSPETPERKHLQPEDPHPGHQNQQQQQHSDPHRWNDKAEGQQTGDRSKPMFENIRQEVTSRAFSSLPKGQMVCSREGNRMMETEPSPGLKVNPEVTGKLFLGVESSRIAK
VKYRGCGRDFSDRSHQSGHQRRHQ
KKP
SVCKKVKREFSHKSVLITHQRTHSGEKS
YVCKESGRGFSAKSNLIRPRRTHTGEKP
YVCGERGG.FSVSGLII.HQRAHSPEKP
YVCREGRRGFGDKSSFIKHQRATLGEKS
YVCKESGRGFS.................
AKSNLIRPRRKKCRHDTTPHPQL.....
>PRDM7_echTel Echinops telfairi (tenrec) genome Afro pseu 5 noDet 2 frameshifts plus stop codon
0 0
0 1
2 GLRAPRPAFMCHHRPAAKGQVEDSEDSDEEWTPRQR 1
2 0
0 GMPGVSLRNESNLKVLSGTAILLTAAEPEQPH PGSPPGEATTSHEHLRQKV 1
2 epELRRRAVMMNSLRERKNLMYQEVSTPCDDNCL 1
2 YGERCHNFFIDTHIAHGATTFVKDS PMDRSNCSILPPGLRIGPSGIPEAGLGVWNEASELPLGLHFVPYEGQVTKDEAATNSGYSWM 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDKSWANwMr 2
1 1
2 EPKPEVNPCPSCPLALSSQQLKHSHPFQSLPGTPAEKHLQAEDFHPRGQKLHHFEHHIRNERAEGLETGDGSKPMLERTRLGKMSKTTYNSPKGQTRSSGETNRIREADLNPGQGVNAEDTRNLFLGIGISRIAK
VRCRECGHGFSVKSSLITHQRIHTGEKP
YVCSECGQGFSQKSVLIRHQRIHTGEKP
YICRECDRGFSRKSHLIKHQRTHSGEKP
YVCRECGQGFSQKSVLITHHRTHSGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSQKSDLIKHERTHS....
>PRDM7a_proCap Procavia capensis (hyrax) ABRQ01227339 Afro pseu 17 noDet frameshift and two stop codons in exon 10
0 0
0 AKDAFRDISIYFSKEEWAEMGEWEKSRYRNVKRNYEALVAI 1
2 GLRAPRPAFMCHRRQAIKAQVDNTEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 AKPRSVASREELRKPQK 0
0 GTPKALLGNESSLKEVSGTAILLNTTGSEQAQKPVSSPGEASTSDQPSRWKL 1
2 EPRRKEAEVKRYNLREGTNPAYQEVGDTQDDDYL 1
2 yCEKYQKFCTDVCPAHGALAFLKDLSVERGHPKHSALTLPPGLRIGASGIPEAGLGVWSEASELPPGLHFGPCERQVTKDNEAANRGYLWP 0
0 ITKGRSCSLYMDRKDESRANWMR 2
1 YVRHAGDKEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRPVQPGCELLVWPGAEDGQELGLQRGSRWKKELASQT 1
2 EARPEIHPCPSCPLAFSTPKFLSHHVKHSHPCQPFPGTLARRPLQPEDPHPGDRRQQHSEQPNWNDKAEGPEIGHVSRPVFEKTRQEGFSEARSSLPKGQMGRSREAERTTETQNSPGQKVNPEDTEILFLRGGISEIAK
VKCGECGQGFSRKSHLIRHQRTHSGMKP
YVCRECRRGFGVKSLLTRHQRTCSGMKP
YVCRECGQGFRWKSHLIRHQRTHSGEKP
FVCSECGRGFSVRSHLFTHQRTHSGEKP
YVCKECGRGFSVKSYLTTHQRTHTGEKP
YVCKECGRGFSWKSHLITHQRTHSGEKP
YVCRQCGRGFSVQSHLIIHQRTHSGDKP
YICRECGRDFTEKSSLIRHRRTHSGEKP
YVCRDCG*GFTRKSLLITHQRTHSGEKP
YVYRECGRGFSCKSYLISHQKTHLGEKP
YVCSDCGRGFSVKSQLVSHKRTHSGEKP
FVCREC*RGFSVKSSLISHQRTHSGEKP
FVCRECGRGFSVKSSLIKHQRTHSGEKP
YVCKECGRGFSQKSSLITHQRTHSGEKP
YVCRECGRGFGLKSYLITHQRTHTGEKP
YICRECG*GFSVKSSLITDQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRAFSKKSSLISHHRTHPAEAV
YVHRECG.....................
>PRDM7b_proCap Procavia capensis (hyrax) ABRQ01392668 Afro pseu 13 noDet CpG stop in ZNF1, 4aa insert exon 4, frameshift exon 5 c to cc, 4aa del exon 9 etc
0 0
0 AKEYFRDISMFFS*ERWVEMSESEKFCYRNMKRNCETTGAG 1
2 GIRVFHPAFMIHPRKTIKAQMDDSEDSDEDWTARQQ 1
2 AKPPSVASREELRKPQK 0
0 GPSRAPLRIKSSLKRVSEPAIVWSTADSEQAQERVQKPVLSRREASASDQPLRRKV 1
2 EPRRHEAEDKRYSLRGGTGPACQEVGEPQDDDYL 1
2 yCEECRNFFIDTCVAHGTPVFIKDISVERGHPNRLALTLPTGLRIGPSSIPDAGLGVWNEASELPPGLHFGPCEGQVTEDEEAANSGYSWL 0
0 VTKGRSCFEYVDGKNEALANWMR 2
1 YVRRARDTEERNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCCTVRPGCELLVWRGAEDSQALG----SRRTMELTSQK 1
2 EARPEIHPCPSCPLAFSTQKFLSYHVNHSHSSEPFPGTHARRHLPREDPRPGYERDQRSEQHNWNDSTGGPERDVSRP VIERTWEGEISEACSSLPRGHMGRSREGERMAETQSSPGLKVTLAK
VRWDEYGQGFGPKSHHITQQTKHSGKKP
CVCKECG*GFRVKSLLKSHQMTHSGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSVKSTLITHQRTHSGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSVKSFLISHQRTHSGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSWKSGLITHQRTHTGEKR
YVCRECGHGFNRPSRLIRHQRTHSGEQP
YVCRECGHGFNRRSQLIRHQRTHTGEQP
YVCRECGQGFSGKSGLNRHQRTHSGEKP
YVYKECGRGFSVKSTLIKHQRGHSGEKP
YVCKECGRGFSRNSGLITHQRTHSGEQP
YVCRECGRGFNQKSGVISHQRIHSGEKP
FVCGECGRRFSWQSNLITHQRTHSGEKP
FVCRECGRGFSAKTSLINHQRIH*GKKP YVCRDGG*
>PRDM7_dasNov Dasypus novemcinctus (armadillo) AAGV020462211 9 xena pseu TRAPP
0 0
0 AQDAFRDISTYFSREEWAEMGRWEKLRYRNVKRNYEALLAI 1
2 GLRAPRPAFMCHRKQSIKPQVDDAEDSDEEWTPRQQ 1
2 0
0 1
2 EPRRKGIDVKMYSLRERKGLAYEEVSEPQDDDYL 1
2 yCEKCQNFFIDSCTVHGPPIFVKDSAVDKGHPNRSALTLPSGLRIGPSGIPEAGLGIWNEASDLPLGLHFGPYEGQVTEDEEAANSGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNYYEYEDGKDKSWANWMR 2
1 YVNCAWDDKEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRTIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKKEFMTGT 1
2 ELKPEIHPCPSCPLAFSSEKFLSQHVRRHHPSQSFPAACAREHFQPQNPRPRGEEQQQHSDQCGWKDKAEGQETENRPKPLFERIKPMGSPRAFYNPPRGQMRSSREGKRMMEIQPSQDQKMNSE RGQLFLGVGIFKTEV
IKFGENRQDFSDKSDHTSHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSNNSHLTRHQRTHTGVKP
YVCRECGQGFSVKPALTKHQRTHTVEKP
yVCSECG GFSVKSTLITHQRTHTGEKP
CVCRECGRGFNNKPDLTKHQRTHTGEKS
YVCRECG GFSVKSTLIIHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSEKSNLTVHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFSEKSNLTVHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRSFSVKSTLITHQRTHTVEKP
YVCMKSEVVVSNKSHLNSHRRMKCGHRT PPPPQL
>PRDM7_choHof Choloepus hoffmanni (sloth) ABVD01893961 2 xena gene noDet 0 0
0 1
2 1
2 0
0 1
2 1
2 ycekcQNFFFENCAAHGPPTLLKDSAVGQGRPKHSALVLPPGLRLGPSGIPEAGLGVWNEASDLPLGLHFGPYEGQVTEDEEATNSGYSWL 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKDKSCANWMR 2
1 YVNCARDDEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRAIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKKELTAEK 1
2 GLKPEIHPCPSCPLAFSTEKFLSQHVQRNHPSQIFPVTYARKHLQPQDPRPGDQQQPQPHSDQCHCSDKAEDQETEKRSKPLFESTKQMGISRAYSSPPEGQMRSSREDKRTMEIEPSQDQKMNPEETRLFVGVGILKTAR
IKCGEYGQGFSVKPNLTTHQRTHTEEKP
YVCRECGRGFGQKPNLSRHQRTHTGEKP
YVCRECGRGFG.................
>PRDMx_monDom Monodelphis domestica (opossum) gene genome no GAS8 fragment KRAB SSXRD SET weak C2H2 domain
0 0
0 GEDAFKDISTYFSKKQWVKLKEWEKVRLKNVKRNYEAMIKI 1
2 GLSVPRPAFMCRGRQNKKVKVEESGDSDEEWIPKQL 1
2 VKTLRFPSRAKQRTHPK 0
0 1
2 DCRRKDVEVHIYSLRERKYQVYQEMWDPQDDDYL 1
2 yCEECQIFFLDSCPLHGPPTFVQDSAMVKGHPYCSAITLPPGLRIGLSGIPGAGLGVWNEASTLPLGLHFGPYKGKMTEDDEAANSGYSWM 0
0 ITKGRNCYEYVDGKEESCSNWMR 2
1 YVNCARDEEEQNLVAFQYHRQIFYRTCRVIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKRPLPELTGE 1
2 GKPGISLCPSTLWASPLIPSSINTRCSKQPP*VFLDSGTGKL*AGRSTAGPATSNRFQLLSDKETSPKEHPSSLWGKTKQVDRREKFSLPQSQQVRGKESSSGEDLSRIQGKSTRQTTMAFQERNR
KECE*GFTHQTNLVTHRWTHSGERP
YVCV*GFTQKLGFSPYTWTL* 0
>PRDMx_macEug Macropus eugenii (wallaby) ABQO010244377 ABQO010410412 ABQO011136158 ABQO010410657
0 0
0 GEDTYKDISMYFSKKQWMELREWEKIRLKNVKQNYEAMIKI 1
2 gFSAPRPTFMCHGKQNKEAKVEESGDFDEEWIRKQP 1
2 0
0 1
2 ECRRKEAEVHIYNLRERKYQVYQEIWDPQDDDYL 1
2 FCEECQTFFLETCAVHGPPKFVQDSVMVKGHPYCSAITLPPGLRIGLSGIPGAGLGIWNEASNLPLGLHFGPYEGQMTEDDEAANSGYSWM 0
0 2
1 YVNCARDEEEQNLVAFQYHRKIFYRTCQIIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGSKWKRPPITLT 1
2 espGIHVCPFCPLGSPLMHSQSTYAAQTSPQICLDSRTRNNYEPDQLLPPSSSCVSDKVEISQKQRPSSLCGKTKQVNLVEMLSLPQSPQVSKKSSSMDWDVSRIQGKSAKQTTQGFQKGDKKGFGS
YKCGEYKQGFTSKSVLNRHRQKHSGKKP
YVCEECGRGFTQVSNLTTHRQTHSGEKP
YVCEECGRGFARKLNLTTHRRTHSGEKP
YVCEECGRGFTQGSSLITHRRTHSGEKP
YVCEECGRGFAWKLNLTTHRRTHSGEKP
YVCKECGRGFTQGSSLITHRRTHSGEKP
YVCKECGRGFTQGSNLTTHRRTHSGEKP
YVCKECGRGFAWKSNLTTHRRTHSGEKP
YVCKECGRGFTQVSNLIAHRRTHSGEKF
YVYGQEFTWKSDLSTCR* 0
>PRDMx_sarHar Sarcophilus harrisii (tasmanian_devil) AFEY01386448 two distal frameshifts, syntenic -PSMC4
0 0
0 EEDSFKDISMYFSKKQWMELRDWEKVRFKNVKRNYEAMIKI 1
2 GLTASRPTFMCRGKQNRRAKVEESGDSDEEWMPKQL 1
2 VKASRFSSRLKQKTHLR 0
0 1
2 eCRKKDAAVHIYNLRERKYPIYQEIWDPQDDDYL 1
2 FCEECQTFFLETCAVHGPPKFVQDGAMIKGYPYCSAITLPPGLRIGLSGIPNAGLGVWNEGSNLPMGLHFGPYEGKSTEDDEAANSGYSWM 0
0 ITKGRNSYEYVDGKEESCSNWMR 2
1 YVNCAREEEEQNLVAFQYQRQIFYRTCRVIRPGCELLVWYGDEYGQELGIKWGRKWKRPLTGIT 1
2 tspGIHLCPSCPSDFSTHAFLSQQVPKQPSQGFLDSTTGSHGLGNLHPDQLLPPGYSCVSDKAETSRKEHPSTLWEKIKKVDLEEPASLPQRQHVREEESNLGEWDLSRIQGESVKLTSLALQEESQEGLGQ
YKCGEGKQRYSSKPGLIRHRQRTHSGEKC
YVCEECKRGFARRSYLNIHRRRHSGQKP
HVCEECKRGFADKSTLIRHRWTHSKEKP
YICEECKQGFTQKSYLIKHRWKHLGEKP
YVCKECKQRFTQRSYLNTHRWRHRQRS
LLCMRSAGEDLHRDHLIIHRWTHSGERP
YVCEECKGGFTQRSYLNTHTDGNVGKEEP
YVCEECR* 0
>PRDMxa_ornAna Ornithorhynchus anatinus (platypus) gene genome chrX5 fragment X5 +- 20577549 no iMet possible in first exon phase 2
0 0
0 1
2 1
2 0
0 1
2 RIGKKPQVRDFNLRKQKRKIYNENYRPEDDDYL 1
2 yCEICQTFFLEKCVLHGPPVFVQDLPVEKWRPNRSTITLPPGMQIKVSGIPNAGLGVWNQATSLPRGLHFGPYMGIRTKNEKESHSGYSWM 0
2 IVRGKNYEYLDGKDKAFSNWMR 2
1 YVNCARSEREQNLVAIQYQGEIYYRTCRVIPPGQELLVWYGLEYGRHLGILPNNNNPEP 1
2 ERAKARVRKSERIEKAMARVRKSEQIERAKARVRTSERIERAMATV RKSERIERAKVTVKKSEQIERAMGRVRKSERIERAKDMGRKKALGGLPRPCRGGLSDETQQRKGGGHEQLGQKPGPSEA RAGPAEGSATPRR
HCCDVCRKAFKRLSHLRQHKRIHTGEKP
LVCKVCRRTFSDPSNLNRHSRIHTGLRP
YVCKLCRKAFADPSNLKRHVFSHTGHKP
FVCEKCGKGFNRCDNLKDHSAKHSEDNSTPKP* 0
>PRDMxb_ornAna Ornithorhynchus anatinus (platypus) gene genome chrX5 tandem fragment slight frameshift taa to ta YVN exon X5 +- 20605294 20611704 no iMet possible in first exon phase 2 gg as expected
0 0
0 1
2 1
2 0
0 1
2 RSGKKPQVRDFNLRKQKRKMYTEESEPEDDDYL 1
2 yCEDCQTFFLEKCSVHGPPVFVQDCEAKRCQQNRSEVTLPPGLLIKMSGIPNAGLGVWNQATSLPRGLYFGPFVGIRKNNVKDSLSGYSWA 0
0 ILRGRNYEYLDGKNTSFSNWMR 2
1 YVNCPRTKYEQNLVAIQYHREIYYRTTPCDSTRSRVAGVVWRRVRSYLGIFWKSETPKS 1
2 ERPHSSGGSFAPSARSGGVKQRIWSKRRSAALQRTRERRNSTHDFPPKHEDTAARQDERQCPDRGRAKQRGVRKSEQIERAKAMGRKKALGGLSPPRRERLSDEAGQRKKSGHEQFWQKPGPSEAWAGPAEGSTIPRR
HCCDVCGKAFNRLSRLKQHKRVHTGEKP
LVCKICKRAFSDPSNLNRHAKRHTGEKP
FVCRVCGRSFNRSDNMNEHRWKHTSNNIIP NTGHMSATVVENASLCINRNYQIYKERATYL* 0
>PRDM7_danRer Danio rerio (zebrafish) Q6P2A1 transcript BC064665 no KRAB SSXRD or exon 5 but knuckle SET early ZNf C2H2 array
0 MSLSP 1
2 DLPPSEEQNLEIQGSATNCYSVVIIEEQDDTFNDQPF 1
2 YCEMCQQHFIDQCETHGPPSFTCDSPAALGTPQRALLTLPQGLVIGRSSISHAGLGVFNQGQTVPLGMHFGPFDGEEISEEKALDSANSWV 0
0 ICRGNNQYSYIDAEKDTHSNWMK 2
1 FVVCSRSETEQNLVAFQQNGRILFRCCRPISPGQEFRVWYAEEYAQGLGAIWDKIWDNKCISQ 1
2 GSTEEQATQNCPCPFCHYSFPTLVYLHAHVKRTHPNEYAQFTQTHPLESEAHTPITEVEQCLVASDEALSTQTQPVTESPQEQISTQNGQPIHQTENSDEPDASDIYTAAGEISDEI
HACVDCGRSFLRSCHLKRHQRTIHSKEKP
YCCSQCKKCFSQATGLKRHQHTHQEQEKNIESPDRPSDI
YPCTKCTLSFVAKINLHQHLKRHHHGEYLRLVESGSLTAETEEDHT
EVCFDKQDPNYEPPSRGRKSTKNSLKGRGCPKKVAVGRPRGRPPKNKNLEVEVQKIS
PICTNCEQSFSDLETLKTHQCPRRDDEGDNVEHPQEASQ
YICGECIRAFSNLDLLKAHECIQQGEGS
YCCPHCDLYFNRMCNLRRHERTIHSKEKP
YCCTVCLKSFTQSSGLKRHQQSHLRRKSHRQSSALFTAAI
FPCAYCPFSFTDERYLYKHIRRHHPEMSLKYLSFQEGGVLSVEKP
HSCSQCCKSFSTIKGFKNHSCFKQGEKV
YLCPDCGKAFSWFNSLKQHQRIHTGEKP
YTCSQCGKSFVHSGQLNVHLRTHTGEKP
FLCSQCGESFRQSGDLRRHEQKHSGVRP
CQCPDCGKSFSRPQSLKAHQQLHVGTKL
FPCTQCGKSFTRRYHLTRHHQKMHS* 0
>PRDM7_salSal Salmo salar NM_001173912
0 MESEWKSGGEEESGSEGERTPSSSHRDP 1
2 VCVSEQMKRAWLRQMNLRSRARVGYTEEEELRDEEYF 1
2 FCEECKSFFIEECELHGPPLFIPDTPAPLGAPDRARLTLPPGLEVRTSAIPGAGLGVFNHGHSVTQGTHYGPYEGELTDKELDMESGYSWV 0
0 IYKSKQRDEYIDGKRDTHSNWMR 2
1 YVNCARSEDEQNLVAFQYRGGILYRCCKPIAVGEELLVWYGEKYARDLGIVFDFLWDKKCSAR 1
2 GVNESSQSQIFSCSGCLFSFTAQTYLYKHIKRCHREECVRLPRSGGIRAETLAPPSGSQRCSTTPDRTPITLLTQKHRDTGKPAP
HHCSQCGKSFRRSGDLKVHQRTHTGERP
YHCSQCGKRFSVSGHLKTHQRTHTGERP
YHCSQCGKSFCRSGDLKVHQRTHTGERP
YHCSQCGKRFSVSRHLKRHQHIHTGERP
YHCSQCGKSFSASWSVKRHQITVHSVGRVSVSQEA* 0
>PRDM7_oncMyk Oncorhynchus mykiss testis FP324541 CR372724
0 mTPSSSHRDPVC 1
2 VSEQRKRAWLKQVNLCSRARVRVGYTEEEELREEDYF 1
2 FCEECKSFFIEECELHGPPLFIQDTPAPLGAPDRARLTLPPGLEVRTSAIPGAGLGVFNYGHSVTQGTHYGPYEGELTDTELAMESGYSWV 0
0 IYKSKQSDEYIDAKRETHSNWMR 2
1 YVNCARNEEEQNLVAFQYRGGILYRCCKPLAVGEELLVWYGEEYARDLGIIFDFLWDRKSSAR 1
2 GVNESSQSQIFSCSGCPFSFTAQIYLYKHTKRCHREEYVRLPRSGGIRSETLAPPSGSQRCSTTPDRTPITLLTQKHQDTGKPRP
HHCSQCGKSFHRSGDLKVHQRTHTGERP
YHCSQCGKRFSVSGNLKTHQRIHTGERP
YPCSQCGKSFHRSDLKVHQRTHTGEKP
YHCSQCGKRFSVSGNLKTHQRIHTGERL
YPCSQCGKSFHRSELKVQQRTRPGKKTISLFPVWE*
>PRDM7_ictPun Ictalurus punctatus FD367165 FD063496 C-terminus missing second gene present
0 MKTEAKDGGTEGI 2
1 VKKETLELSISNHGNSFHIIPEVVSIKEEEADVKDFL 1
2 YCEVCKSVFFSKCEVHGPALFIADSPVPMGVADRARQTLPPGLEIQKSGIPDAGLGVFNKGETVPVGAHFGPYQGELVDKEEAMNSVYSWV 0
0 IYMSRQCEKYIDAKREVHANWMR 2
1 YVNCAHSDGEQNLVAFQYRGGILYRCCRPINPGQELLVWYEEKYASDVGPIFAQLWNIKCSLSGKVHT
Other genes of relevance
It is instructive to consider certain closely related placental KRAB, ZNF and PRDM genes that may have some connection to the origin of PRDM7 and PRDM9. Nomenclature is very unsatisfactory in these gene families, as can be seen from lack of correspondence between gene name and intronation which is exceedingly well conserved in metazoa. For example, HKR1 a conventional ZNF family member, is egregiously misnamed. The methylase component is exceedingly old with clear antecedents in bacteria. Evidently gene duplications in an early intronless stem eukaryote were subsequently intronated randomly in different paralogs and shuffled into various larger proteins. Within PRDM*, the gene tree is (((PRDM7/9,PRDM11),(PRDM4,PRDM10)),PRDM6) with others only related by a PR (SET) domain.
A set of fragmentary sequences from murid rodents is also of some comparative interest. These include common strain variants of lab mouse as well as close relatives. Only the terminal zinc finger array is available for most of these. While these are likely PRDM7 (rather than PRDM9 which rodents never had), it is not possible to decisively establish this with GAS8 synteny in any of the rodents (or lagomorphs) currently the subject of a genome project.
>PRDM11_homSap Homo sapiens (human) 511 aa knuckle, SET, no early zinc finger or array 0 MLKMAEPIASLMIVECRACLRCSPLFLYQREK 0 0 DRMTENMKECLAQTNAAVGDMVTVVKTEVCSPLRDQEYGQPC 2 1 SRRPDSSAMEVEPKKLKGKRDLIVPKSFQQVDFW 1 2 FCESCQEYFVDECPNHGPPVFVSDTPVPVGIPDRAALTIPQGMEVVKDTSGESDVRCVNEVIPKGHIFGPYEGQISTQDKSAGFFSWL 0 0 IVDKNNRYKSIDGSDETKANWMR 2 1 YVVISREEREQNLLAFQHSERIYFRACRDIRPGEWLRVWYSEDYMKRLHSMSQETIHRNLAR 1 2 GEKRLQREKSEQVLDNPEDLRGPIHLSVLRQGKSPYKRGFDEGDVHPQAKKKKIDLIFKDVLEASLESAKVEAHQLALSTSLVIRKVPKYQDDAYSQCATTMTHGVQNIGQTQG EGDWKVPQGVSKEPGQLEDEEEEPSSFKADSPAEASLASDPHELPTTSFCPNCIRLKKKVRELQAELDMLKSGKLPEPPVLPPQVLELPEFSDPAGKLVWMRLLSEGRVRSGLCGG* 0 >PRDM4_homSap Homo sapiens (human) 801 aa knuckle, SET, early zinc and array 0 MHHR 2 1 MNEMNLSPVGMEQLTSSSVSNALPVSGSHLGLAASPTHSAIPAP 1 2 GLPVAIPNLGPSLSSLPSALSLMLPMGIGDRGVMCGLPERNYTLPPPPYPHLESSYFRTILP 1 2 GILSYLADRPPPQYIHPNSINVDGNTALSITNNPSALDPYQSNGNVGLEPGIVSIDSRSVNTHGAQSLHPSDGHEVALDTAITMENVSRVTSPISTDGMAEELTMDGVAGEHSQIPNGSRSHEPLSVDSVSN NLAADAVGHGGVIPMHGNGLELPVVMETDHIASRVNGMSDSALSDSIHTVAMSTNSVSVALSTSHNLASLESVSLHEVGLSLEPVAVSSITQEVAMGTGHVDVSSDSLSFVSPSLQMEDSNSNKENMATLFTI 1 2 WCTLCDRAYPSDCPEHGPVTFVPDTPIESRARLSLPKQLVLRQSIVGAEV 1 2 GVWTGETIPVRTCFGPLIGQQSHSMEVAEWTDKAVNHIWK 0 0 IYHNGVLEFCIITTDENECNWMMFVRKAR 2 1 NREEQNLVAYPHDGKIFFCTSQDIPPENELLFYYSRDYAQQI 1 2 GVPEHPDVHLCNCGKECNSYTEFKAHLTSHIHNHLPTQGHSGSHGPSHSKERKWKCSMCPQAFISPSKLHVHFMGHMGMKP HKCDFCSKAFSDPSNLRTHLKIHT 12 GQKN YRCTLCDKSFTQKAHLESHMVIHTGEKN LKCDYCDKLFMRRQDLKQHVLIHTQ 21 ERQ IKCPKCDKLFLRTNHLKKHLNSHEGKRD YVCEKCTKAYLTKYHLTRHLKTCKGPTS SSSAPEEEEEDDSEEEDLADSVGTEDCRINSAVYSADESLSAHK* 0 >PRDM10_homSap Homo sapiens (human) 1160 aa knuckle, SET, early zinc and array 0 MDSKDESSHVWPTSAEHEQNAAQ 0 0 VHFVPDTGTVAQIVYTDDQVRPPQQVVYTADGASYTSVDGPEHTLVYIHPVEAAQ 0 0 TLFTDPGQVAYVQQDATAQQ 0 0 ASLPVHNQVLPSIESVDGSDPLATLQTPLGRLEAKEEEDEDEDEDTEEDEEEDGEDTDLDDWEPDPPRPFDPHDL 1 2 WCEECNNAHASVCPKHGPLHPIPNRPVLTRARASLPLVLYIDRFLGGVFSKRRIPKRTQFGPVEGPLVRGSELKDCYIHLK 0 0 VSLDKGDRKERDLHEDLWFELSDETLCNWMMFVRPAQNHLEQNLVAYQYGHHVYYTTIKNVEPKQELK 0 0 VWYAASYAEFVNQKIHDISEEERK 1 2 VLREQEKNWPCYECNRRFISSEQLQQHLNSHDEKLDVFSR 2 1 TRGRGRGRGKRRFGPGRRPGRPPKFIRLEITSENGEKSDDGTQ 0 0 DLLHFPTKEQFDEAEPATLNGLDQPEQTTIPIPQLPQETQSSLEHEPETHTLHLQPQHEESVVPTQSTLTADDMRRAKRIR 0 0 LELQ 0 0 NAALQHLFIRKSFRP FKCLQCGKAFREKDKLDQHLRFHGREGNCP LTCDLCNKGFISSTSLESHMKLHSDQKT YSCIFCPESFDRLDLLKDHVAIHINDGY FTCPTCKKRFPDFIQ 00 VKKHVRSFHSEKI YQCTECDKAFCRPDKLRLHMLRHSDRKD FLCSTCGKQFK 00 RKDKLREHMQRMHNPEREAKKADRISRSKTFKPRITSTDYDSFT FKCRLCMMGFRRRGML 00 VNHLSKRHPDMKIEEVPELTLPIIKPNRD YFCQYCDK 00 VYKSASKRKAHILKNHPGAELPPSIRKLRPAGPGEPDPMLSTHTQLTGTIATPP VCCPHCSKQYSSK 00 TKMVQHIRKKHPEFAQLSNTIHTPLTTAVISATPAVLTTDSATGETVVTTDLLTQAMTELSQTLTTDYRTPQGDYQRIQYIPVSQSASGLQQPQHIQLQVVQVAS 0 0 ATSPHQSQQSTVDVGQLHDPQPYPQHAIQVQHIQVSEPTASAPSSAQ 0 0 VSGQPLSPSAQQAQQGLSPSHIQGSSSTQGQALQQQQQQQQNSSVQHTYLPSAWNSFRGY 1 2 SSEIQMMTLPPGQFVITDSGVATPVTTGQVKAVTS 0 0 GHYVLSESQSELEEKQTSALSGGVQVEPPAHSDSLDPQTNSQQQTTQYIITTTTNGNGSSEVHITKP* 0 >PRDM15_homSap Homo sapiens (human) 1507 aa knuckle, SET, early zinc finger and intronated array 0 MPRRRPPASGAAQFPERIATRSPDPIPLCTFQRQ 0 0 PRAAPVQPPCRLFFVTFAGCGHRWRSESKPGWISRSRSGIALRAARPP 1 2 GSSPPRPAAPRPPPPGGVVAEAPGDVVIPRPRVQPMRVARGGPWTPNPAFREAESW 2 1 SQIGNQRVSEQLLETSLGNEVSDTEPLSPASAGLRRNPALPP 1 2 GPFAQNFSWGNQENLPPALGKIANGG 1 2 GTGAGKAECGYETESHLLEPHEIPLNVN 0 0 THKFSDCEFPYEFCTVCFSPFKLLGMSGVEGVWNQHSRSASMHTFLNHSATGIREAGCRKDMP 0 0 VSEMAEDGSEEIMFI 12 WCEDCSQYHDSECPELGPVVMVKDSFVLSRAR 2 1 SWPASGHVHTQAGQGMRGYEDRDRADPQQLPEAVPAGLVRRLSGQQLPCRSTLTWGRLCHLVAQGR 2 1 SSLPPNLEIRRLEDGAEGVFAITQLVKRTQFGPFESRRVAKWEKESAFPLK 0 0 VFQKDGHPVCFDTSNEDDCNWMMLVRPAAEAEHQNLTAYQHGSDVYFTTSRDIPPGTELRVWYAAFYAKKMDKPMLKQAGSGVH 1 2 AAGTPENSAPVESEPSQWACKVCSATFLELQLLN 12 EHLLGHLEQAKSLPPGSQSEAAAPEKEQDTPRGEPPAVPESENVATKEQKKKPRRGRKPKVSKAEQPLVIVEDKEPT 12 EQVAEIITEVPPDEPVSATPDERIMELVLGKLATTTTDTSSVPK 21 FTHHQNNTITLKRSLILSSRHGIRRKLIKQLGEHKR VYQCNICSKIFQNSSNLSRHVRSH 12 GDKL FKCEECAKLFSRKESLKQHVSYKHSRNE 00 VDGEYR YRCGTCEKTFRIESALEFHNCRT 12 DDKT FQCEMCFRFFSTNSNLSKHKKKHGDKK FACEVCSKMFYRKDVMLDHQRRHLE 12 GVRRVKblueLEAGGENLVRYKKEP SGCPVCGK 00 VFSCRSNMNKHLLTHGDKK YTCEICGRKFFRVDVLRDHIHVHFK 00 DIALMDDHQREEFIGKIGISSEENDDNSDESADSEPHK YSCKRCQ 00 LTFGRGKEYLKHIMEVHKEKG YGCSICNRRFALKATYHAHMVIHRENLPDPNVQK 21 YI HPCEICGRIFNSIGNLERHKLIHT 12 GVKS HACEQCGKSFARKDMLKEHMRVHDNVRE YLCAECGK 12 GMKTKHALRHHMKLHKGIKE YECKECHRRFAQKVNMLKHCKRHT 12 GIKD FMCELCGKTFSERNTMETHKLIHT 12 VGKQ WTCSVCDKKYVTEYMLQKHVQLTHDKVEA QSCQLCGTKVSTRASMSRHMRRKHPE 0 0 VLAVRIDDLDHLPETTTIDASSIGIVQ 0 0 PELTLEQEDLAEGKHGKAAKRSHKRKQKPEEEAGAPVPEDATFSEYSEKETEFTGSVGDETNSAVQSIQQ 0 0 VVVTLGDPNVTTPSSSVGLTNITVTPITTAAATQFTNLQPVAVGHLTTPERQLQLDNSILTVTFDTVSGSAMLHNRQNDVQIHPQPEASNPQSVAHFINLTTLVNSITPLGSQLSDQHPLTWRAVPQTDVLPPSQPQAPPQQAAQPQVQAEQQQQQMYSY* 0 >PRDM6_homSap Homo sapiens (human) 595 aa knuckle, SET, no early zinc finger, short array 0 MLKPGDPGGSAFLKVDPAYLQHWQQLFPHGGAGPLKGSGAAGLLSAPQPLQPPPPPPPPERAEPPPDSLRPRPASLSSASSTPASSSTSASSASSCAA AAAAAALAGLSALPVSQLPVFAPLAAAAVAAEPLPPKELCLGATSGPGPVKCGGGGGGGGEGRGAPRFRCSAEELDYYLYGQQRMEIIPLNQHTSDPNN 1 2 RCDMCADNRNGECPMHGPLHSLRRLVGTSSAAAAAPPPELPEWLRDLPREVCLCTSTVPGLAYGICAAQRIQQGTWIGPFQGVLLPPEKVQAGAVRNTQHLWE 0 0 IYDQDGTLQHFIDGGEPSKSSWMRYIRCARHCGEQNLTVVQYR 2 1 SNIFYRACIDIPRGTELLVWYNDSYTSFFGIPLQCIAQDEN 1 2 LNVPSTVMEAMCRQDALQPFNKSSKLAPTTQQRSVVFPQTPCSRNFSLLDKSGPIESGFNQINVKNQRVLASPTSTSQLHSEFSDWHL WKCGQCFKTFTQRILLQMHVCTQNPDR 21 P YQCGHCSQSFSQPSELRNHVVTHSSDRP FKCGYCGRAFAGATTLNNHIRTHTGEKP FK 21 CERCERSFTQATQLSRHQRMPNECKP ITESPESIEVD* 0
>ZNF133_homSap Homo sapiens (human) 653 aa KRAB, early zinc finger and array 0 MAFRDVAVDFTQDEWRLLSPAQRTLYREVMLENYSNLVSL 1 2 GISFSKPELITQLEQGKETWREEKKCSPATCP 1 2 DPEPELYLDPFCPPGFSSQKFPMQHVLCNHPPWIFTCLCAEGNIQPGDPGPGDQEKQQQASEGRPWSDQAEGPEGEGAMPLFGRTKKRTLGAFSRPPQRQPVSSRNGLRGVELEASPAQTGNPEETDKLLKRIEVLGFGT VNCGECGLSFSKMTNLLSHQRIHSGEKP YVCGVCEKGFSLKKSLARHQKAHSGEKP IVCRECGRGFNRKSTLIIHERTHSGEKP YMCSECGRGFSQKSNLIIHQRTHSGEKP YVCRECGKGFSQKSAVVRHQRTHLEEKT IVCSDCGLGFSDRSNLISHQRTHSGEKP YACKECGRCFRQRTTLVNHQRTHSKEKP YVCGVCGHSFSQNSTLISHRRTHTGEKP YVCGVCGRGFSLKSHLNRHQNIHSGEKP IVCKDCGRGFSQQSNLIRHQRTHSGEKP MVCGECGRGFSQKSNLVAHQRTHSGERP YVCRECGRGFSHQAGLIRHKRKHSREKP YMCRQCGLGFGNKSALITHKRAHSEEKP CVCRECGQGFLQKSHLTLHQMTHTGEKP YVCKTCGRGFSLKSHLSRHRKTTSVHHR LPVQPDPEPCAGQPSDSLYSL* 0 >HKR1_homSap Homo sapiens (human) 659aa KRAB, early zinc finger and array 0 MRVNHTVSTMLPTCMVHRQTMSCSGAGGITAFVAFRDVAVYFTQEEWRLLSPAQRTLHREVMLETYNHLVSL 1 2 EIPSSKPKLIAQLERGEAPWREERKCPLDLCP 1 2 ESKPEIQLSPSCPLIFSSQQALSQHVWLSHLSQLFSSLWAGNPLHLGKHYPEDQKQQQDPFCFSGKAEWIQEGEDSRLLFGRVSKNGTSKALSSPPEEQQPAQSKEDNTVVDIGSSPERRADLEETDKVLHGLEVSGFGE IKYEEFGPGFIKESNLLSLQKTQTGETP YMYTEWGDSFGSMSVLIKNPRTHSGGKP YVCRECGRGFTWKSNLITHQRTHSGEKP YVCKDCGRGFTWKSNLFTHQRTHSGLKP YVCKECGQSFSLKSNLITHQRAHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFRQHSHLVRHKRTHSGEKP YICRECEQGFSQKSHLIRHLRTHTGEKP YVCTECGRHFSWKSNLKTHQRTHSGVKP YVCLECGQCFSLKSNLNKHQRSHTGEKP FVCTECGRGFTRKSTLSTHQRTHSGEKP FVCAECGRGFNDKSTLISHQRTHSGEKP FMCRECGRRFRQKPNLFRHKRAHSGA FVCRECGQGFCAKLTLIKHQRAHAGGKP HVCRECGQGFSRQSHLIRHQRTHSGEKP YICRKCGRGFSRKSNLIRHQRTHSG* 0 >ZNF343_homSap Homo sapiens (human) 599aa KRAB, early zinc finger and array 0 MMLPYPSALGDQYWEEILLPKNGENVETMKKLTQNHKAK 1 2 GLPSNDTDCPQKKEGKAQIV 0 0 VPVTFRDVTVIFTEAEWKRLSPEQRNLYKEVMLENYRNLLSL 1 2 AEPKPEIYTCSSCLLAFSCQQFLSQHVLQIFLGLCAENHFHPGNSSPGHWKQQGQQYSHVSCWFENAEGQERGGGSKPWSARTEERETSRAFPSPLQRQSASPRKGNMVVETEPSSAQRPNPVQLDKGLKELETLRFGA INCREYEPDHNLESNFITNPRTLLGKKP YICSDCGRSFKDRSTLIRHHRIHSMEKP YVCSECGRGFSQKSNLSRHQRTHSEEKP YLCRECGQSFRSKSILNRHQWTHSEEKP YVCSECGRGFSEKSSFIRHQRTHSGEKP YVCLECGRSFCDKSTLRKHQRIHSGEKP YVCRECGRGFSQNSDLIKHQRTHLDEKP YVCRECGRGFCDKSTLIIHERTHSGEKP YVCGECGRGFSRKSLLLVHQRTHSGEKH YVCRECRRGFSQKSNLIRHQRTHSNEKP YICRECGRGFCDKSTLIVHERTHSGEKP YVCSECGRGFSRKSLLLVHQRTHSGEKH YVCRECGRGFSHKSNLIRHQRTH* 0 >ZNF589_homSap Homo sapiens (human) 364 aa KRAB, early zinc finger and array 0 MWAPREQLLGWTAE 1 2 ALPAKDSAWPWEEKPRYL 0 0 GPVTFEDVAVLFTEAEWKRLSLEQRNLYKEVMLENLRNLVSL 1 2 AESKPEVHTCPSCPLAFGSQQFLSQDELHNHPIPGFHAGNQLHPGNPCPEDQPQSQHPSDKNHRGAEAEDQRVEGGVRPLFWSTNERGALVGFSSLFQRPPISSWGGNRILEIQLSPAQNASSEEVDRISKRAETPGFGAVTFGECALAFNQKSNLFRQKAVTAEKSSDKRQS QVCRECGRGFSRKSQLIIHQRTHTGEKP YVCGECGRGFIVESVLRNHLSTHSGEKP YVCSHCGRGFSCKPYLIRHQRTHTREKS FMCTVCGRGFREKSELIKHQRIHTGDKP YVCRD* 0 >ZNF169_homSap Homo sapiens (human) 603aa KRAB, no early zinc finger but array 0 MSPGLLTTRKEALMAFRDVAVAFTQKEWKLLSSAQRTLYREVMLENYSHLVSL 1 2 GIAFSKPKLIEQLEQGDEPWREENEHLLDLCP 1 2 EPRTEFQPSFPHLVAFSSSQLLRQYALSGHPTQIFPSSSAGGDFQLEAPRCSSEKGESGETEGPDSSLRKRPSRISRTFFSPHQGDPVEWVEGNREGGTDLRLAQRMSLGGSDTMLKGADTSESGAVIRGNYRLGLSKKSSLFSHQKH HVCPECGRGFCQRSDLIKHQRTHTGEKP YLCPECGRRFSQKASLSIHQRKHSGEKP YVCRECGRHFRYTSSLTNHKRIHSGERP FVCQECGRGFRQKIALLLHQRTHLEEKP FVCPECGRGFCQKASLLQHQSSHTGERP FLCLECGRSFRQQSLLLSHQVTHSGEKP YVCAECGHSFRQKVTLIRHQRTHTGEKP YLCPQCGRGFSQKVTLIGHQRTHTGEKP YLCPDCGRGFGQKVTLIRHQRTHTGEKP YLCPKCGRAFGFKSLLTRHQRTHSEEEL YVDRVCGQGLGQKSHLISDQRTHSGEKP CICDECGRGFGFKSALIRHQRTHSGEKP YVCRECGRGFSQKSHLHRHRRTKSGHQL LPQEVF* 0 >ZNF596_homSap Homo sapiens (human) 504 aa KRAB, no early zinc finger but array 0 MPSP 0 0 DSMTFEDIIVDFTQEEWALLDTSQRKLFQDVMLENISHLVSI 1 2 GKQLCKSVVLSQLEQVEKLSTQRISLLQ 1 2 GREVGIKHQEIPFIQHIYQKGTSTISTM 0 0 RSHTQEDPFLCNDLGEDFTQHIALTQNVITYMRTKHFVSKKFGKIFSDWLSFNQHKEIHTKCKSYGSHLFDYAFIQNSALRPHSVTHTREIT LECRVCGKTFSKNSNLRRHEMIHTGEKP HGCHLCGKAFTHCSDLRKHERTHTGEKP YGCHLCGKAFSKSSNLRRHEMIHTREKA QICHLCGKAFTHCSDLRKHERTHLGDKP YGCLLCGKAFSKCSYLRQHERTHNGEKP YECHLCGKAFSHCSHLRQHERSHNGEKP HGCHLCGKAFTESSVLKRHERIHTGEKP YECHVCGKAFTESSDLRRHERTHTGEKP YECHLCGKAFNHSSVLRRHERTHTGEKP YECNICGKAFNRSYNFRLHRRVHTGEKP YVCPLCGKAFSKFFNLRQHERTHTKKAMNM* 0
>GAS8_homSap Homo sapiens (human) synteny marker right centromeric positive strand C16orf3- in second intron growth arrest-specific del cancer MAPKKKGKKGKAKGTPIVDGLAPEDMSKEQVEEHVSRIREELDREREERNYFQLERDKIHTFWEITRRQLEEKKAELRNKDREMEEAEERHQVEIKVYKQKVKHLLYEHQNNLTEMKAEG TVVMKLAQKEHRIQESVLRKDMRALKVELKEQELASEVVVKNLRLKHTEEITRMRNDFERQVREIEAKYDKKMKMLRDELDLRRKTELHEVEERKNGQIHTLMQRHEEAFTDIKNYYNDI TLNNLALINSLKEQMEDMRKKEDHLEREMAEVSGQNKRLADPLQKAREEMSEMQKQLANYERDKQILLCTKARLKVREKELKDLQWEHEVLEQRFTKVQQERDELYRKFTAAIQEVQQKT GFKNLVLERKLQALSAAVEKKEVQFNEVLAASNLDPAALTLVSRKLEDVLESKNSTIKDLQYELAQVCKAHNDLLRTYEAKLLAFGIPLDNVGFKPLETAVIGQTLGQGPAGLVGTPT* >CDH12_homSap Homo sapiens (human) synteny marker chr 5 794 aa MLTRNCLSLLLWVLFDGGLLTPLQPQPQQTLATEPRENVIHLPGQRSHFQRVKRGWVWNQFFVLEEYVGSEPQYVGKLHSDLDKGEGTVKYTLSGDGAGTVFTIDETTGDIHAIRSLDRE EKPFYTLRAQAVDIETRKPLEPESEFIIKVQDINDNEPKFLDGPYVATVPEMSPVGAYVLQVKATDADDPTYGNSARVVYSILQGQPYFSIDPKTGVIRTALPNMDREVKEQYQVLIQAK DMGGQLGGLAGTTIVNITLTDVNDNPPRFPKSIFHLKVPESSPIGSAIGRIRAVDPDFGQNAEIEYNIVPGDGGNLFDIVTDEDTQEGVIKLKKPLDFETKKAYTFKVEASNLHLDHRFH SAGPFKDTATVKISVLDVDEPPVFSKPLYTMEVYEDTPVGTIIGAVTAQDLDVGSSAVRYFIDWKSDGDSYFTIDGNEGTIATNELLDRESTAQYNFSIIASKVSNPLLTSKVNILINVL DVNEFPPEISVPYETAVCENAKPGQIIQIVSAADRDLSPAGQQFSFRLSPEAAIKPNFTVRDFRNNTAGIETRRNGYSRRQQELYFLPVVIEDSSYPVQSSTNTMTIRVCRCDSDGTILS CNVEAIFLPVGLSTGALIAILLCIVILLAIVVLYVALRRQKKKDTLMTSKEDIRDNVIHYDDEGGGEEDTQAFDIGALRNPKVIEENKIRRDIKPDSLCLPRQRPPMEDNTDIRDFIHQR LQENDVDPTAPPYDSLATYAYEGSGSVAESLSSIDSLTTEADQDYDYLTDWGPRFKVLADMFGEEESYNPDKVT*
>PRDM7_musMus1 Mus musculus genomic strain SIERQCGQYFSDKSNVNEHQKTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQNSHLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSDLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSDLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSVLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSVLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSVLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSNLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSVLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSVLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSNLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGWGFTQKSDLIQHQRTHTREKp >PRDM7_musMus2 Mus musculus strain WSB/EiJ GU183911 and EU719625 missing a repeat SIERQCGQYFSDKSNVNEHQKTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQNSHLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSDLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSDLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSVLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSVLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSVLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSNLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSVLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSVLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSVLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSNLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGWGFTQKSDLIQHQRTHTREK >PRDM7_musMus3 Mus musculus strain MOLF/EiJ GU183913 SIERQCGQYFSDKSNVNEHQKTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSDLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSVLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSDLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSNLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSVLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSDLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSNLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSVLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTEKSSLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSNLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSVLIQHQRTHTGEKP >PRDM7_musMus4 Mus musculus strain PWD/PhJ GU183912 = PWD/Ph FJ212287 SIERQCGQYFSDKSNVNEHQKTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSDLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSVLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSDLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSNLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSVLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSDLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSNLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTEKSSLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSNLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSVLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSVLIQHQRTHTGEKP >PRDM7_musMus5 Mus musculus strain CAST/EiJ GU183909 SIERQCGQYFSDKSNVNEHQKTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSNLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSVLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSDLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSNLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTEKSSLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGWGFTAKSNLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSSLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSNLIQHQRTHTGEKPa YVCRECGWGFTQKSNLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGWGFTQKSDLIQHQRTHTREK* >PRDM7_musMus6 Mus musculus strain C57BL10.F HQ704390 SIERQCGQYFSDKSNVNEHQKTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQNSHLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSDLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTVKSVLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQNSHLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSVLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQNSHLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSDLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSVLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSNLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGWGFTQKSDLIQHQRTHTREK >PRDM7_musMol Mus musculus molossinus GU216230 SIERQCGQYFSDKSNVNEHQKTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSNLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSVLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSDLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSNLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTEKSSLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGWGFTAKSNLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSSLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSNLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGWGFTQKSNLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGWGFTQKSDLIQHQRTHTREK* >PRDM9_musCas Mus musculus castaneus SIERQCGQYFSDKSNVNEHQKTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSNLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSVLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSDLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTARSNLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSDLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSNLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTEKSSLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGWGFTAKSNLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSSLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSNLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGWGFTQKSNLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGWGFTQKSDLIQHQRTHTREKp >PRDM9_musPah Mus pahari SIERQCGQYFSDKSNVNEHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSNLITHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTGKSPLIRHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSNLITHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTGKSPLIRHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSHLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTEKSNLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSPLIRHQRTHTGEKP YVCTECGRGFTQKSNLITHQRTNTGEKP >PRDM9_musMac Mus macedonicus SIERQCGQYFSDKSNVNEHQKTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSDLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTVKSDLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSNLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSDLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTVKSHLTQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSDLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSHLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSNLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSNLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQNSHLTQHQRTHTGEKS YVCRECGWGFKQKSDLIQHQRTHTREKp >PRDM9_musSpi Mus spicilegus SIERQCGQYFSDKSNVNEHQKTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSNLIQHQRTHTGEK YVCRECGRGFTQKSNLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSDLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTVKSHLTQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSDLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSHLTQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSNLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTAKSNLIKHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQNSHLTQHQRTHTGEKS YVCRECGWGFKQKSDLIQHQRTHTREKp >PRDM9_merUng Meriones unguiculatus GTGRECGQCFSDKSNVSEHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFMQRSNLISHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFMQRSNLISHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTVKSVLISHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTVKPHLISHQRTHTGEKP HVCRECGRGFTQRSNLIRHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTVKPHLISHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTVKPHLISHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTVKSVLISHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTVKSVLIRHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECRRGFTQRSTLIRHQRTHTGEKP HVCRECGRGFTRGSHLLRHQRTHTGEVL >PRDM9_micAgr Microtus agrestis RVGGERGQCFSDKSNVNEHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTRKSNLNVHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTRKALLISHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKALLISHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSYLILHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTGKSNLNVHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSYLILHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTGKSLLIRHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSYPILHQRTHTGEKp >PRDM9_arvTer Arvicola terrestris RVEGECGQCFNDKSNVNERQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTRKSVLILHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSVLINHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSHLIFHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSHLILHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTWKSVLILHQRTHTGERP YVCRECGRGFTRKSHLILHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSHLILHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTRKSVLILHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTRKSVLINHQRTHTGEKp >PRDM9_perPol Peromyscus polionotus RIETECGQRFSDKSNVNESQRTHSEEKP YVCRECGQGFIQKSVLICHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGQGFTWKSHLIRHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGKGFIRKSHLICHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGQGFIQKSHLICHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGQGFTQKSVLICHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGQGFIRKSYLICHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGKGFTWKSVLIRHQRTHTVEKp >PRDM9_perLeu Peromyscus leucopus RIETECGQRFSDKSNANESQRTHSEEKP YVCRECGQGFTRKSYLICHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGQGFIQKSVLIRHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGQGFTRKSYLICHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGQGFIQKSVLIRHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGQGFTWKSVLICHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGQGFTRKSYLICHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGQGFTWKSHLIRHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGQGFTRKSYLICHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGQGFIQKSHLICHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGQGFTRKSYLICHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGQGFTWKSVLIRHQRTHTAEKp >PRDM9_perMan Peromyscus maniculatus RTETECGQHFSDKSNANESQRTHSEEKP YVCRECGQGFTWKSVLIRHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGQGFTWKSVLICHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGQGFTWKSVLICHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGQGFIQKSHLIRHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGQGFIRKSHLICHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGQGFAQKSVLIYHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGQGFTRKSHLICHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGQGFAQKSVLICHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGQGFTWKSVLICHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGQGFIQKSHLIRHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGQGFIQKSHLIRHQRTHTGEKp >PRDM9_apoSyl Apodemus sylvaticus RVERQRGQCFSDKSNVSERQGTHTGEKP CVCRECGRGFTQKSHLNRHQRTHTGEKP HVCRECGRGFTQKSHLNRHQRTHTGEKP HVCRECGRGFTLKSNLNRHQRTHTGEKP CVCRECGRAFTQKSDLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSNLNQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTRKSLLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSDLNRHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGLTQKSNLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTLKSDLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTRKSDLNRHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTQKSNLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTLKSDLIQHQRTHTGEKP YVCRECGRGFTRKSDLNRHQRTHTGEKp >PRDM7_ratNor Rattus norvegicus RIERQCGQCFSDKSNVSEHQRTHTGEKP YICRECGRGFSQKSDLIKHQRTHTEEKP YICRECGRGFTQKSDLIKHQRTHTEEKP YICRECGRGFTQKSDLIKHQRTHTGEKP YICRECGRGFTQKSDLIKHQRTHTEEKP YICRECGRGFTQKSSLIRHQRTHTGEKP YICRECGLGFTQKSNLIRHLRTHTGEKP YICRECGLGFTRKSNLIQHQRTHTGEKP YICRECGQGLTWKSSLIQHQRTHTGEKP YICRECGRGFTWKSSLIQHQRTHTVEKp
Online references
Open 39 abstracts on PRDM9 and related issues. Or use the reverse chronological list below to get free full text for individual articles when that is available:
pdf 2011 Richon Chemogenetic analysis of human protein methyltransferases. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2011 Aug;78(2):199-210. pdf 2011 Hinch The landscape of recombination in African Americans. Nature. 2011 Jul 20. doi: 10.1038/nature10336. pmc 2011 Smagulova Genome-wide analysis reveals novel molecular features of mouse recombination hotspots. Nature. 2011 Apr 21;472(7343):375-8. htm 2011 Kaupi Distinct properties of the XY pseudoautosomal region crucial for male mouse meiosis. Science 18 Feb 2011;DOI: 10.1126/science.1195774 abs 2011 Briknarova The PR/SET domain in PRDM4 is preceded by a zinc knuckle. Proteins 2011 Jul;79(7):2341-5. doi: 10.1002/prot.23057. pmc 2011 Fledel Variation in human recombination rates and its genetic determinants. PLoS One 2011;6(6):e20321. abs 2011 Neaves Unisexual reproduction among vertebrates. Trends Genet. 2011 Mar;27(3):81-8. abs 2011 Ponting What are the genomic drivers of the rapid evolution of PRDM9? Trends Genetics (2011) 1–7 htm 2011 Yanover Extensive protein and DNA backbone sampling improves structure-based specificity prediction for C2H2 zinc fingers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Feb 22 pdf 2011 Ubeda Red Queen theory of recombination hotspots. J Evol Biol. 2011 Mar;24(3):541-53. abs 2010 Hochwagen Meiosis: a PRDM9 guide to the hotspots of recombination. Curr Biol. 2010 Mar 23;20(6):R271-4. abs 2010 Klug The discovery of zinc fingers and practical applications in gene regulation and genome manipulation. Q Rev Biophys. 2010 Feb;43(1):1-21. abs 2010 Berg PRDM9 variation strongly influences recombination hot-spot activity and meiotic instability in humans. Nat Genet. 2010 Oct;42(10):859-63. abs 2010 McVean PRDM9 marks the spot. Nat Genet. 2010 Oct;42(10):821-2. pdf 2010 Kong Fine-scale recombination rate differences between sexes, populations and individuals. Nature. 2010 Oct 28;467(7319):1099-103. pmc 2010 Parvanov Prdm9 controls activation of mammalian recombination hotspots. Science. 2010 Feb 12;327(5967):835. pmc 2010 Lorenz The ancient mammalian KRAB zinc finger gene cluster on human chromosome 8q24.3 BMC Genomics. 2010 Mar 26;11:206. pmc 2010 Neale PRDM9 points the zinc finger at meiotic recombination hotspots. Genome Biol. 2010;11(2):104. pmc 2010 Sandovici PRDM9 sticks its zinc fingers into recombination hotspots and between species. F1000 Biol Rep. 2010 May 24;2. pmc 2010 Billings Patterns of recombination activity on mouse chromosome 11 revealed by high resolution mapping. PLoS One. 2010 Dec 8;5(12):e15340. htm 2010 Cheung Genetic control of hotspots. Science. 2010 Feb 12;327(5967):791-2. pdf 2010 Urnov Highly efficient endogenous human gene correction using designed zinc-finger nucleases. Nature. 2005 Jun 2;435(7042):646-51. htm 2010 Zheng Detecting sequence polymorphisms associated with meiotic recombination hotspots in the human genome. Genome Biol. 2010;11(10):R103. htm 2010 Baudat PRDM9 is a major determinant of meiotic recombination hotspots in humans and mice. Science. 2010 Feb 12;327(5967):836-40. htm 2010 Myers Drive against hotspot motifs in primates implicates the PRDM9 gene in meiotic recombination. Science. 2010 Feb 12;327(5967):876-9. pmc 2009 Berglund Hotspots of biased nucleotide substitutions in human genes. PLoS Biol. 2009 Jan 27;7(1):e26. pmc 2009 Thomas Evolution of C2H2-zinc finger genes revisited. BMC Evol Biol. 2009 Mar 4;9:51. pmc 2009 Oliver Accelerated evolution of the Prdm9 speciation gene across diverse metazoan taxa. PLoS Genet. 2009 Dec;5(12):e1000753. pmc 2009 Thomas Extraordinary molecular evolution in the PRDM9 fertility gene. PLoS One. 2009 Dec 30;4(12):e8505. htm 2009 Willis Origin of species in overdrive. Science. 2009 Jan 16;323(5912):350-1. htm 2009 Irie Single-nucleotide polymorphisms of the PRDM9 (MEISETZ) gene in patients with nonobstructive azoospermia. J Androl. 2009 Jul-Aug;30(4):426-31. htm 2009 Mihola A mouse speciation gene encodes a meiotic histone H3 methyltransferase. Science. 2009 Jan 16;323(5912):373-5. abs 2008 Brayer The protein-binding potential of C2H2 zinc finger domains. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2008;51(1):9-19. pmc 2008 Duret The impact of recombination on nucleotide substitutions in the human genome. PLoS Genet. 2008 May 9;4(5):e1000071. pmc 2008 Miyamoto Two single nucleotide polymorphisms in PRDM9 (MEISETZ) gene may be a genetic risk factor for Japanese patients with azoospermia by meiotic arrest. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2008 Nov-Dec;25(11-12):553-7. htm 2008 Cho Prediction of DNA binding sites for zinc finger proteins. BBRC 2008 May 9;369(3):845-8. pmc 2007 Coop Live hot, die young: transmission distortion in recombination hotspots. PLoS Genet. 2007 Mar 9;3(3):e35. pmc 2007 Fumasoni Family expansion and gene rearrangements contributed to the functional specialization of PRDM genes in vertebrates. BMC Evol Biol. 2007 Oct 4;7:187. pdf 2006 Phillips A family of zinc-finger proteins is required for chromosome-specific pairing and synapsis during meiosis. Dev Cell. 2006 Dec;11(6):817-29. htm 2006 Birtle Meisetz and the birth of the KRAB motif. Bioinformatics. 2006 Dec 1;22(23):2841-5. pdf 2006 Hayashi Meisetz, a novel histone tri-methyltransferase, regulates meiosis-specific epigenesis. Cell Cycle. 2006 Mar;5(6):615-20. pdf 2005 Hayashi A histone H3 methyltransferase controls epigenetic events required for meiotic prophase. Nature 2005 Nov 17;438(7066):374-8. abs 2000 Laity DNA-induced alpha-helix capping in conserved linker sequences is a determinant of binding affinity in Cys(2)-His(2) zinc fingers. J Mol Biol. 2000 Jan 28;295(4):719-27.
Article author
I researched this article in its entirety in April and July of 2011. This is a moderately difficult topic as human genes go, so is still being revised with new sections added each week. Although copyrighted, all the information here is in the public domain and can be used by anyone without additional permissions if properly sourced; however if used extensively for a peer-reviewed scientific publication, it would be appropriate (after consultation) to include me among the non-leading co-authors.
Rather than make article edits, please contact me by email for clarifications, corrections or additions to the content -- I will make edits as appropriate to maintaining a consistent approach. Another option is to register at the UCSC genomewiki site and create your own page within the comparative genomics category.
This is a scientific research article on a vertebrate gene family, not a resource for genetic counseling nor a source of medical advice. Technical terms from genetics and molecular biology are not explained here if keywords have a satisfactory treatment at wikipedia or in undergraduate genetics texts -- thanks in advance for not sending inappropriate email.
My last dozen published research papers in PNAS, Nature, Science etc can be found here. Watch for 5 additional comparative genomics paper to appear in 2011. I've also written over a thousand pages of comparative genomics for other human genes, authored the original user guide to the UCSC human genome browser and in 1999 an advanced tutorial on metazoan genome annotation still widely available online. I thank the UCSC Genomics Group (Hiram Clawson, Brian Raney) for software and manuscript resources, Evim Foundation for logistical support, and the Sperling Foundation for financial support under project grant 2011.GNTCS.004.